1. Choose correct option
A. Which is not a property of living being?
a. Metabolism b. Decay c. Growth d. Reproduction
B. A particular plant is strictly seasonal plant. Which one of the following is best suited if it is to be studied in the laboratory?
a. Herbarium b. Museum c. Botanical garden d. Flower exhibition
C. A group of students found two cockroaches in the classroom. They had a debate whether they are alive or dead. Which life property will help them to do so?
a. Metabolism b. Growth c. Irritability d. Reproduction
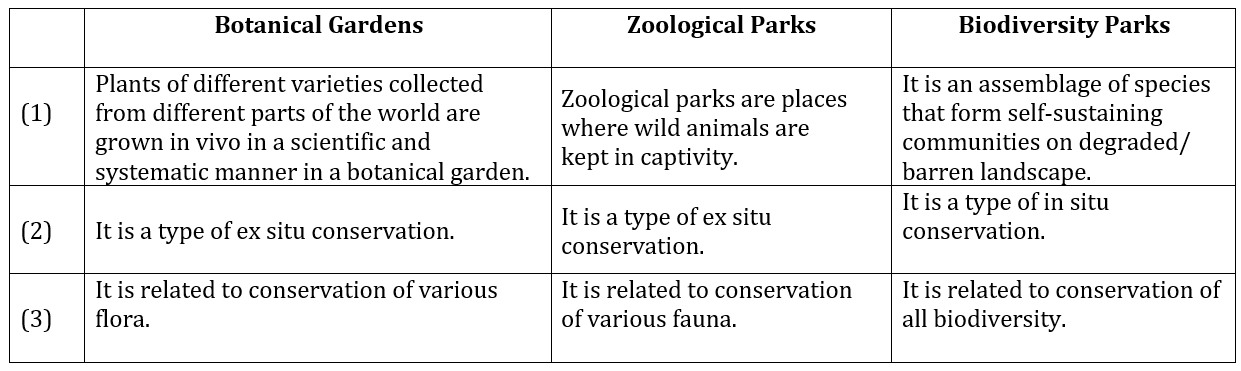
2. Distinguish between botanical gardens, zoological park and biodiversity park with reference to characteristics.
3. Answer the following questions
A. Jijamata Udyan, the famous zoo in Mumbai has acclimatised Humboldt penguins. Why should penguins be acclimatised when kept at a place away from their natural habitat?
Ans.
(1) Zoological park (zoo) is a type of ex-situ conservation in which wild animals are kept in captivity. (2) Humboldt penguins are native to South America and the surrounding environment differs significantly at
Jijamata Udyan (zoo) in Mumbai. (3) In order to ensure that these penguins survive longer and are healthy they need to be acclimatised (adjust) to their new environment slowly. (4) If they are not acclimatised or the facilities in the zoo where the penguins are kept are not optimal/ suitable, they may develop abnormal stress and exhibit unusual behaviours due to it. (5) These penguins may also be more prone to contracting certain diseases, since they are suited to living in a particular climatic condition. (6) The enclosure of these penguins consists of water pool, air handling units and a chiller system to maintain
temperatures between 12 – 14°C, where the penguins were kept for around 8 to 10 days to get acclimatised to their new environment before allowing any visitors inside the zoo. Hence, Humboldt penguins need to be acclimatised to their new surroundings, when kept at a place away from their natural habitat.
B. Riya found peculiar plant on her visit to Himachal Pradesh. What are the ways she can show it to her biology teacher and get information about it?
Ans.
(1) Riya can press and mount the plant specimen on a herbarium sheet and preserve the dried plant material, until she returns back from her visit.
(2) She can also write any available information regarding the collected specimen on the herbarium sheet, which
can be useful for further studies with her biology teacher.
(3) Various taxonomical aids can be useful to get information about this peculiar plant.
C. At Andaman, authorities do not allow tourists to collect shells from beaches. Why it must be so?
Ans.
(1) Seashells are an important part of the coastal ecosystem and are crucial for the survival of various marine creatures.
(2) They provide material for building nests of birds and also act as a substratum for attachment of algae, sea grass, sponges and various microbes.
(3) Fishes use shells for hiding from predators, whereas hermit crabs use shells as temporary shelters.
(4) Removal of seashells from seashores may also indirectly affect the rate of shoreline erosion.
Hence, in an attempt to protect the ecosystem, authorities in Andaman do not allow tourists to collect shells from beaches.
D. Why do we have green house in botanical gardens?
Ans.
(1) Greenhouse is a structure with suitable walls and a roof in which plants are grown under regulated climatic conditions.
(2) Most botanical gardens exhibit ornamental plants which require stringent/ optimum climatic conditions for their growth and/or flowering.
(3) The greenhouse associated with botanical gardens are also used to grow and propagate those plants that may not survive seasonal changes.
Hence, in order to provide optimum temperature for better growth and flowering and also to protect the plants from certain diseases, there are greenhouses in botanical gardens.
E. What do you understand from terms like in situ and ex situ conservation?
Ans.
(1) In situ conservation: It includes conservation of species in their natural habitats. Grazing, cultivation and collection of products from the forests is banned in such areas. Legally protected areas include national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves.
(2) Ex situ conservation: It includes conservation of species outside their natural habitats. Species are conserved in botanical gardens, culture collections and zoological parks.
4. Write short notes
A. Role of human being in biodiversity conservation.
Ans.
(1) Due to rapid increase in human population and industrialization, humans have over utilized natural resources; leading to degradation of the environment and hence only humans can help conserve the ecosystem.
(2) Humans are capable of conserving and improving the quality of nature and thus, can play a major role in biodiversity conservation.
(3) In order to conserve biodiversity and its environmental resources, humans must use the resources rationally and avoid excessive degradation of environment.
(4) Human beings are stakeholders of the environment and need to come together to overcome pollution and improve the environment quality in order to conserve biodiversity. E.g. Ban or limit on use of harmful products (plastic, chemicals, etc.) that are toxic to various birds, animals, etc.
(5) Human beings also play a role in conservation of biodiversity by establishment of various sites for in situ (national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves) and ex situ (botanical gardens, culture
collections and zoological parks) conservation.
B. Importance of botanical garden.
Ans. The importance of botanical gardens is as follows:
(1) It is a place where there is an assemblage of living plants maintained for botanical teaching and research purpose.
(2) Botanical gardens are important for their records of local flora.
(3) Botanical gardens provide facilities for the collection of living plant materials for botanical studies.
(4) Botanical gardens also supply seeds and material for botanical investigations.
(5) The development of botanical gardens in any country is associated with its history of civilization, culture, heritage, science, art, literature and various other social and religious expressions.
(6) Botanical gardens besides possessing an outdoor garden may contain herbaria, research laboratory, greenhouses and library.
(7) Botanical gardens are not only important for botanical studies, but also to develop tourism in the country.
5. How can you, as an individual, prevent the loss of Biodiversity?
Ans. As individuals, we can prevent loss of biodiversity in the following ways:
(1) Increasing awareness about environmental issues. Making posters that provide more information about biodiversity conservation, to raise public awareness.
(2) Increased support and/ or active participation in government policies and actions laid down for conservation of biodiversity.
(3) Protect various plant and animal species in our surrounding.
(4) Set up bird and bat houses wherever possible.
(5) Prevent felling of trees especially native plants or trees in a particular area.
(6) Reduce, recycle and reuse resources. Especially, reduce pollution and use of plastic bags and other materials that are potential threats for the environment.
(7) Use environment friendly products, segregate and dispose garbage correctly.
(8) Convince people about the importance of trees and the need to participate in tree plantation campaign.
(9) Obey the rules that fall under Biodiversity Act.