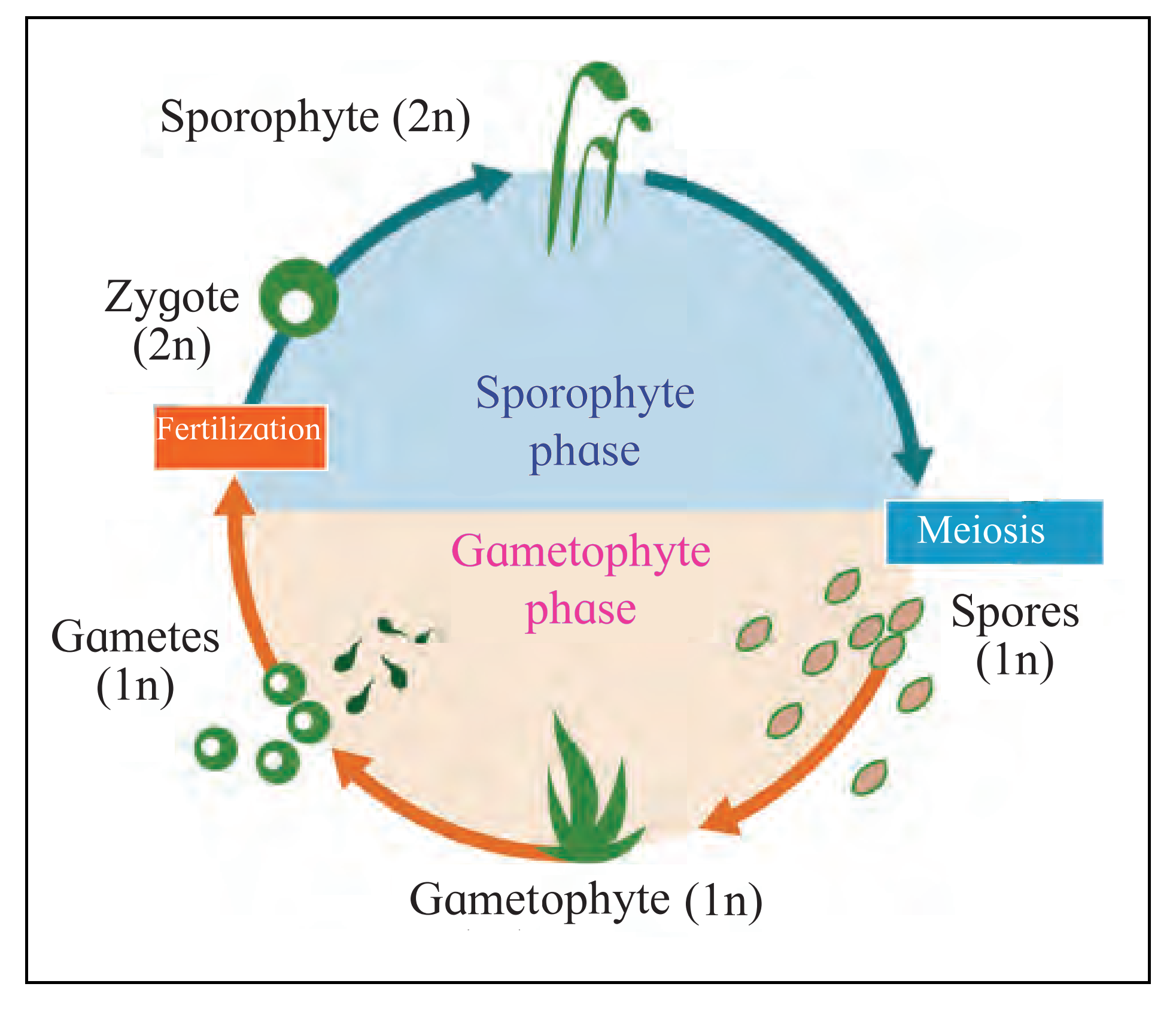
1. Choose correct option
A. Which is the dominant phase in Pteridophytes?
a. Capsule
b. Gametophyte
c. Sporophyte
d. Embryo
B. The tallest living gymnosperm among the following is ……….
a. Sequoia sempervirens
b. Taxodium mucronatum
c. Zamia pygmaea
d. Ginkgo biloba
C. In Bryophytes ……….
a. Sporophyte and gametophyte generations are independent
b. Sporophyte is partially dependent upon gametophyte
c. Gametophyte is dependent upon Sporophyte
d. Inconspicuous gametophyte
D. A characteristic of Angiosperm is ………
a. Collateral vascular bundles
b. Radial vascular bundles
c. Seed formation
d. Double fertilization
E. Angiosperms differ from Gymnosperms in having ……….
a. Vessels in wood
b. Mode of nutrition
c. Siphonogamy
d. Enclosed seed
2. How you place the pea, jowar and fern at its proper systematic position? Draw a flow chart with example of.
Ans: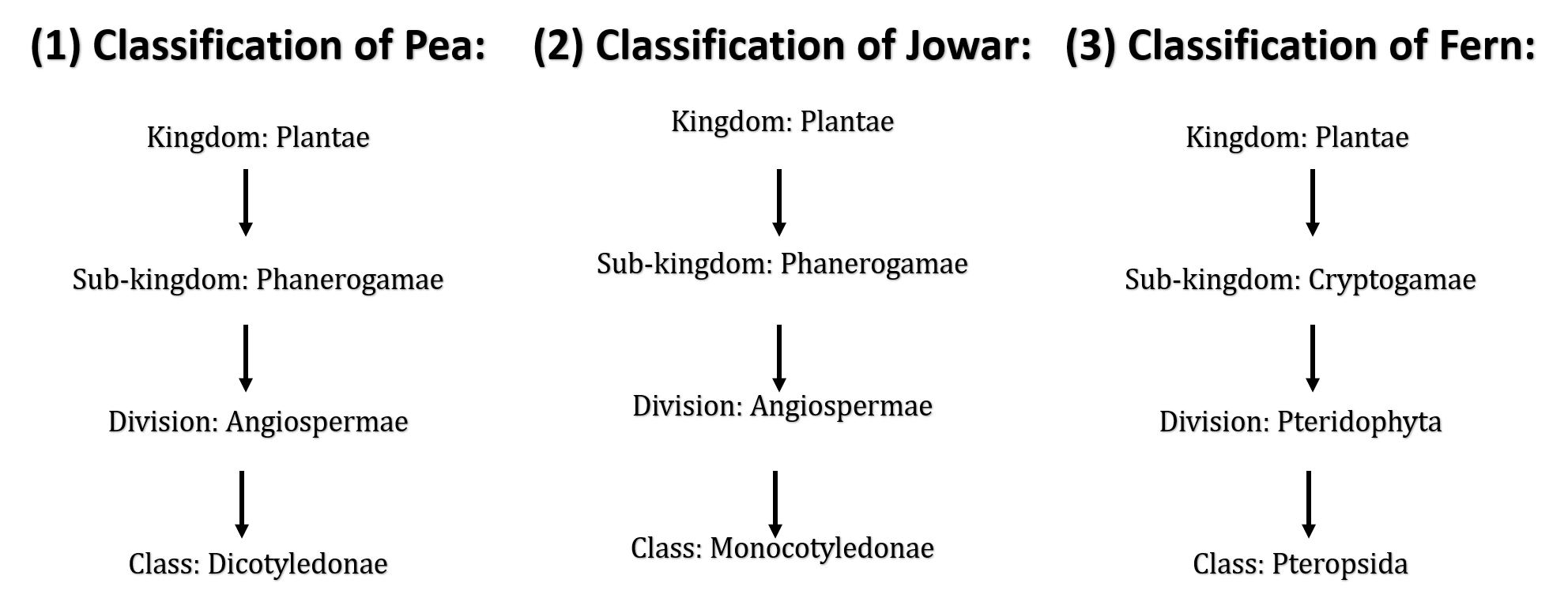
3. Complete the following table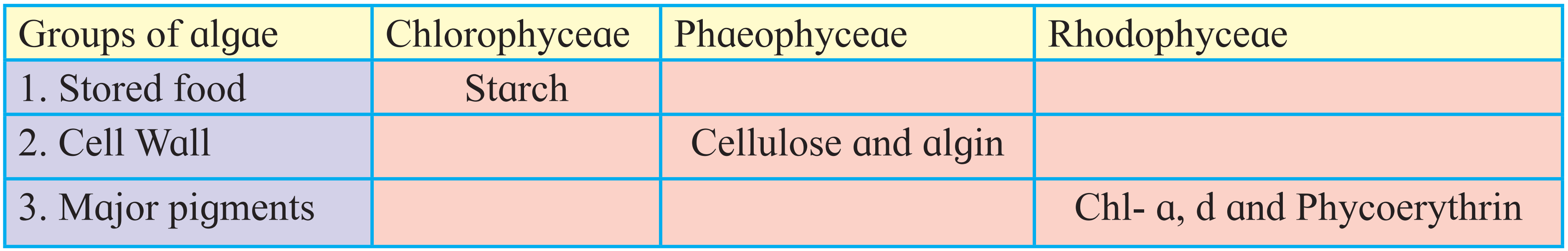
Ans.
4. Differentiate between Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae based on the following characters
a. Type of roots
b. Venation in the leaves
c. Symmetry of flower
Ans: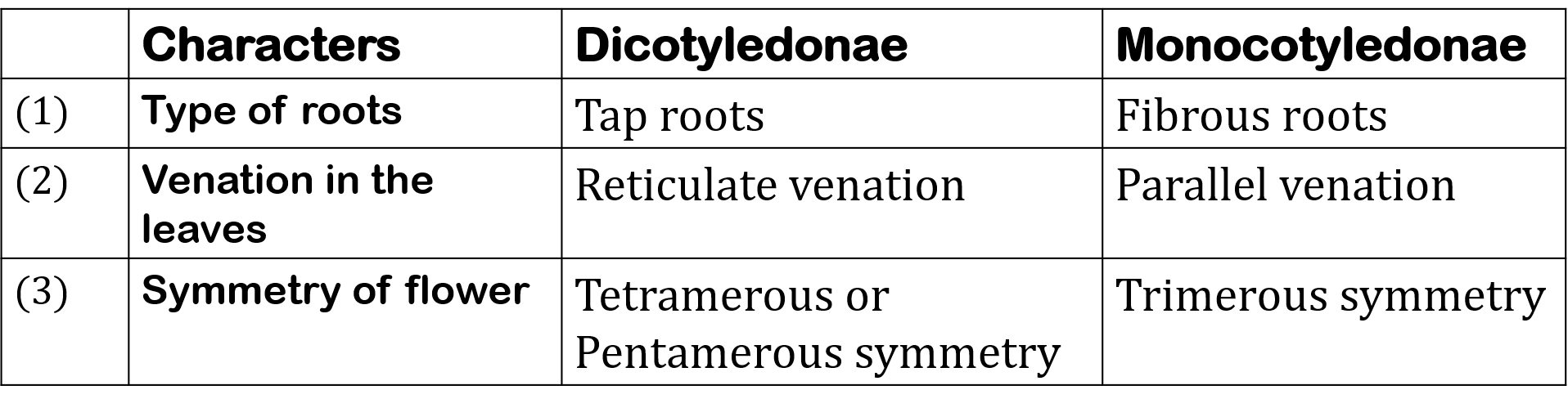
5. Answer the following questions
A. We observe that land becomes barren soon after monsoon. But in the next monsoon it flourishes again with varieties we observed in season earlier. How you think it takes place?
Ans.
(1) After monsoon, plants like mosses (bryophytes), ferns (pteridophytes), small herbaceous plants, etc become dry, due to which land becomes barren.
(2) However, spores of bryophytes, pteridophytes and seeds of herbaceous plants, grass remain in barren land.
(3) During next monsoon, these spores and seeds germinate due to availability of water and other favourable conditions.
(4) Bryophytes and pteridophytes require water for reproduction. Hence they flourish during monsoon season.
(5) Along with bryophytes and pteridophytes varieties of higher plants like grasses, some seasonal herbs or shrubs grow on barren land during monsoon due to favourable conditions.
B. Fern is a vascular plant. Yet it is not considered a Phanerogams. Why?
Ans.
(1) Fern belongs to sub-kingdom Cryptogamae.
(2) Cryptogams produce spores but do not produce seeds.
(3) Also, in cryptogams the sex organs arc concealed.
(4) Phanerogams are seed producing plants and their sex organs are visible. Hence, fern is a vascular plant. Yet it is not considered a Phanerogams.
C. Chlamydomonas is microscopic whereas Sargassum is macroscopic; both are algae. Which characters of these plants includes them in one group?
Ans.
(1) Both Chlamydomonas and Sargassum belong to division Thallophyta.
(2) Members of Thallophyta range from unicellular (e g. Chlamydomonas) to multicellular (e.g. Sargassum).
(3) Both are aquatic plants containing photosynthetic pigments.
(4) In both Chlamydomonas and Sargassum plant body is not differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
(5) The stored food is mainly in the form of starch and its other forms.
(6) Cell wall is made up of cellulose and other components.
Due to these characters, both Chlamydomonas and Sargassum are included in one group i.e. Thallophyta.
6. Girth of a Maize plant does not increase over a period of time. Justify.
Ans:
(1) Maize plant belongs to class monocotyledonae.
(2) In monocotyledonous plants, vascular bundles are closed type.
(3) Thus, cambium is absent between xylem and phloem, due to which secondary growth does not occur in these plants.
(4) Increase in girth of a stem occurs by secondary growth. Thus, girth of a maize plant does not increase over a period of time.
7. Radha observed a plant in rainy season on the compound wall of her school. The plant did not have true roots but rootlike structures were present. To which group the plant may belong?
Ans: The plant observed by Radha belongs may belong to division Bryophyta, as it shows root like structures i.e. rhizoids and absence of vascular tissue.
8. Draw neat labelled diagrams
A. Spirogyra
Ans: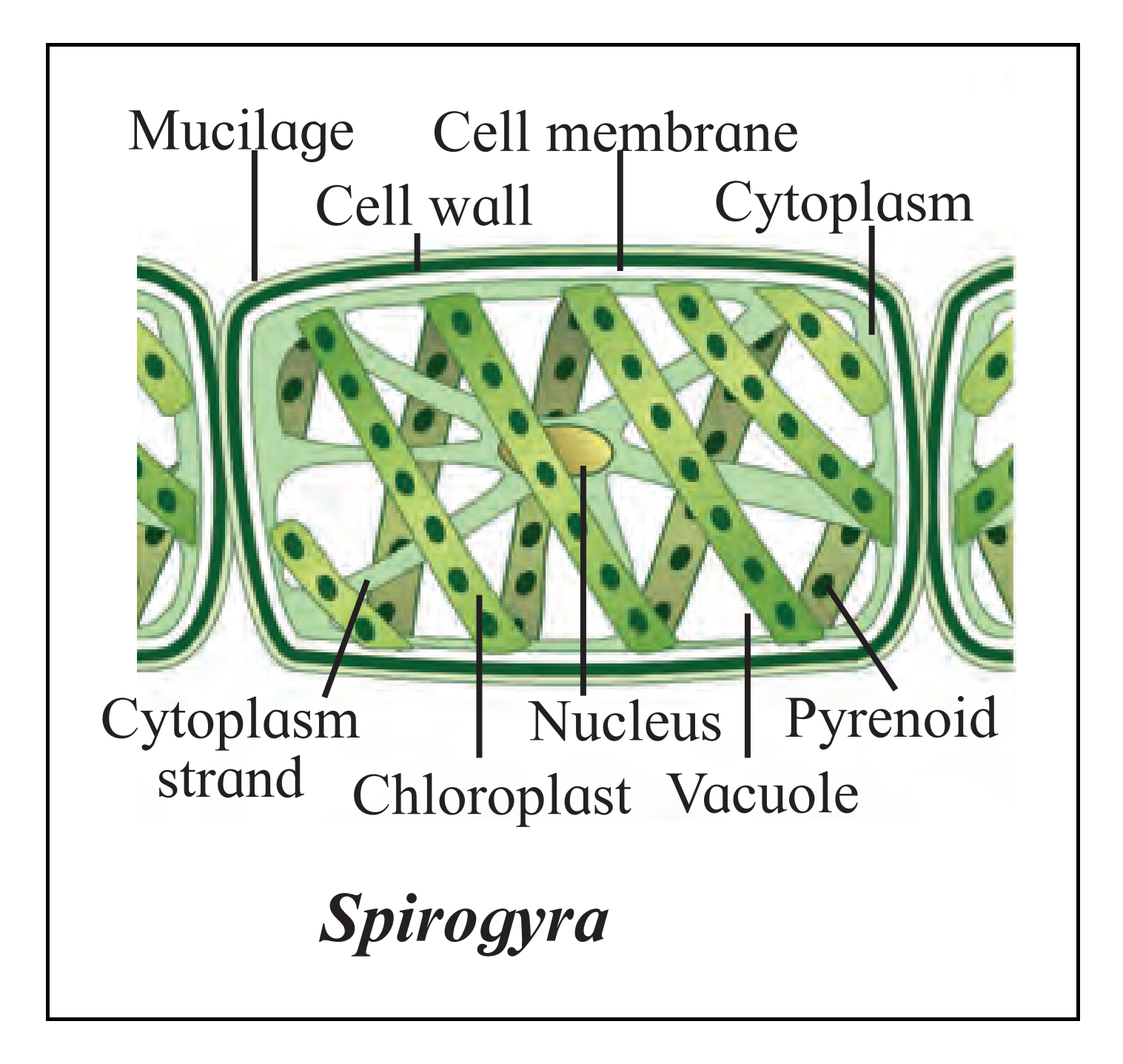
B. Chlamydomonas
Ans:
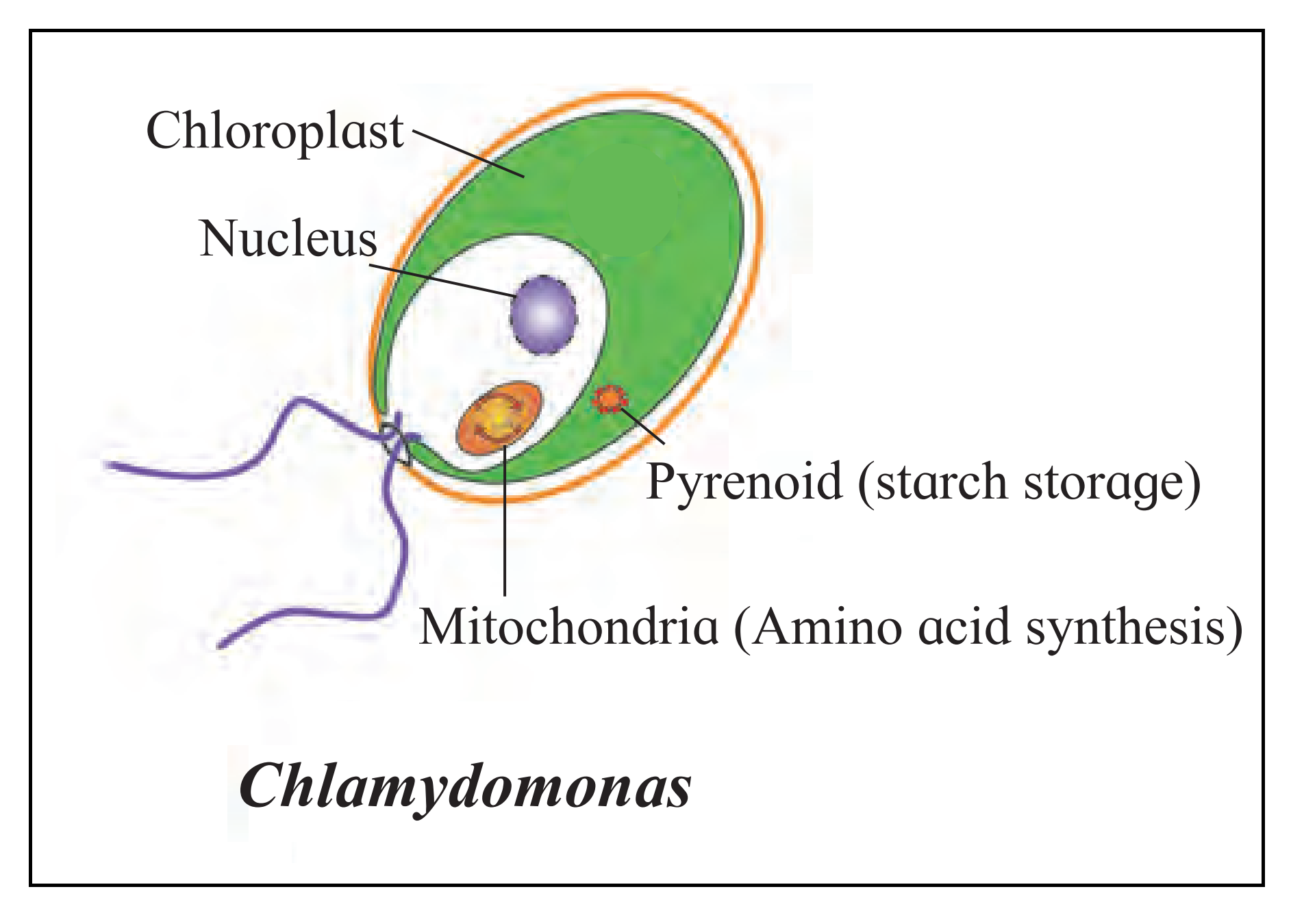
C. Funaria
Ans:
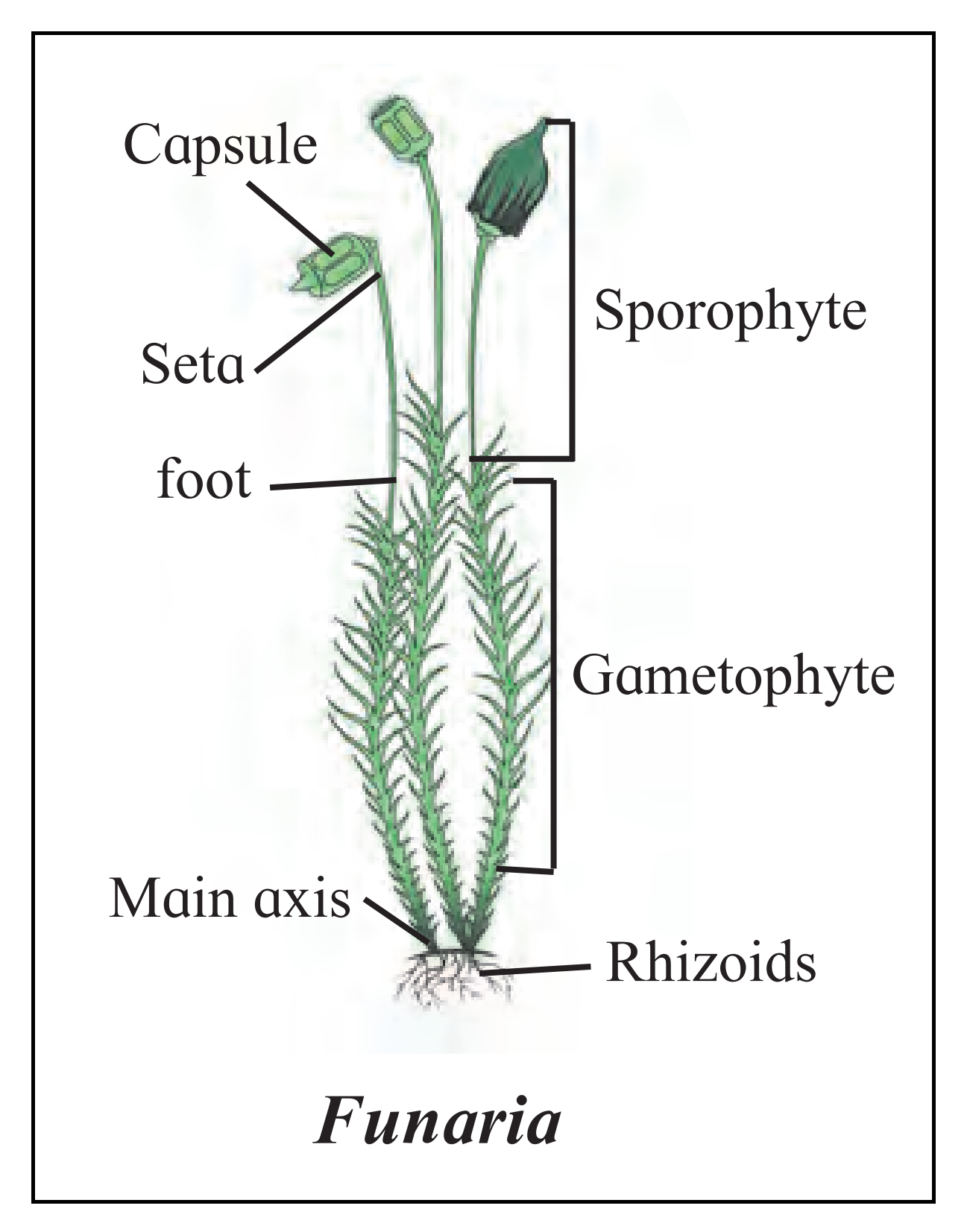
D. Nephrolepis
Ans:
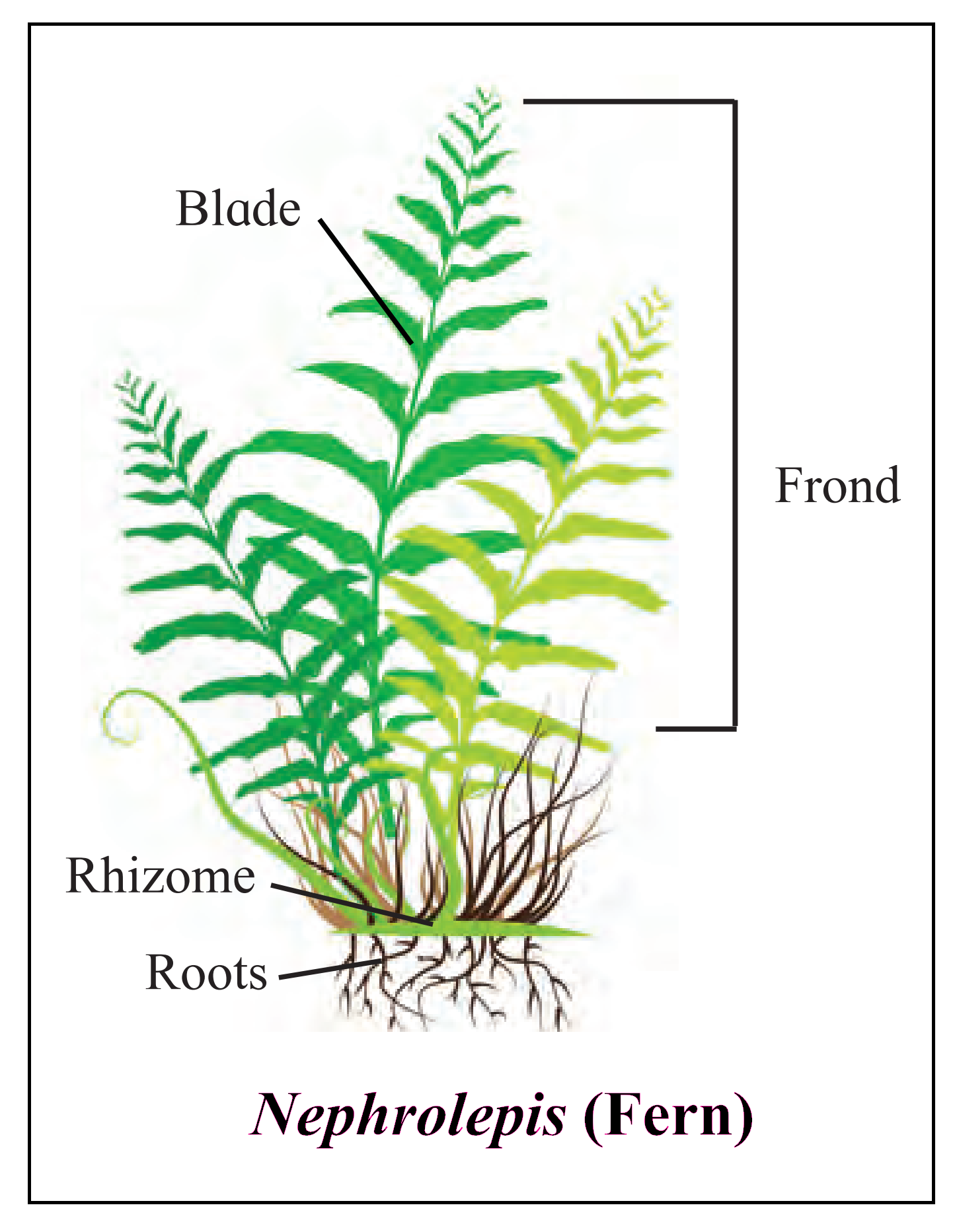
E. Haplontic and haplodiplontic life cycle
Ans: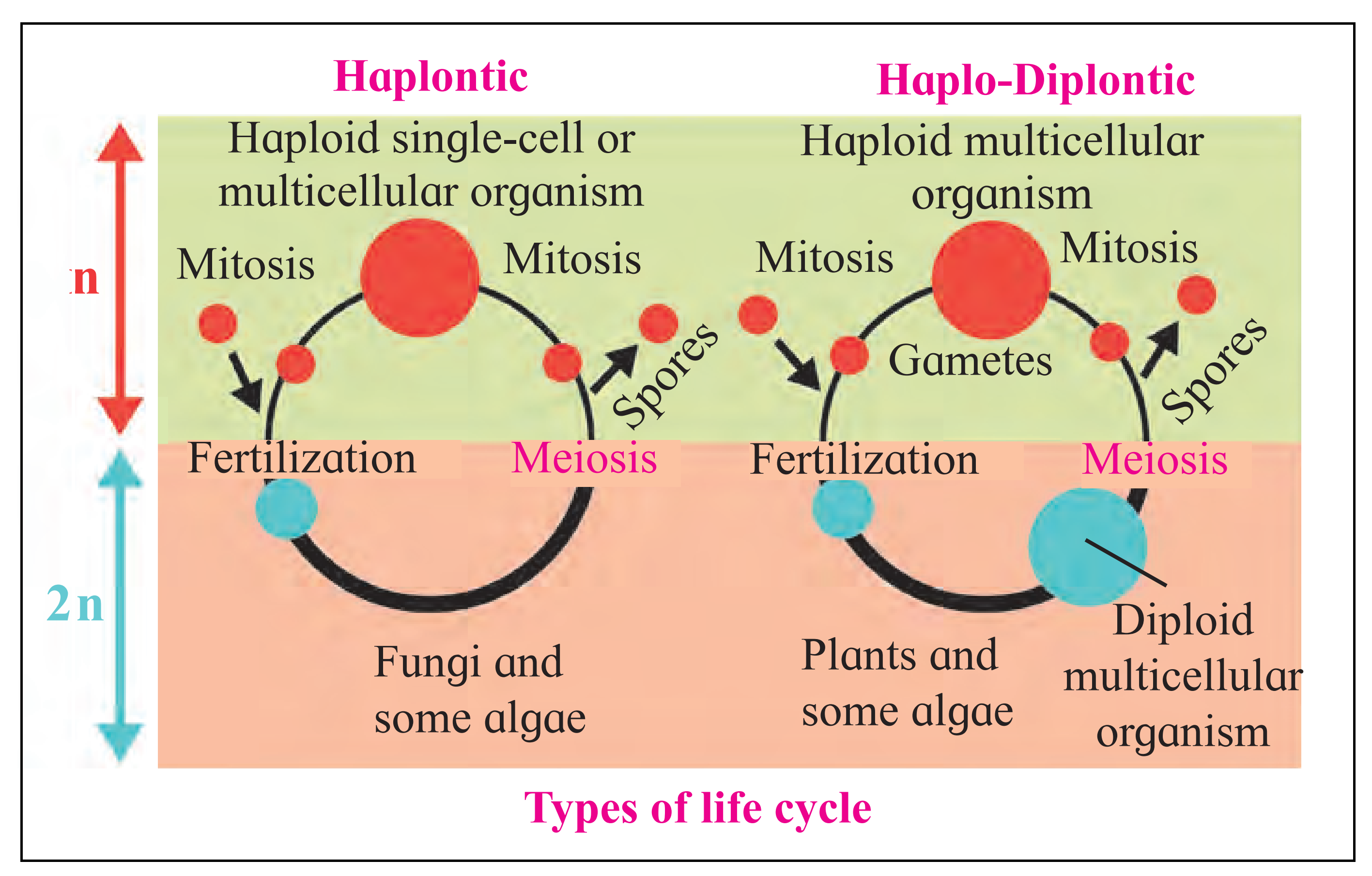
9. Identify the plant groups on the basis of following features.
A. Seed producing plants
B. Spore producing plants
C. Plant body undifferentiated into Root, Stem and leaves
D. Plant need water for fertilization
E. First vascular plants
Ans:
(1) Phanerogams (Angiospermae and Gymnospermae)
(2) Cryptogams (Thallophyta, Bryophyta and Pteridophyta)
(3) Thallophyta, Bryophyta
(4) Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta
(5) Pteridophytes
10. Observe the following diagram. Correct it and write the information in your words.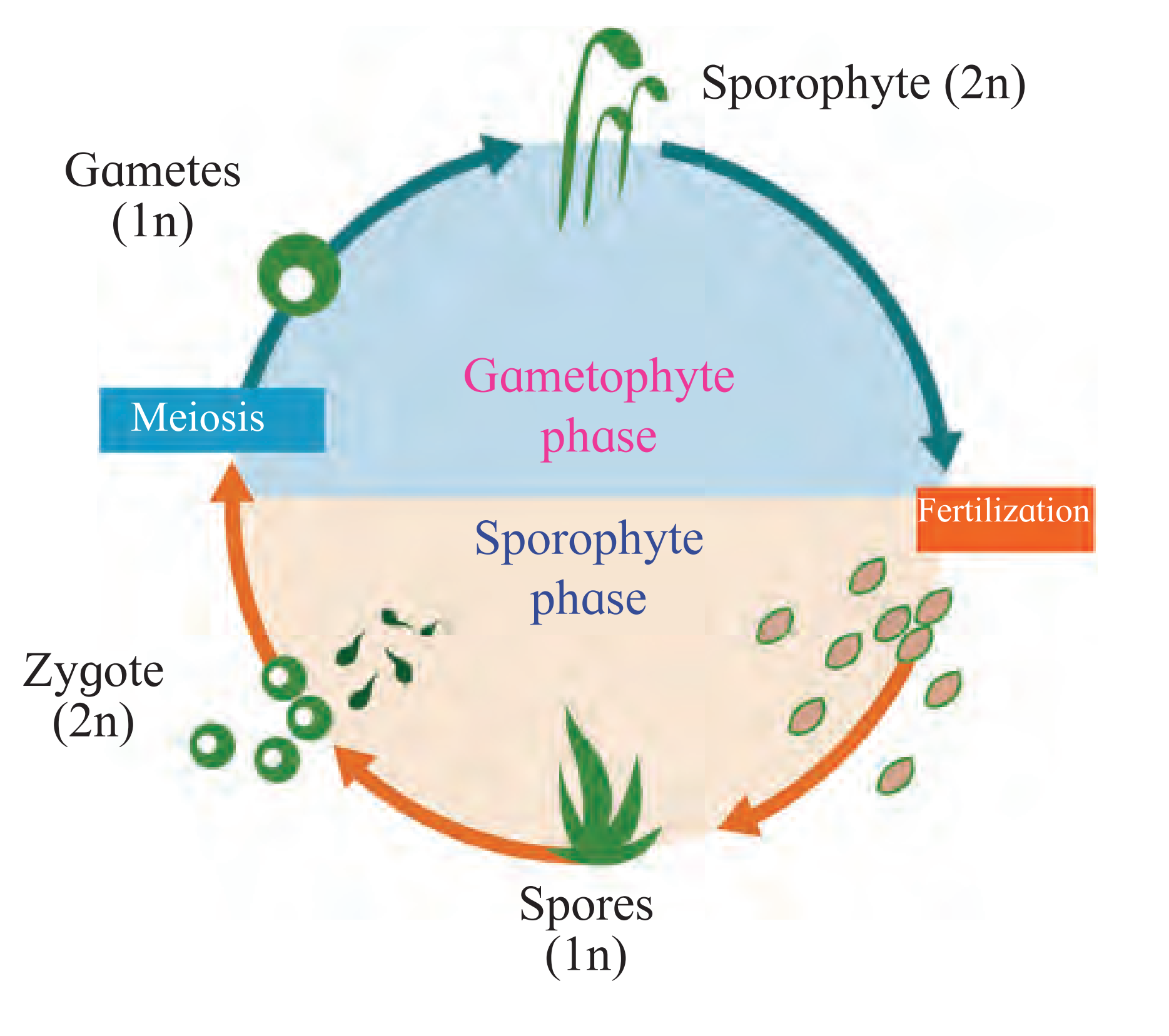
Ans: