
1. (A) Complete the sentences by choosing a correct option.
(1) …….. was the first Director General of the Archaeological Survey of India.
(a) Alexander Cunningham
(b) William Jones
(c) John Marshall
(d) Friedrich Max Muller
Ans. Sir Alexander Cunningham
(2) ………… translated the Sanskrit text of ‘Hitopadesh’. (July ’19)
(a) James Mill
(b) Friedrich max Muller
(c) Mountstuart Elphinstone
(d) Sir John Marshall
Ans. Friedrich Max Mulle
(B) Identify the wrong pair in the following, correct it and rewrite.
(1) ‘Who were the Shudras’ – Dr Babasaheb Ambedkar
(2) ‘Stri-Purush Tulana’ – Feminist writing
(3) ‘The Indian War of Independence 1857’ – Marxist History
(4) Grant Duff – Colonial History.
Ans. Wrong Pair : The Indian War of Independence – Marxist History
Correct Statement : The Indian War of Independence was written by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar in 1857 and is an nationalistic historiography.
2. Explain the following with its reason.
(1) Writing of the regional history received a momentum. (March ’19; July ’19)
Ans. (1) Marathi historians like Nilkantha Janardan Kirtane, Vishwanath Kashinath Rajwade and Vishnu Shastri Chiplunkar criticized, and exposed the prejudiced attitude of the British historians. (2) The nationalistic historiography helped in the triggering of the independence movement of the Indian people against the British. (3) In this aspect the book, ‘The Indian War of Independence, 1857’, written by Vinayak Damodar Savarkar is of great importance. (4) Hence, writing of the regional history received momentum.
(2) Bakhar is an important type of historical documents.
Ans. (1) ‘Bakhar’ is an important type of historical documents of medieval times. It contains eulogies of the heroes and stories of historic events, battles, lives of great men. (2) Marathi bakhars are of various types. ‘Sabhasad Bakhar’ was written by Krishnaji Anant Sabhasad during the reign of Chhatrapati Rajaram Maharaj. It is an important bakhar for getting information about the rule of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. (3) ‘Bhausahebanchi Bakhar’ describes the Battle of Panipat. Another bakhar, entitled ‘Panipatachi Bakhar’, is also about the same event. (4) ‘Holkaranchi Kaiphiyat’ provides information about the Holkars and their contributions to the Maratha rule.(5) Bakhars can be divided into various types such as biographies of kings, dynastic history, descriptions of events, history of a sect, autobiographies, regarding grievance, based on mythologies and state administration by a king.
3. Write detailed answers to the following questions :
(1) What is Marxist History?
Ans. (1) The concern for the means of production, modes of production and the industrial relations were at the centre in the writings of Marxist historians. (2) Accordingly, to analyse the impact of every social event of significance has remained the basic theme of Marxist historiography. (3) Marxist historians in India studied the transitions within the caste system. (4) Among the notable Indian historians who adopted Marxist ideological framework, scholars like Damodar Dharmanand Kosambi, Comrade Shripad Amrut Dange, Ram Sharan Sharma, Comrade Sharad Patil have contributed notably.
(2) What is the contribution of Itihasacharya V.K. Rajwade to historiography ? (Nov. ’20: Sept. ’21)
Ans. Rajwade is well-known for his writings in Marathi on varied subjects like history, linguistics, etymology, grammar, etc. (2) He was of the firm opinion that we should write our own history. (3) He compiled
and edited 22 volumes of ‘Marathyanchya Itihasachi Sadhane’. (4) He wrote very scholarly prefaces to each of the 22 volumes. (5) He stated, ‘History is the all-inclusive image of the past societies. It does not include only the stories of political images, conspiracies and wars for seizing power.’ (6) He insisted that history should be written only using the authentic documentary source.
4. (a) Complete the following chart. (July ’19; Sept. ’21)
Ans. 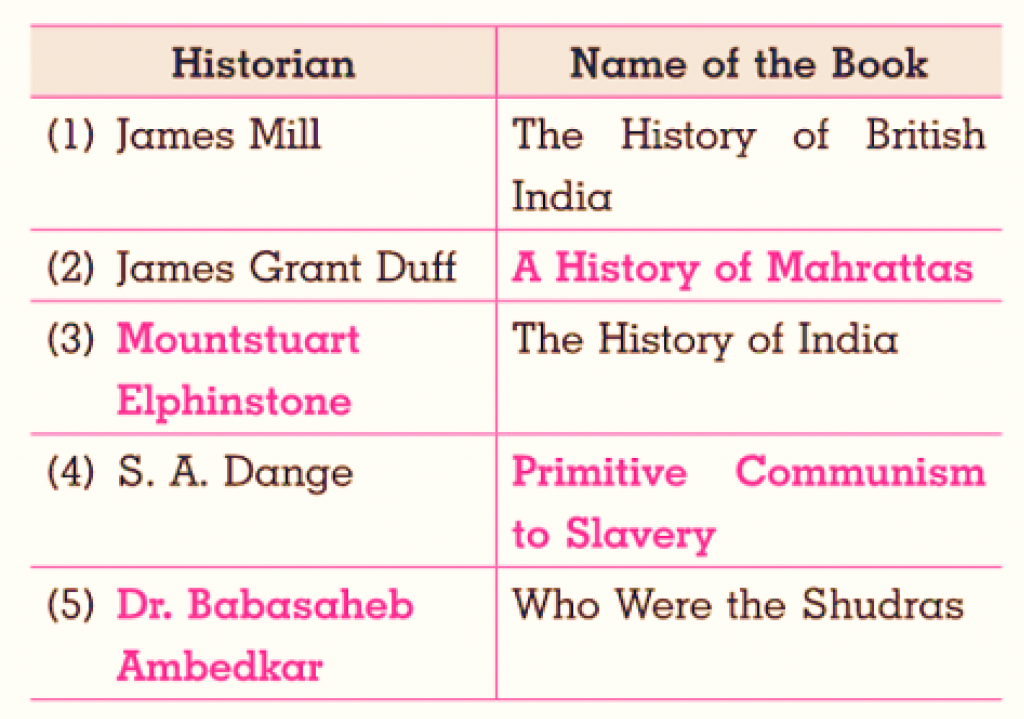
(b) Complete the following concept chart.
Ans. 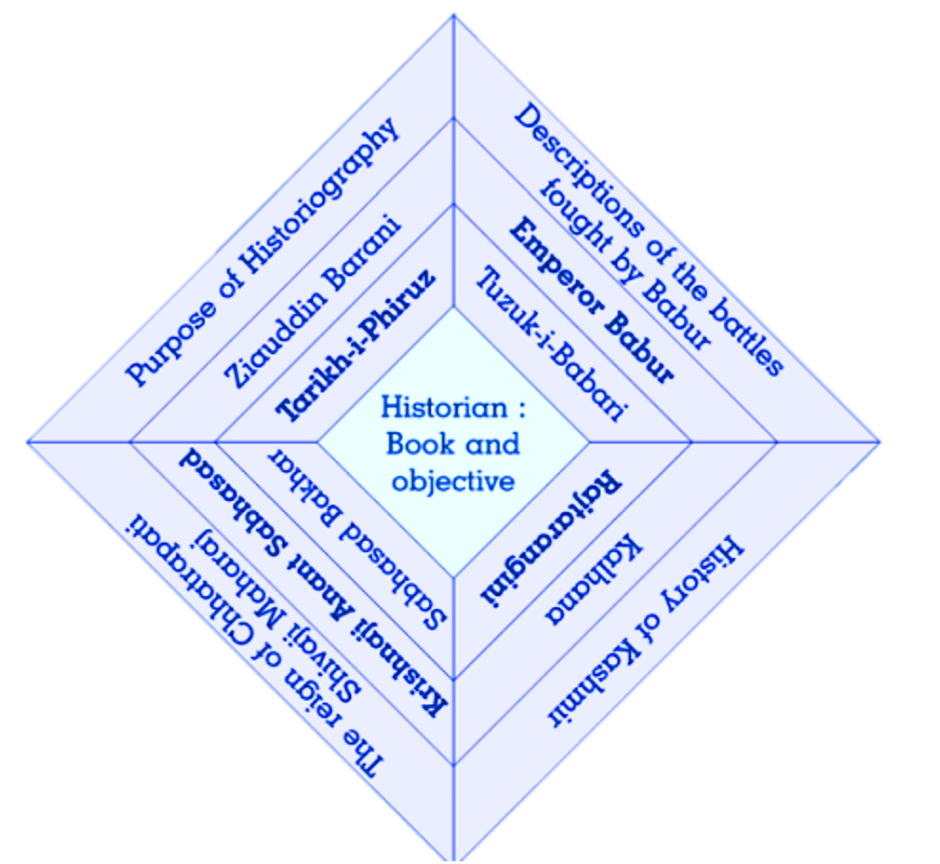
5. Write short notes
(1) Orientalist historiography.
Ans. (1) Many European scholars felt curious about civilisations and countries of the East. Some of those scholars felt admiration and respect for them. These scholars were known as ‘Orientalists’. (2) The orientalists studied the similarities between Sanskrit and some of the European languages. (3) They focused more on Vedic tradition and Sanskrit literature. (4) Their studies resulted into formulating the notion of an ancient language that could be the mother of all Indo-European languages. (5) Among the Orientalist scholars, Friedrich Max Muller deserves a special mention.
(2) Nationalistic historiography.
Ans. (1) The writings of Indian historians who were trained in the British educational system show an inclination to restore the pride in the ancient glory of India and the selfesteem of the Indian readers. Their
writings are known as ‘Nationalistic Historiography’. (2) Nationalistic writings in Maharashtra were inspired by Vishnushastri Chiplunkar. He criticised the prejudiced history of ancient India written by British officers. (3) The nationalistic historians tried to seek the golden era of Indian history. They are at times blamed for ignoring the critical analysis of the historical truth. (4) Mahadev Govind Ranade, Ramkrishna Gopal Bhandarkar, Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, Rajendra Lal Mishra, Ramesh Chandra Majumdar, Kashi Prasad Jayswal, Radha Kumud Mukherjee, Bhagawan Lal Indraji, Vasudev Vishnu Mirashi and Anant Sadashiv Altekar are the names of some renowned scholars among the nationalistic historians.
(3) Subaltern history.
Ans. (1) The seeds of subaltern history are found in the Marxist historiography. (2) The role of the Italian historian Antonio Gramsci is very important in developing the idea that history should be written starting from the bottommost ranks of people in the society. (3) In fact, subaltern means the ‘bottommost ranks’. (4) Folklore has been considered as a very important source of writing subaltern histories. (5) Ranjit Guha, an Indian historian played a major role in establishing subaltern history as an important academic school of historiography. (6) However, we may point out that much before the onset of subaltern ideology similar thoughts were expressed by Mahatma Jyotirao Phule and Dr Babasaheb Ambedkar.
