Q.1 A) Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence.
1) A Lawyer is ……..
a) a Professional person
b) a Businessman
c) an employee
2) Raw material is converted into finished product by ………. industry.
a) genetic
b) extractive
c) manufacturing
3) Actual buying and selling of goods is known as ……….
a) profession
b) trade
c) industry
4) National level code of conduct is prepared for ……………
a) professionals
b) businessmen
c) employees
5) Construction of dams is an activity done under ………… industry.
a) primary
b) secondary
c) tertiary
6) The problem of distance is solved by ……….
a) bank
b) transport
c) warehousing
7) Commerce is a branch of …………
a) business
b) industry
c) trade
8) Monetory Returns in business is called………
a) fees
b) salary
c) profit
9) A business unit depends upon ………… for selling its output.
a) industry
b) society
c) employees
10) Warehousing creates………. utility in goods.
a) place
b) time
c) form
Ans.
A – 4, B – 3, C – 5, D – 1
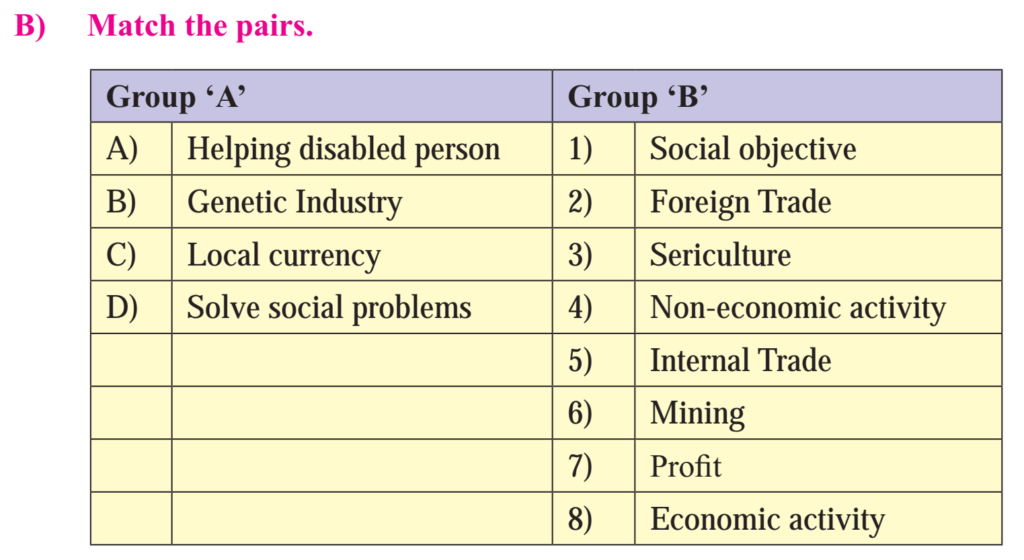
C) Give one word / phrase / term for the following sentences.
1) A regular activity concerned with production and distribution of goods and services for profits.
Ans. Business
2) Human activities that are conducted for earning money.
Ans. Economic activities
3) Buying and selling of goods against money or money’s worth.
Ans. Trade
4) Activities that remove all the difficulties in trade.
Ans. Auxiliaries to trade
5) The type of industries that creates immovable wealth.
Ans. Construction Industry
6) Name the business activity which is concerned with production of goods and services.
Ans. Industry
7) Name the business activity which is concerned with distribution of goods and services.
Ans. Commerce
8) The activity which provides mobility to men and material.
Ans. Transport
9) An aid to trade which creates time utility.
Ans. Warehousing
10) An occupation by which a person agrees to provide expert services for a fees.
Ans. Profession
D) State True or False.
1) Business is an economic activity.
Ans. True
2) Every profession is practiced for earning money.
Ans. True
3) Primary industries are concerned with nature.
Ans. True
4) Trade includes commerce.
Ans. False
5) Warehousing removes difficulty of time.
Ans. True
6) Trade includes buying and selling of goods and services.
Ans. True
7) Profit leads to increase in overall efficiency of the organization.
Ans. True
8) Plant nursery is an example of extractive industry.
Ans. False
9) Industry creates form utility.
Ans. True
10) Retailer is the link between manufacturer and wholesalers.
Ans. False
E) Find the odd one
1) Agricultural Industry, Extractive Industry, Genetic Industry, Manufacturing Industry.
Ans. Manufacturing industry
2) Import Trade, Export Trade, Wholesale Trade, Entrepot Trade.
Ans. Wholesale trade
3) Banking, Insurance, Transport, Manufacturing.
Ans. Manufacturing
4) Tea, Milk, Coffee, Machinery.
Ans. Machinery
F) Complete the sentences.
1) Economic activities are those activities which are conducted to earn money
2) Commerce includes marketing of goods and services.
3) Business is an economic activity.
4) The basic purpose of business is to earn profit.
5) Professionals, charge fees in exchange of expert services.
6) Employer is the person who offers the work.
7) Profit is considered as a reward for assuming several business risks.
8) Industry creates form utility.
9) In wholesale trade, goods are purchased and sold in bulk.
10) Retailer is the link between wholesaler and customer.
Ans.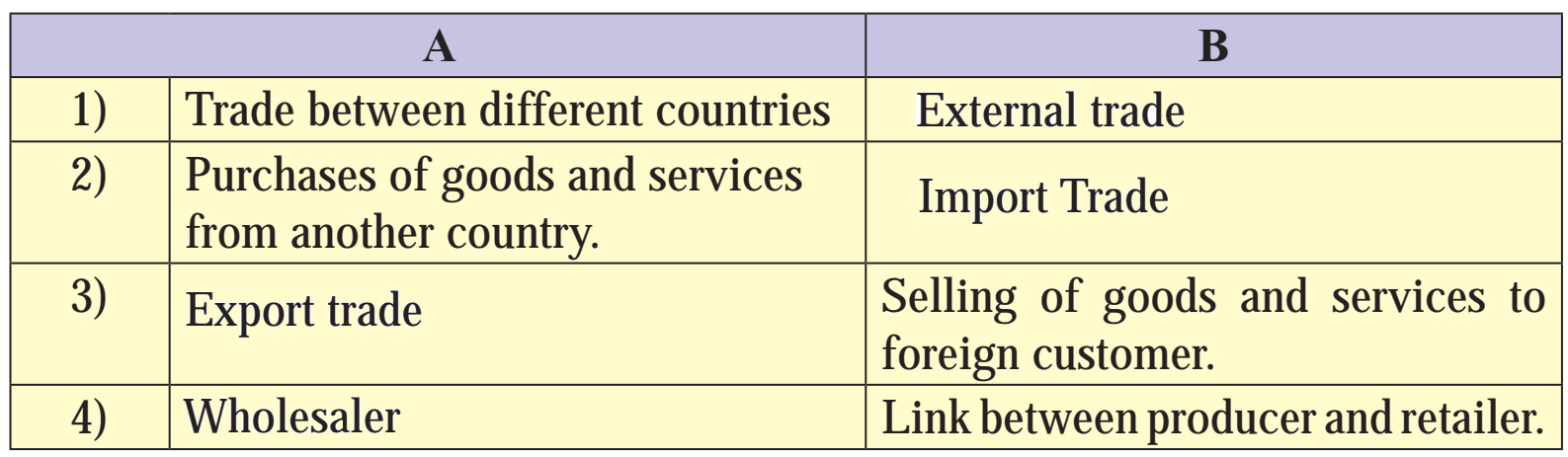
H) Answer in one sentence.
1) What is an Economic Activity?
Ans. Activities that involve production, distribution and consumption of goods and services for money or money’s worth at all levels within a society is called economic activity.
2) What is Non-economic Activity?
Ans. Non-economic activities are those human activities which are performed to satisfy personal, social, religious, cultural and sentimental requirement without monetary expectations.
3) What do you mean by Wholesale Trade?
Ans. In wholesale trade, goods are purchased and sold in bulk. A wholesaler purchases in large quantities from the producers and sells in small quantities to the retailers. He is the link between the producer and the retailer.
4) What is the meaning of Retail Trade?
Ans. Retail trade is business activity associated with the sale of goods to the final consumers. A retailer is the one who purchases from the wholesaler or sometimes directly from the producer and sells them in smaller quantities to final consumer. Retailer is the link between wholesaler or sometimes manufacturer and ultimate consumer.
5) What do you mean by Import Trade?
Ans. When goods and services are purchased from another country it is called as import trade.
6) What is the meaning of Export Trade?
Ans. When goods and services are sold to foreign buyers then it is called as export trade.
7) What is an Entrepot Trade?
Ans. It is the combination of import/export trade. It involves importing the goods from one country and reselling these goods to another country. e.g. Indian Seller importing goods from Japan and re-exporting same goods to Africa.
8) What is meant by Auxiliaries to Trade?
Ans. All those activities that facilitate smooth flow of goods from manufacturing centers to the consumption centers are called aids to trade or auxiliaries to trade.
9) What is Trade?
Ans. Trade denote buying and selling of goods and services. Trade is an exchange of goods and services with money or money’s worth.
10) What do you mean by Commerce?
Ans. Commerce is that part of business activity which is concerned with distribution of goods and services produced by industry.
11) What is Primary Industry?
Ans. Primary industry is a category of industry which is concerned with nature. It is a nature-oriented industry. E.g.: farming, extraction of oil & minerals, animal husbandry.
12) What is Secondary Industry?
Ans. Secondary industry is a category of industry which converts the raw material provided by primary industry into finished products. E.g. Tomatoes provided by primary industry are used for making sauce and ketchup.
13) What do you mean by Genetic Industry?
Ans. Genetic industry is a type of primary industry which is engaged in reproduction and multiplication of plants and animals. E.g. Animal husbandry, sericulture, horticulture etc.
I) Correct the underlined word and rewrite the sentence.
1) Business is non-economic activity.
Ans. Business is economic activity
2) Barter exchange is an exchange with money.
Ans. Barter exchange is an exchange with goods.
3) Profession can be transferred to other person.
Ans. Profession cannot be transferred to other person.
4) Capital is required for employment.
Ans. Capital is required for business.
5) Industry creates place utility.
Ans. Transport creates place utility.
6) Commerce represents supply side of market.
Ans. Industry represents supply side of market.
7) The basic purpose of business is to provide services.
Ans. The basic purpose of business is to earn profit.
Q.2 Explain the following terms/concepts.
1) Business
Ans. Business is one of the economic activities performed by human beings. It represents organised efforts by an individual or group of individuals. It involves systematic attempt by business persons to produce goods and services (production) and sell them in the market (distribution), with a view to earn the reward in the form of profit.
2) Profession
Ans. Profession is that part of economic activities under which a person uses his educational knowledge and special skills to render services for earning some income (fees). E.g. Doctor, lawyer, chartered accountant etc. use their domain knowledge and skills to render services to clients and earn fees (money) in exchange.
3) Employment
Ans. Employment is an economic activity in which people work for others. There exists an employer-employee relationship in this economic activity. Employer is the person who offers the work while employee is the person who accepts the work. Remuneration and terms & conditions are agreed by both, employer and employee.
4) Home Trade
Ans. When trade (buying and selling of goods and services) takes place within the geographical boundaries of a country, it is known as home or internal trade. This type of trade is conducted with local currency. Home trade is further divided into wholesale and retail trade.
5) Foreign Trade
Ans. When trade takes place between different countries, it is known as foreign or external trade. When boundaries of two countries are crossed, then different currencies are used. Foreign trade is further divided into export, import and entrepot trade.
6) Economic Activity
Ans. Economic activity refers to actions that involve production, distribution and consumption of goods & services at all levels within a society. The economic activities facilitate earning livelihood. Business, profession and employment are various forms of economic activities.
7) Non-economic Activity
Ans. Non-economic activity refers to those human activities which are performed to satisfy personal, social, religious, cultural and sentimental requirement without monetary expectations. Example: Reading books, serving people, cooking by mother etc.
Q.3 Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
1) Jaysukh oil mills produce refined oil. The entire production is purchased by Rupesh oil Depot, who in turn sells it to various retailers. Mrs. Prachi purchased 2 kg oil from Balaji Groceries. Identify:
i) Wholesaler
ii) Retailer
iii) Consumer
Ans. i) A wholesaler is the one who purchases goods in large quantities from the producers and sells in small quantities to the retailers. In this case, Rupesh Oil Depot is wholesaler as it purchases refined oil in large quantities from Jaysukh Oil Mills (producer) and then sells it to various retailers.
ii) A retailer is the one who purchases goods from the wholesaler (or sometimes directly from producer) and sells them in smaller quantities to final consumer. In this case, Balaji Groceries is retailer as it purchases refined oil from Rupesh Oil Depot (wholesaler) and sells it in smaller quantities to final consumers.
iii) A consumer purchases goods from retailers in smaller quantities for his personal consumption. In this case, Mrs. Prachi is consumer as she purchases refined oil from Balaji Groceries (retailer) in smaller quantity (2 kg) for her own consumption.
2) Mr. Pranav is a tin manufacturer in India. Mr. Jack of England sells goods to M/s. Frank Corporation in North America and Mr. Williams of USA buys various goods from Brazil.
i) Who is importer?
ii) Who is manufacturer?
iii) Who is exporter?
Ans:
i) An importer is the one who purchases goods and services from another country. In this case, there are two importers:
a. Mr. Williams of USA is an importer as he buys various goods from Brazil (another country than his country of his residence).
b. M/s. Frank Corporation in North America is also an importer as the corporation purchases goods from Mr. Jack of England.
ii) A manufacturer is the one who produces or manufactures the goods. In this case, Mr. Pranav from India is a manufacturer as he manufactures tin.
iii) An exporter is the one who sells goods and services to buyers in foreign country. In this case, there are two exporters:
a. Mr. Jack of England as he sells goods to M/s. Frank Corporation in North America.
b. The person from Brazil who sells goods to Mr. Williams from USA.
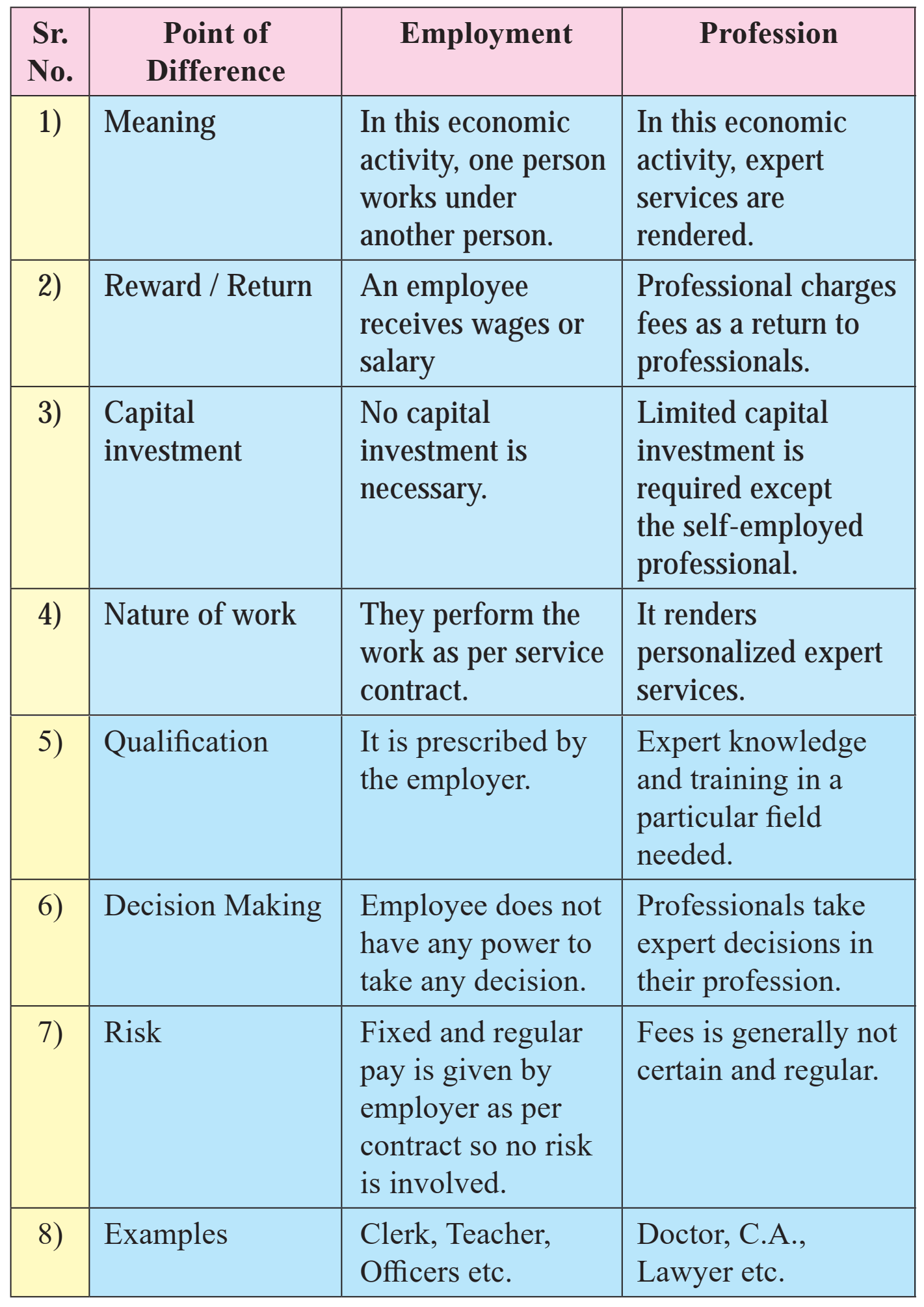
Q.4 Distinguish between.
1) Industry and Commerce
Ans.
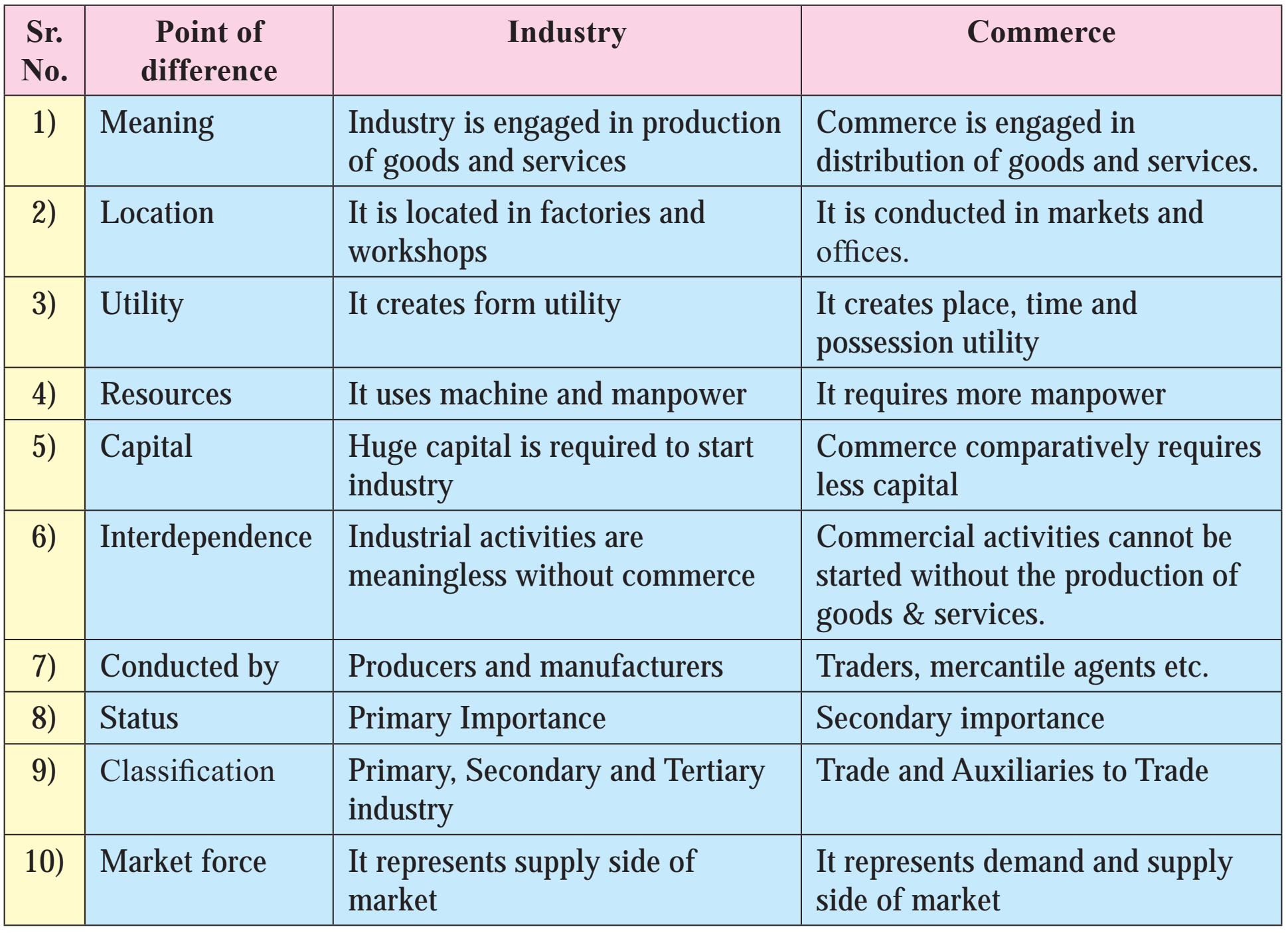
2) Business and Commerce
Ans.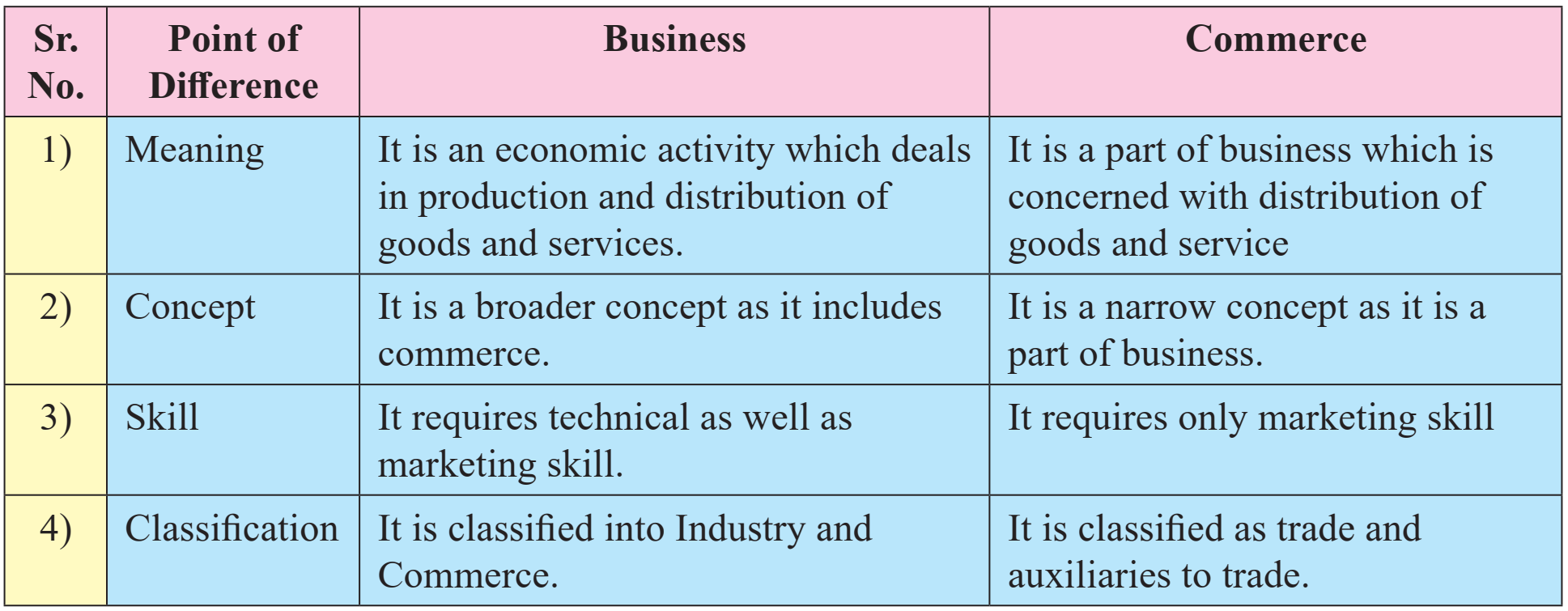
3) Business and Profession
Ans.
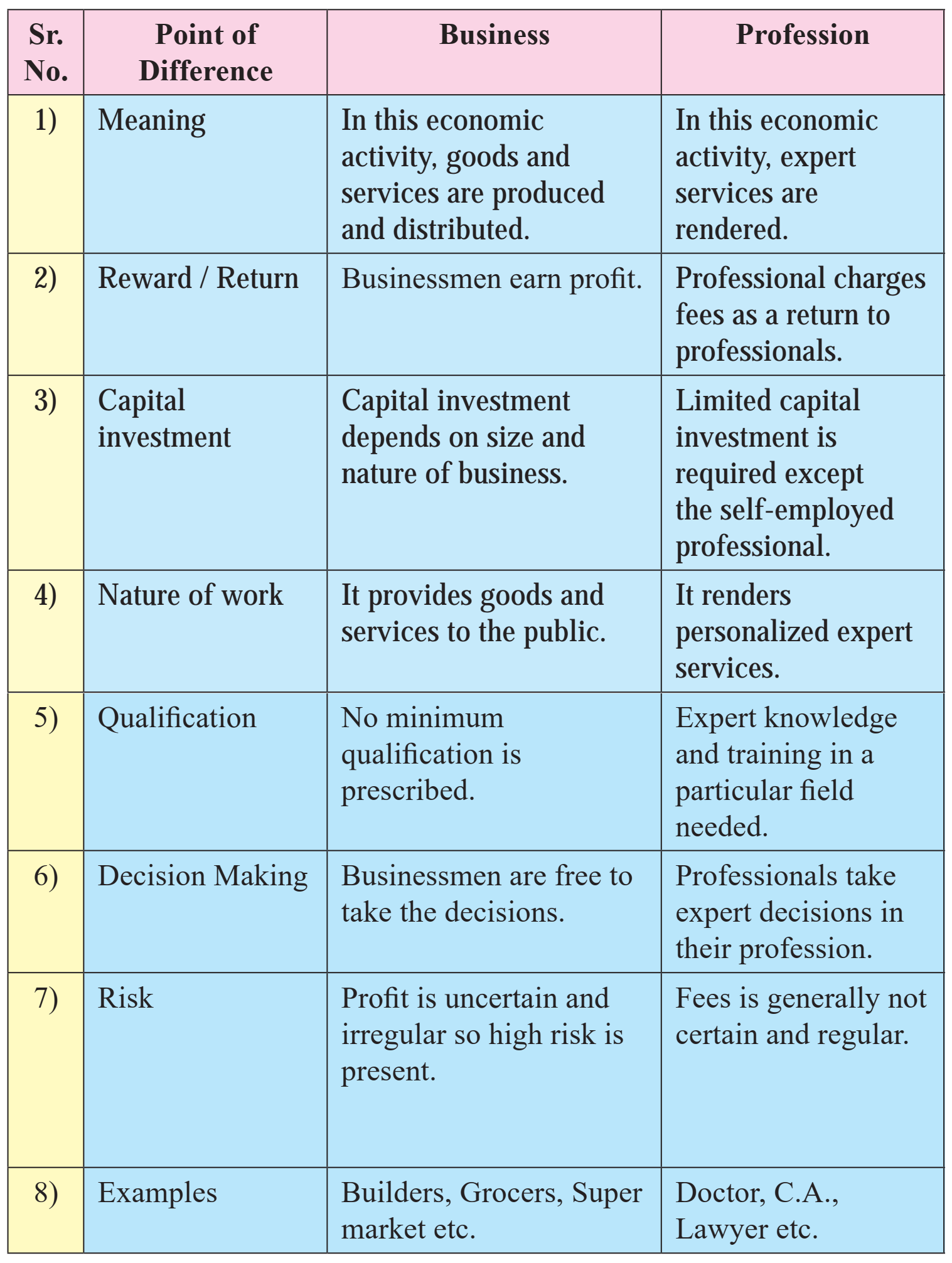
4) Employment and Profession
Ans.