(A) Select the correct answer from the options given below and rewrite the statements:
1. A sole trading concern ensures Maximum business secrecy.
2. The members of the Hindu undivided family business are called coparceners.
3. The head of joint Hindu Family Business is called as KARTA.
4. Registration of partnership firm is compulsory in Maharashtra
5. The liability of the shareholders in the joint Stock Company is Limited.
6.A Joint Stock Company is an artificial person created by Law.
7. Registration of a Joint Stock Company is Compulsory.
8. The liability of members of a Co-operative Society is Limited.
9. Indian Co-operative Society’s Act was passed in 1912.
10.The common seal acts as a signature of the company.
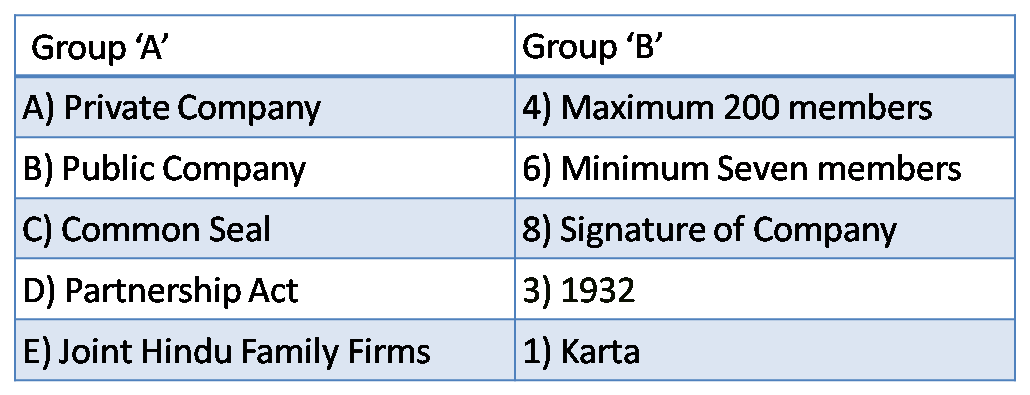
(B) Match the pairs.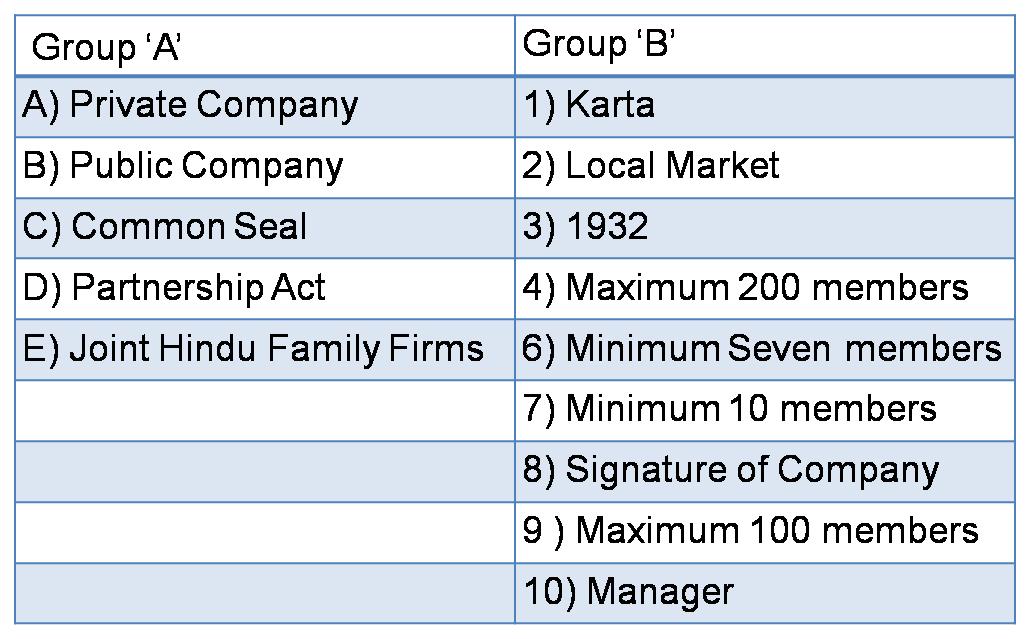
Ans :
C) Give one word / phrase / term.
1) An elected body of representatives of co-operative Society for its day to day administrations.
Ans : Managing committee.
2) The owner is the sole manager and decision maker of his business.
Ans : Sole Trader.
3) One man show type of business organization.
Ans : Sole trading Concern.
4) The members of the Joint Hindu Family firm.
Ans : Co-parceners.
5) A Partner who gives his name to partnership firm.
Ans : Nominal partner.
6) There is free transferability of shares in this company.
Ans : Public Company.
7) A partnership agreement in writing.
Ans : Partnership Deed.
8) The motto of the co-operative Society.
Ans : Service.
9) An organization which is service oriented.
Ans : Co-operatives Society.
D) State True or False for the following sentences
1) Sole trader is the decision maker of the business.
Ans : True.
2) Sole trading concern operates in local markets.
Ans : True.
3) Sole proprietorship is useful for small business.
Ans : True.
4) The liability of KARTA is unlimited.
Ans : True.
5) The maximum number of members is unlimited in Joint Hindu Family Firm.
Ans : True.
6) Joint Stock company can raise huge amount of capital.
Ans : True.
7) There is a separation of ownership & management in Joint Stock Company.
Ans : True.
8) Board of Directors manage the business of Joint Stock Company.
Ans : True.
9) Partnership agreement may be oral or written.
Ans : True.
10) In partnership firm, the liability of every partner is limited, joint & serveral.
Ans : False
11) The main motto of co-operative society is to render services to its shareholders.
Ans : False
12) The membership of a co-operative society is compulsory.
Ans : False
E) Find the odd one.
1) Sole proprietorship, Joint Hindu family, Non- Government Organization (NGO) Partnership firm.
Ans : Non-Government Organization (NGO)
2) Active Partner, Shareholder, Nominal partner, Secret partner.
Ans : Shareholder
F) Complete the sentences.
1) Private sector enterprises are owned and managed by private entities.
2) There is only one owner in Sole Trading Concern.
3) Registration of Joint Stock Company is compulsory according to the Companies Act 2013.
4) A partner who takes active participation in the day to day working of the business is known as active partner.
5) When there is no provision in partnership agreement regarding time period for partnership then it is known as Partnership at will.
6) The management of the JHF business is jointly owned by the KARTA.
7) The management of Co-operative society is based on democratic principles.
8) The rule for voting in a Co-operative society is one member one vote.
9) The rule for voting in joint Stock company is one share one vote.
10) The face value of the shares of Co-operative society is very less.
11) Consumer’s co-operatives are formed by consumers.
G) Complete the following table.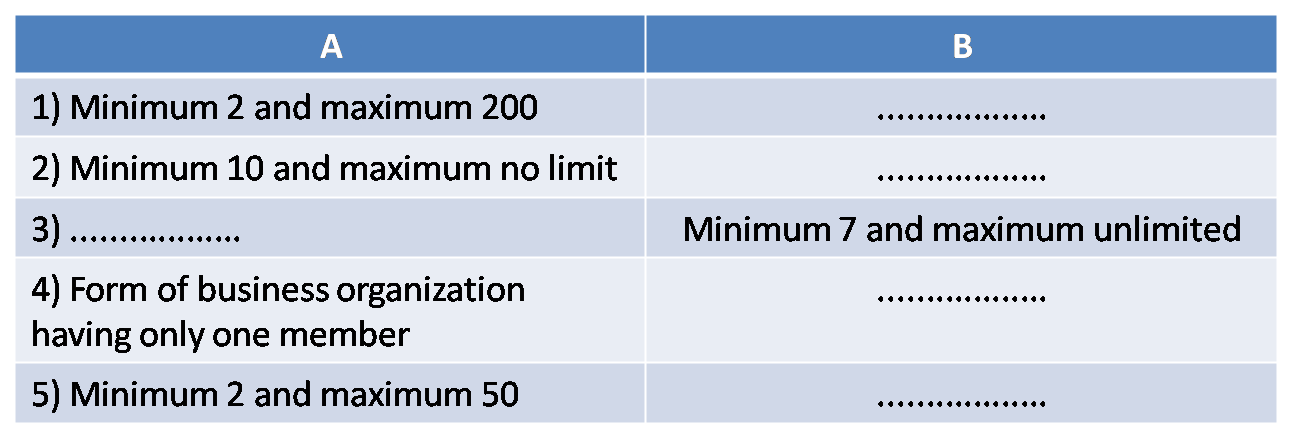
Ans : 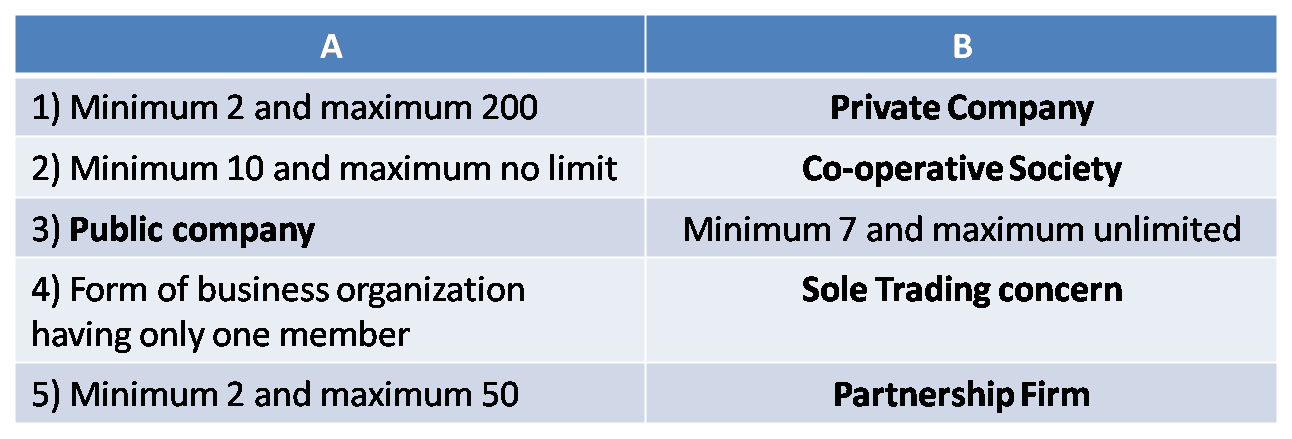
H) Answer in one sentences.
1) What is sole Trading concern?
Ans : Sole Trading Concern is a type of business which is owned, managed, and controlled by one person.
2) What is by partnership firm?
Ans : A business owned and managed by two or more persons sharing profits and losses is called a partnership firm
3) What is the meaning of Joint stock Company?
Ans : Joint Stock Company is an artificial person created by law, having an independent legal status, owned by shareholders and managed by Board of Directors.
4) What is JHF business?
Ans : A joint Hindu Family is a form of business organization which runs from one generation to another according to the Hindu Law.
5) What is by co-operative Society?
Ans : Cooperative Society is a voluntary association of individuals which is formed for providing services to members.
6) What is by minor partner?
Ans : A minor partner is a partner who is admitted into the partnership firm for the benefit of the firm with the consent of all partners.
7) What is Quasi Partner?
Ans : Quasi partner is a partner of the partnership firm who has retired from the firm but has left his capital behind in the firm.
8) What is by partner-in-profits only?
Ans : A partner-in-profits only is a partner who gets into an agreement to share only the profits of the partnership firm and not the losses.
9) What is by general partnership?
Ans : A general partnership is a form of partnership where, the liability of all the partners is unlimited, joint, and several. Every partner has an equal right and it can be formed under the Partnership Act of 1932.
10) What is the meaning of Private Company?
Ans : A Private Limited company is a company which by its articles restricts the right to transfer share, limits the maximum number of members to 200.
11) What is by Public Company?
Ans : A public company means a company which is not a private company.
I) Correct the underlined word and rewrite the following sentences.
1) In public company, shares are not freely transferrable
Ans : In Private Company, shares are not freely transferable.
2) In Private Company, there are minimum 3 (Three) directors.
Ans : In Private company, there are minimum 2 (Two) directors.
3) Registration of Joint Stock Company is not compulsory.
Ans : Registration of Joint Stock Company is compulsory
4) There is less secrecy in Sole Trading concern.
Ans : There is maximum secrecy in Sole Trading concern.
5) In a Partnership firm, minimum three members are required.
Ans : In partnership firm, minimum two members are required.
6) In Joint Hindu Family business, the senior most member of family is called as Co-parcener.
Ans : In Joint Hindu Family business, the senior most member of family is called as Karta.
7) Indian Partnership Act, 1940 is applicable in India.
Ans : Indian Partnership Act, 1932 is applicable in India.
Q.2 Explain the following terms/concepts.
1) Sole Trading Concern.
Ans : The word ‘Sole’ means single and ‘Proprietorship’ means owner. Thus, the name itself suggest that there is only one owner. A sole trader is an independent owner of a business. The proprietor has all the rights and responsibilities of the business and any profit or loss made. e.g. : Grocery Shop, Beauty Parlour, Gift Shop etc.
2) Partnership Firm.
Ans : A business organization owned and managed by more than one person where all partners share profits and losses of the business as well as liability, is known as partnership firm. This form of business organization evolved because of limitation on capital raising capacity and managerial inability of proprietary concern.
3) Joint Hindu Family Business.
Ans : When the family members on an Hindu undivided family run any business like a family business, it is called as Joint Hindu Family business (JHFB). It has originated in and exists only in India. The JHFB is managed by the Karta. It is also known as ‘Hindu Undivided Family Business’ or ‘Joint Hindu Family Firm’.
4) Co-operative Society.
Ans : A Co-operative organization is a voluntary association of individuals formed in order to achieve certain economic objectives. The nature of co-operative organization is service oriented. ‘Each for all and all for each’ is the principle of co-operative society.
5) Joint Stock Company
Ans : A Joint Stock Company is a voluntary association of persons who generally contribute capital. They carry on a particular type of business, which is established by law. The total capital of
Joint Stock Company is known ‘Share Capital’. It is divided into small units called ‘Shares’. Every member holds some shares. These, members are called as ‘Shareholders’. In India, every joint stock company is registered as per “The Companies Act, 2013”.
6) Karta
Ans : The senior most member of the Joint Hindu Family is called as Karta. The Joint Hindu Family Business is managed by Karta. He has experience and knowledge of the family business. Karta takes all business decisions and has unlimited liability. He takes utmost care of co-parceners’ interest in the business.
7) Managing Committee
Ans : The management of co-operative society is in the hands of Managing Committee of members. They are elected representatives of shareholders. All the important
business decisions are taken by managing committee members. The committee members look after day-to-day administration of society.
8) Nominal Partners
Ans : A partner who only lends his name and reputation to the partnership firm is called a nominal partner. He is simply obliging his friends by allowing the firm to use his name as a partner.
He may or may not be given any share in the profits of the firm. He does not contribute to the capital of the business. He is liable to the debts of the firm.
Q.3 Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
1) Mr. Raghunath is running business from last 30 years. This business is ancestoral business of Mr. Raghunath. Kiran and Naman, two sons of Mr. Raghunath are helping him along with their wives.
i) Find out types of business.
ii) Who is Raghunath?
iii) What Kiran & Naman are called?
Ans :
i) It is an example of Hindu Undivided Family Business'(HUF) or Joint Hindu Family Firm (JHFF) or Joint Hindu Family Business (JHFB).
ii) Mr. Raghunath is ‘Karta’ in this family business (senior most member who manages the family business).
iii) Kiran and Naman are ‘co-parceners’ in this business (other members in JHFB who assist the Karta).
2) Mr. Sawant a Chartered Accountant by profession and Mrs. Tambe, an Architect by
profession running a firm namely ‘ST Firms’ in Nagpur.
i) Identify the form of business organization in the above examples.
ii) comment on it.
iii) which two professions are mentioned here.
Ans :
i) It is partnership business where Mr. Sawant and Mr. Tambe are two business partners.
ii) Mr. Sawant and Mr. Tambe have come together for the purpose of business. They have agreed to share profits and losses of the business. The name of their firm is ‘S.T. Firms’ and it is located in Nagpur. The liability of both Mr. Sawant and Mr. Tambe is unlimited.
iii) The two professions mentioned in this example are: Chartered Accountant and Architect.
Q.4 Distinguish between
1) Private Limited Company and Public Limited Company
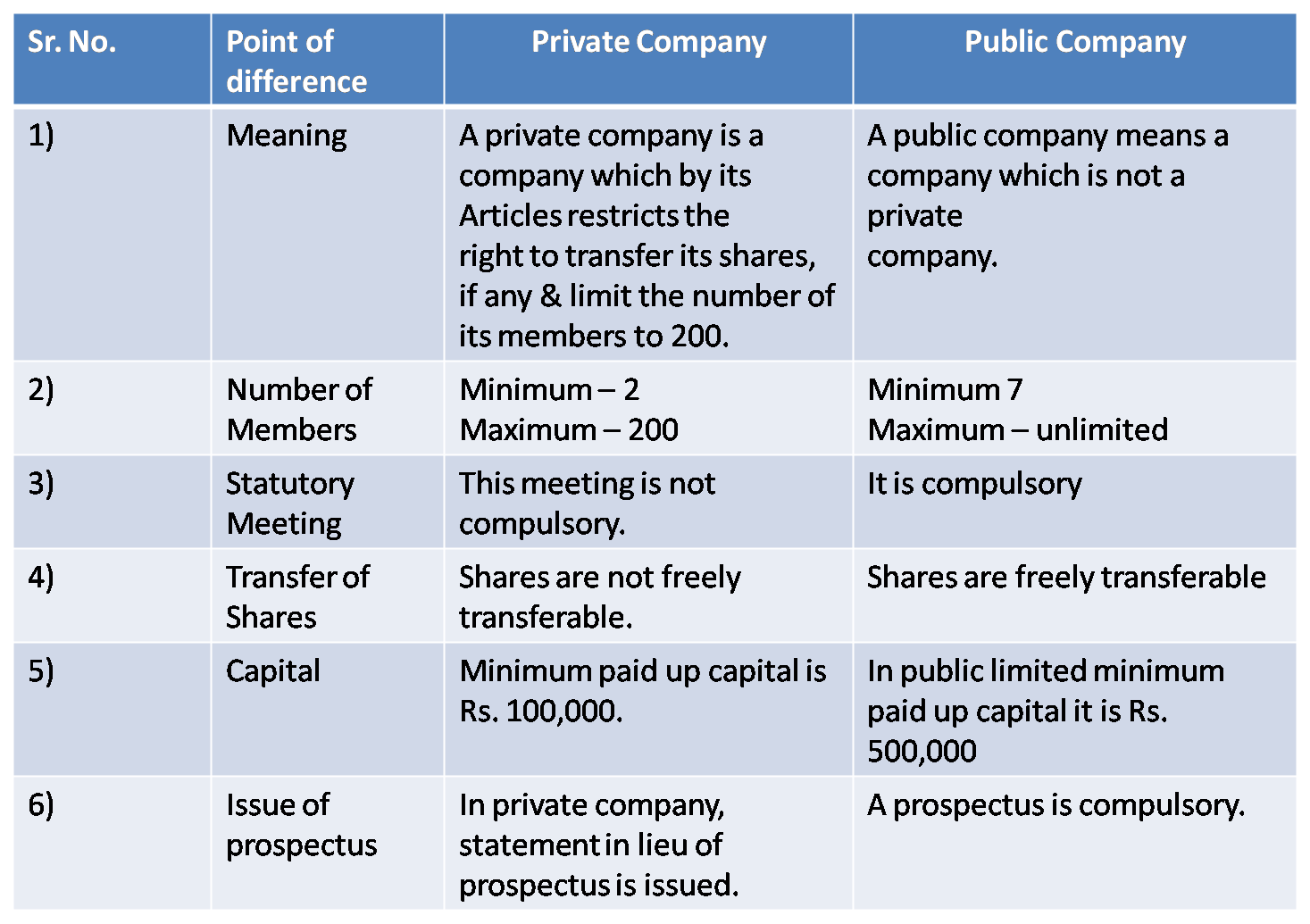
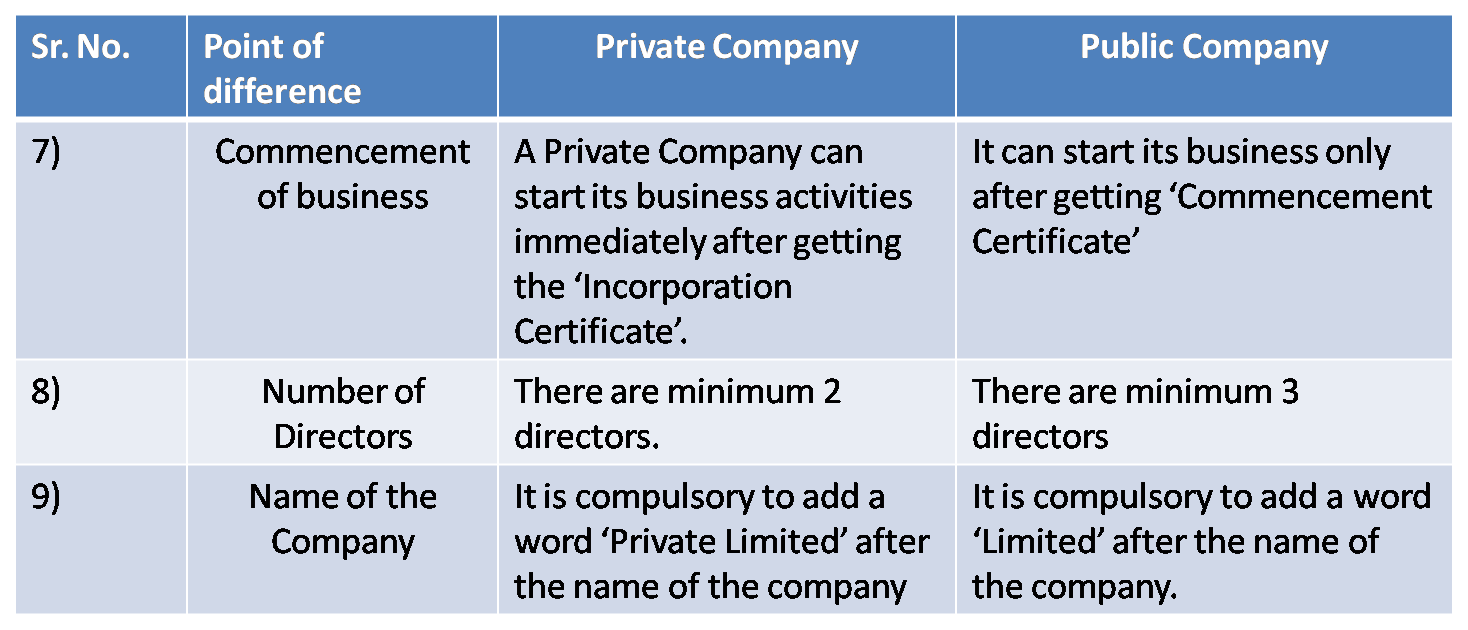
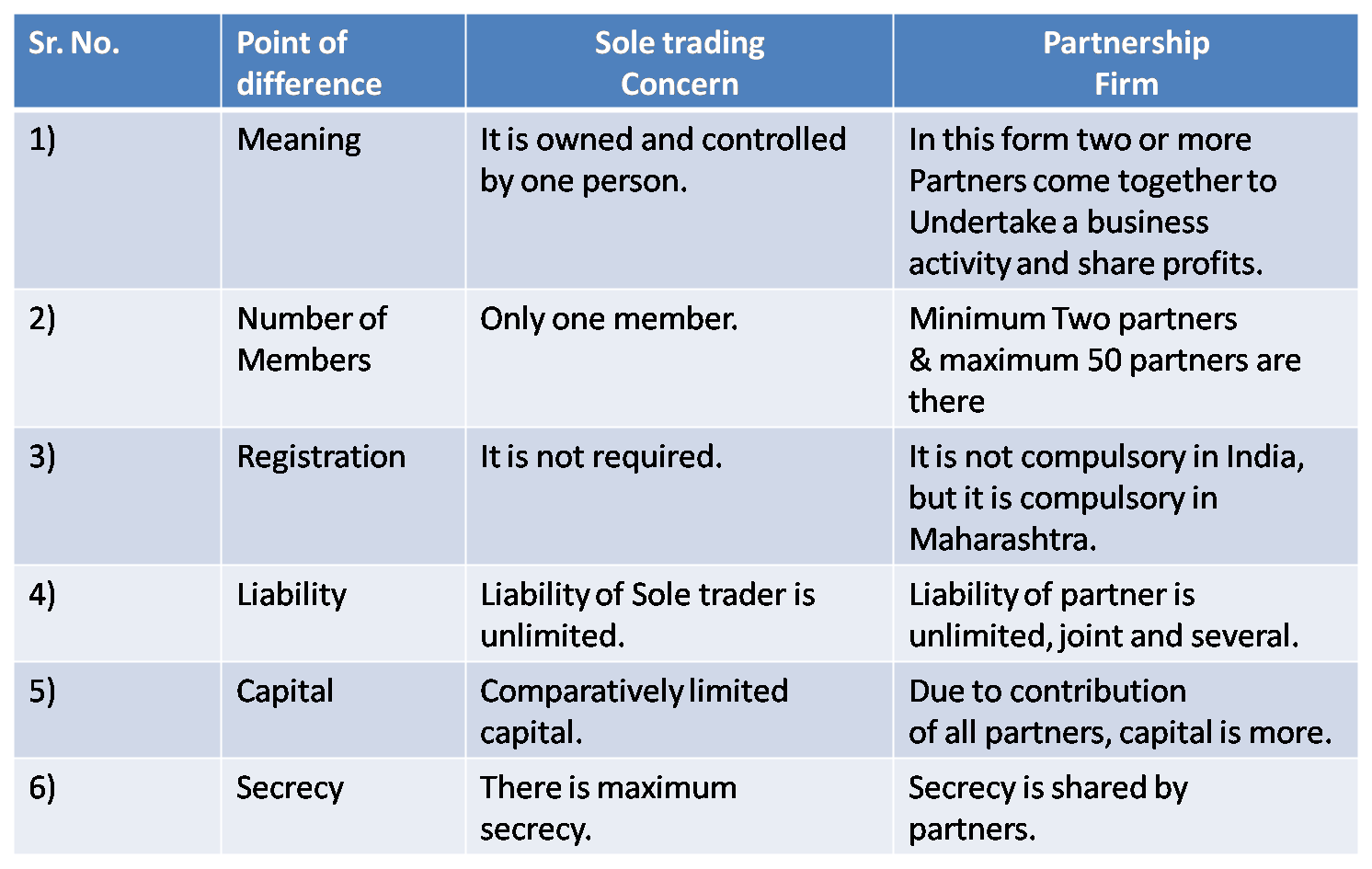
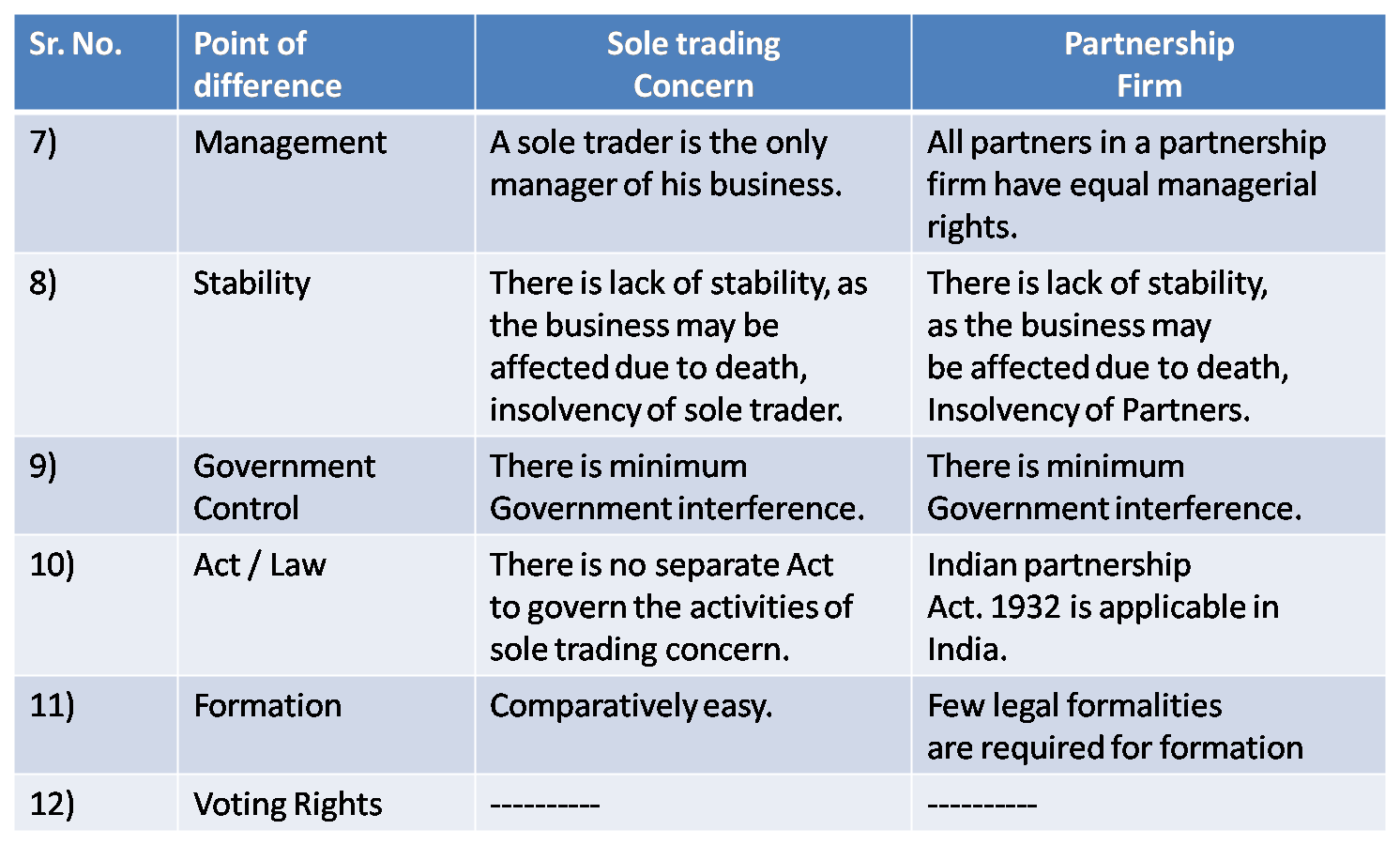
2) Sole Trading Concern & Partnership Firm
Ans :
3) Partnership Firm & Joint Hindu Family
Ans :
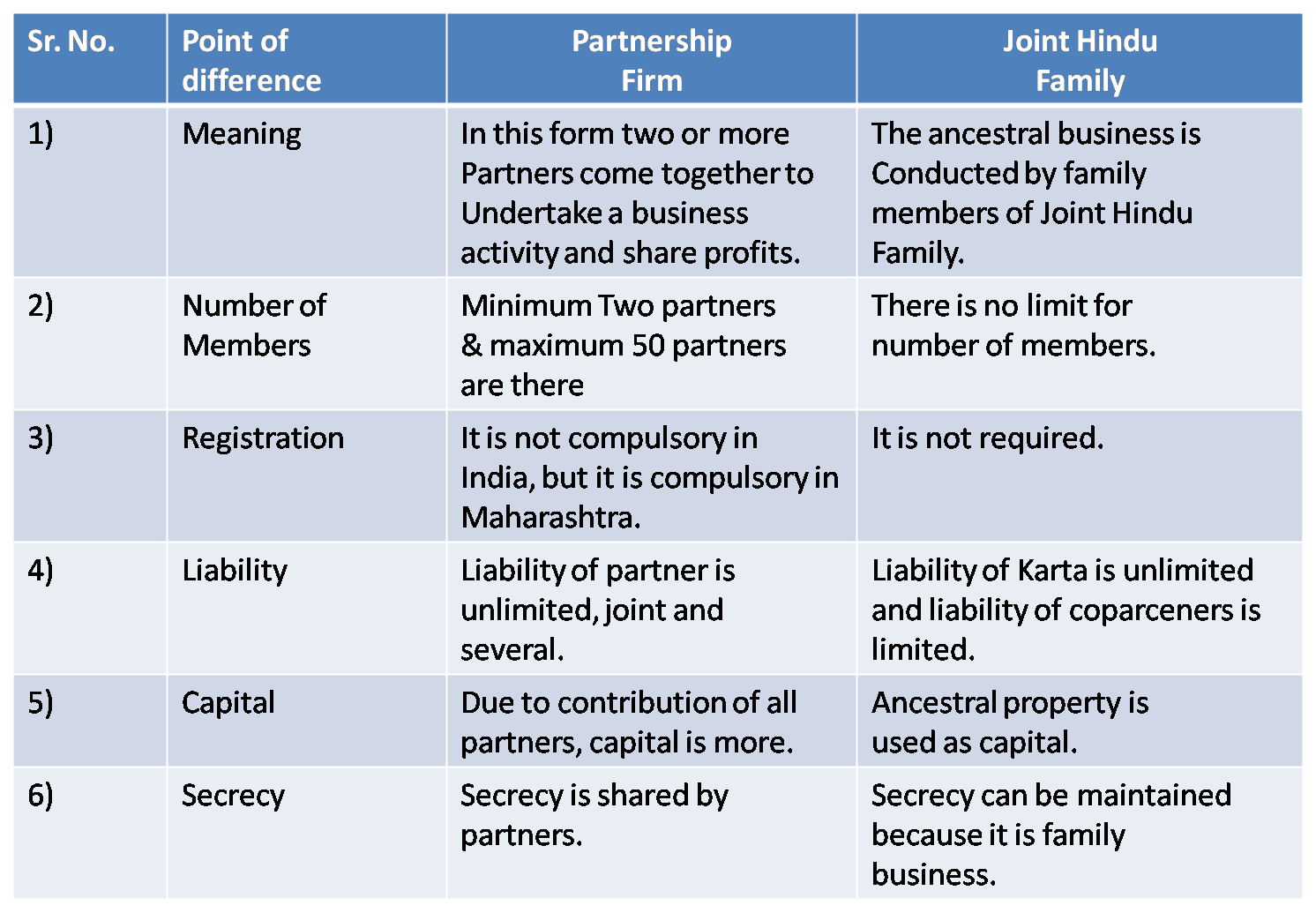
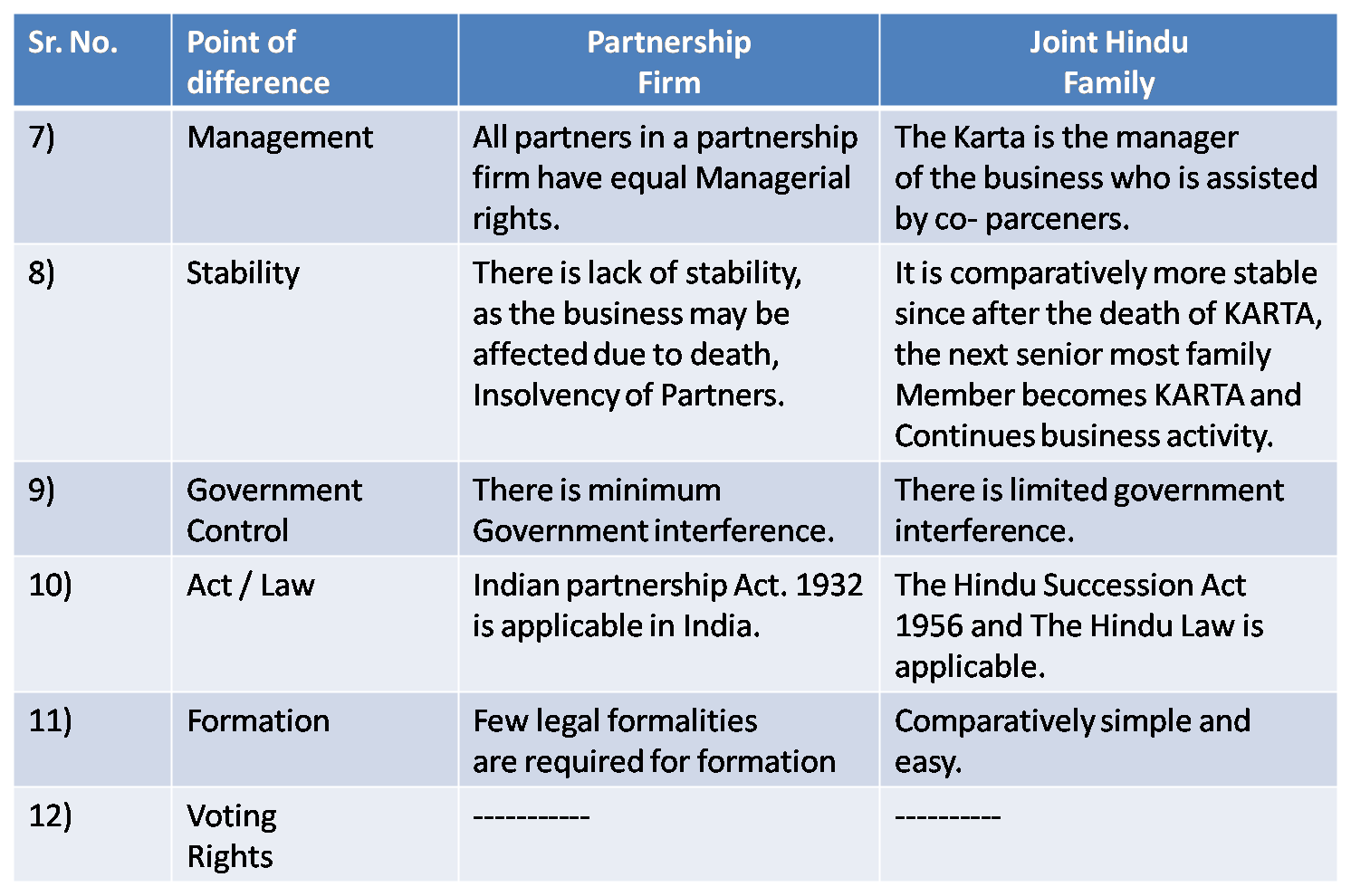
4) Co-operative Society & Joint Stock Company
Ans :
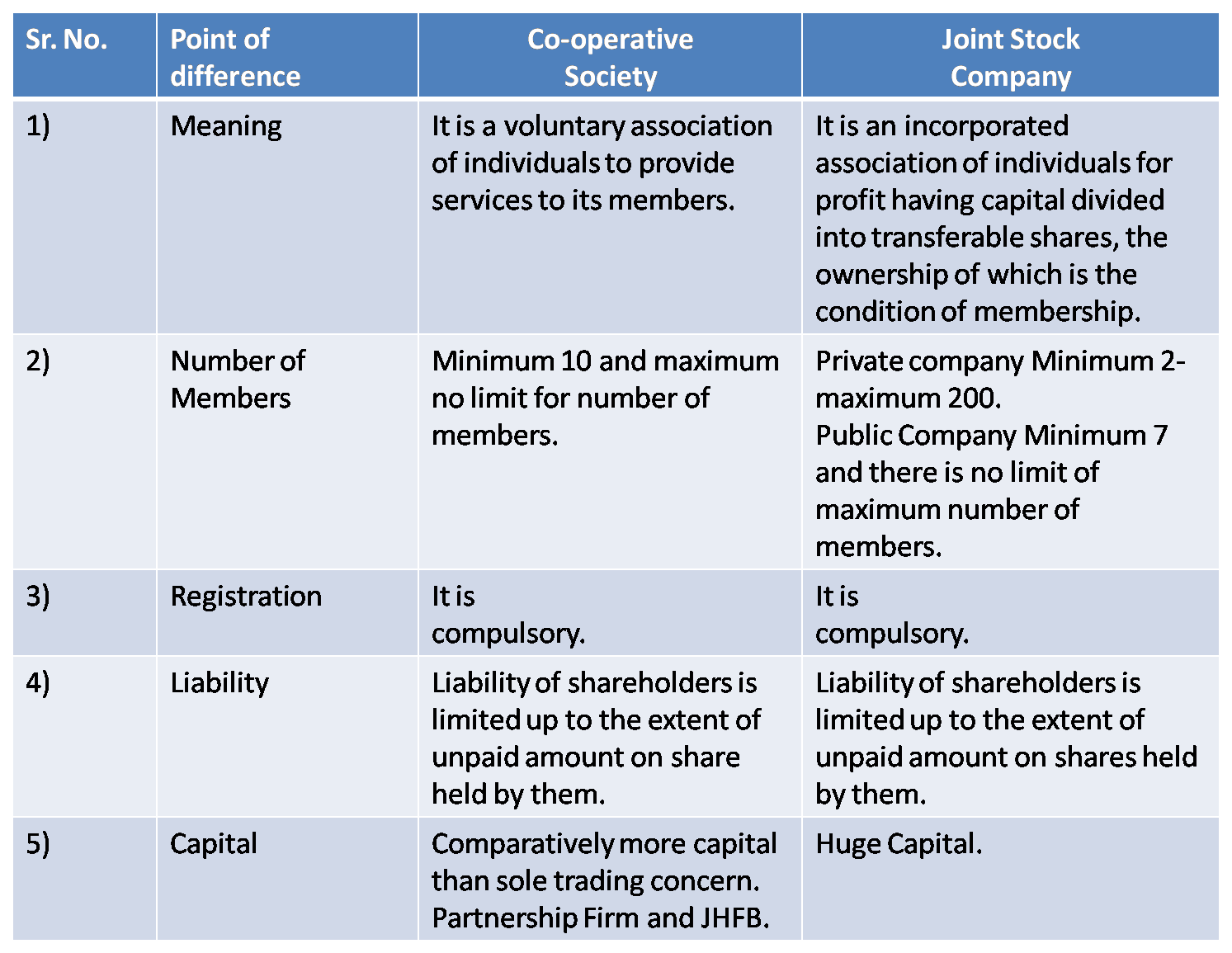
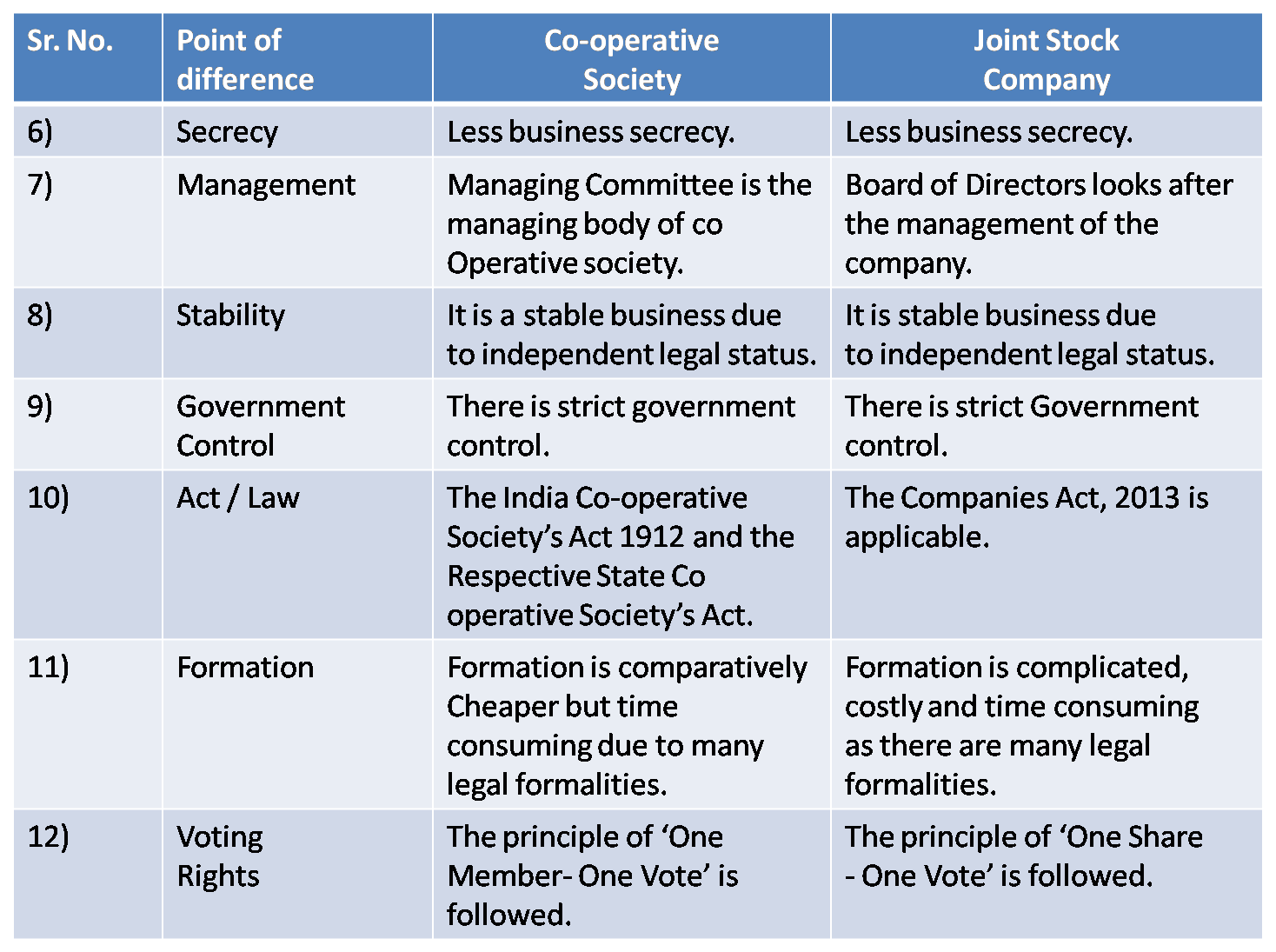
5) Joint Hindu Family Firm and Joint Stock Company
Ans :
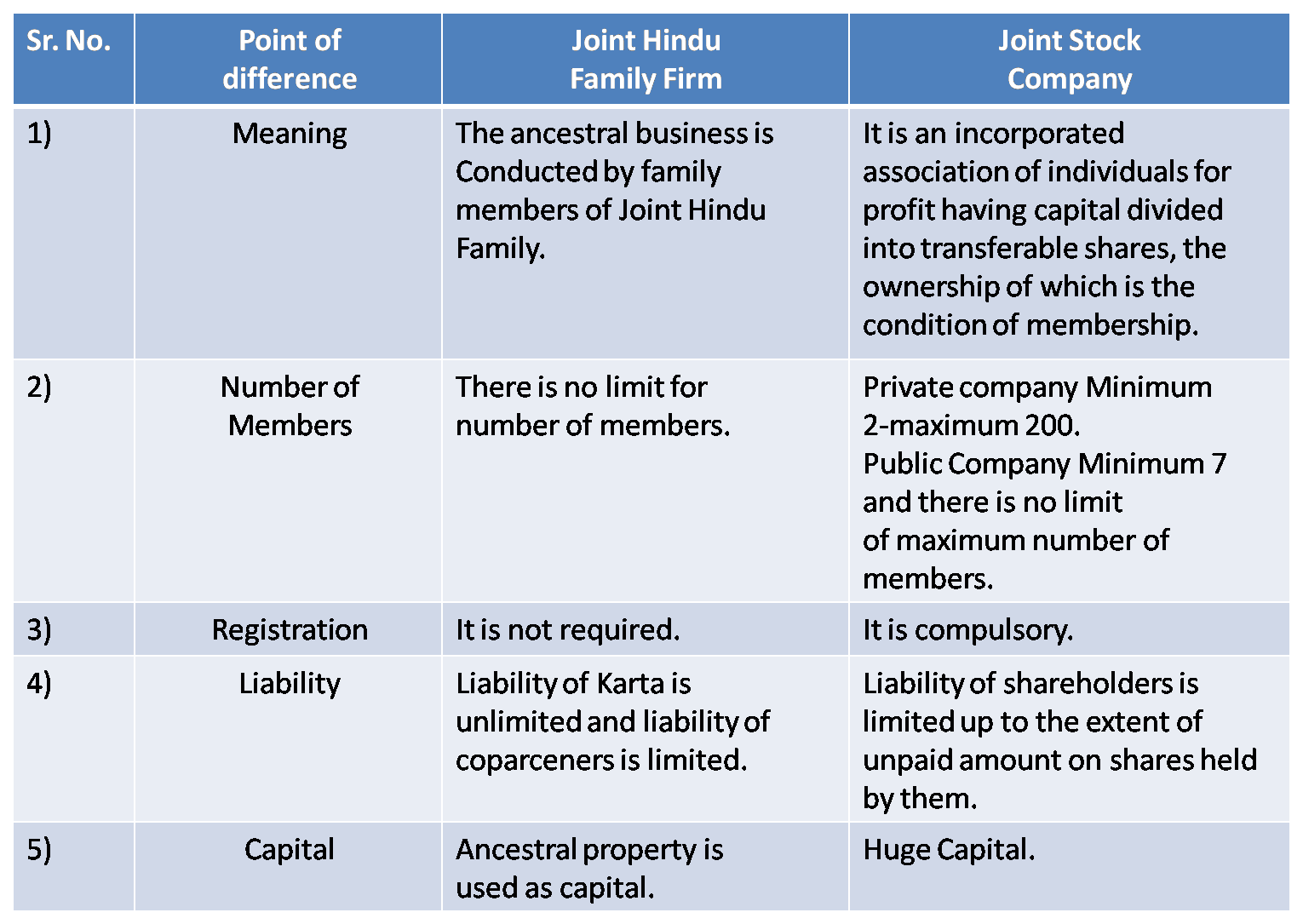
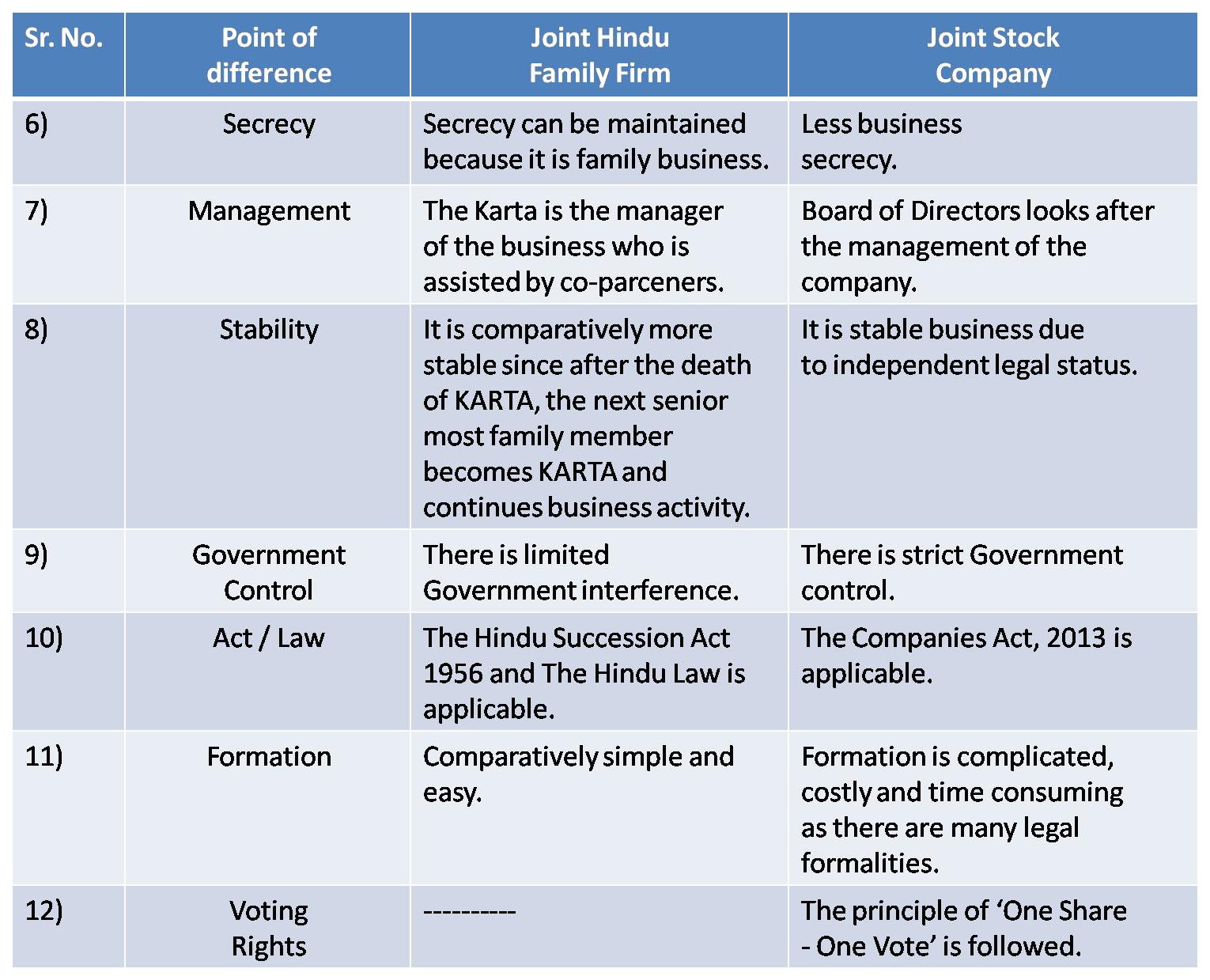
6) Co-operative Society & Partnership Firm
Ans :
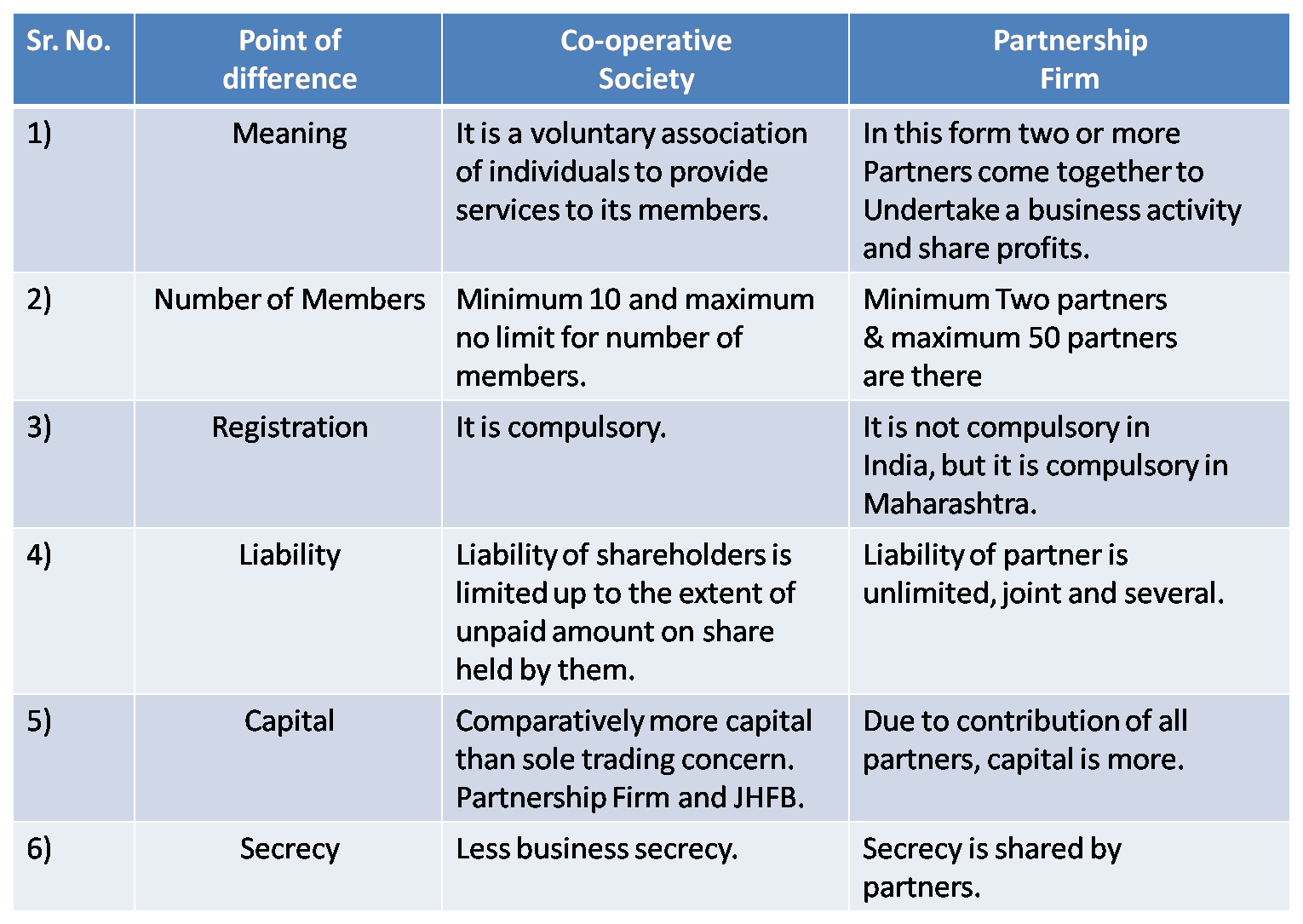
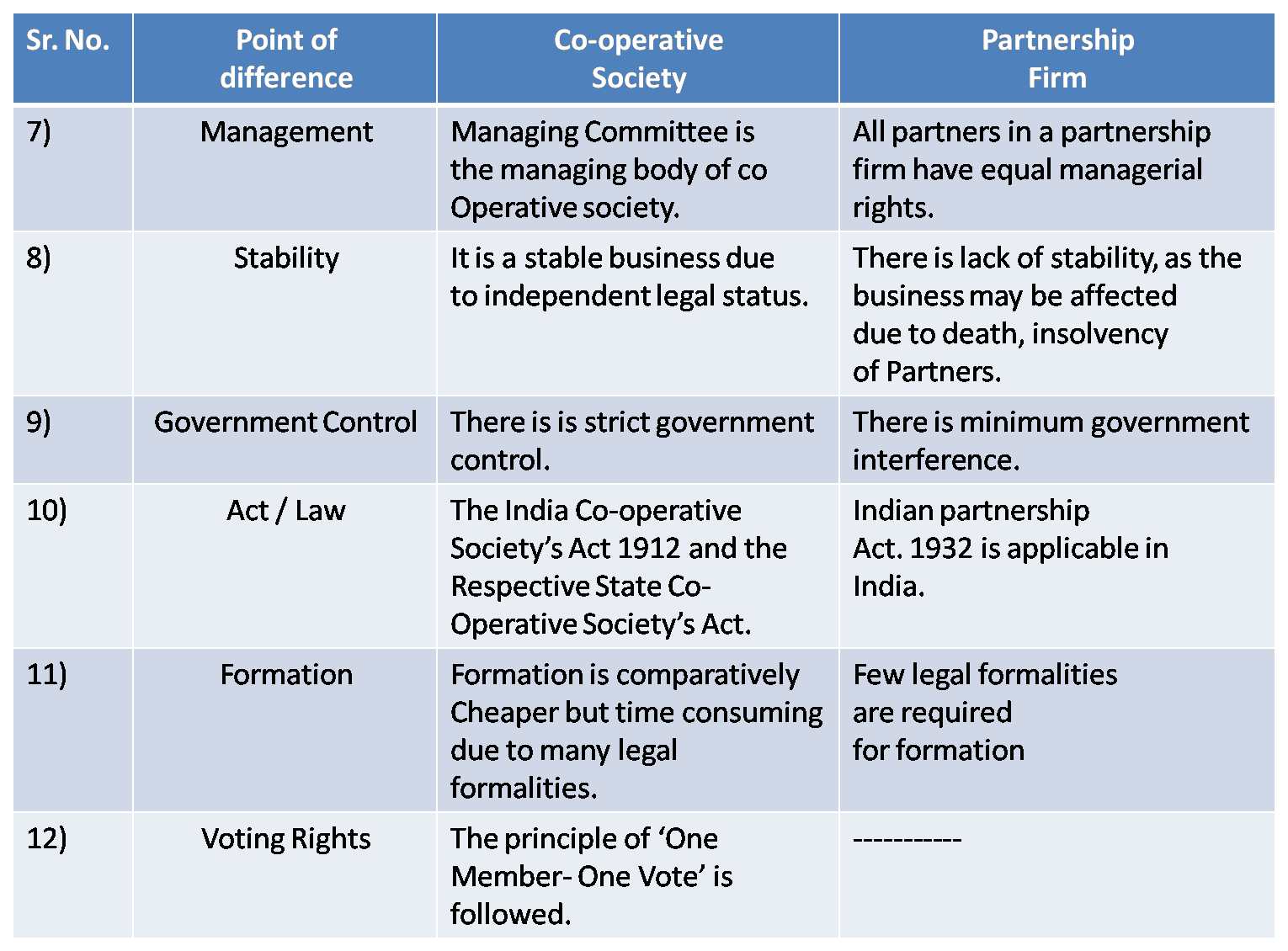
Q.5 Answer in brief.
1) State any four features of Sole Trading Concern.
Ans : Features :
1) Individual Ownership : There is only one owner in sole trading concern. He invests all the capital required for the business. He owns all the assets of the business. He also remains responsible for all the liabilities of the business.
2) No Sharing of Profit and Risk : A proprietor is a single owner of the business. There is nobody to share his profits or losses. He enjoy the profit of the business as well as he bears all risks alone.
3) Self-employment : A sole trading concern is the best suitable form for self-employment. Any unemployed person can start business with small capital and earn for his livelihood. He gets a source of income by starting his own business.
4) Local Market Operations : Large amount of capital and expert managerial ability is required for large scale business. A sole trader has limited capital and limited managerial ability. Hence, generally a sole trader operates in local market.
5) Unlimited Liability : Sole Trader has unlimited liability. Unlimited liability implies that, there is no distinction between personal property and business property of sole trader. If business assets are not sufficient to pay off liabilities of business then personal properties of sole trader may be attached to business properties.
2) State any four types of partners.
Ans :
1) Active Partner : An active partner is one who takes active participation in the day-to-day working of the business. Active partner may act in different capacities such as manager, organizer, adviser and controller of all the affairs of the firm. Active partner contributes to capital, shares profits or losses and has unlimited, joint and
several liability. He is also known as working partner, ordinary partner etc. This partner may get some extra benefits for his services rendered other than share in the profit.
2) Dormant Partner : A dormant partner is one who contributes capital, shares profits and contributes to the losses of the business but does not take part in the working of the concern. A person may have money to invest but they may not be able to devote time for the business such a person becomes a dormant partner.
Dormant partner also known as a sleeping partner and these partners are liable for the liabilities of the business like other partners. He cannot bind the business, i.e. firm, to third party, by his acts.
3) Nominal Partner : A nominal partner is one who only lends his name to the firm. He neither contributes to capital nor shares profits of the business. Due to his presence in firm,
the business may get more credit in the market or may promote its sales. A nominal partner is liable to those third parties who give credit to the firm on the assumption of that person being a partner in the firm.
4) Secret Partner : The partner who is not known to third parties is termed as Secret partner. His membership in the firm is kept secret from outsiders. Secret partner contributes to capital, shares profits of the firm, assumes unlimited liability and he is liable for the losses of the business. He can take part in the working of the business.
3) Describe any four types of Co-operative Society.
Ans : 1) Consumers Co-operative societies : Consumer’s Cooperatives are formed by the consumers to obtain their daily requirements at reasonable prices.
These societies protect lower and middle class people from the exploitation. The profits of the society are distributed among members in the ratio of purchases made by them during the year. e.g. Super Bazaar, Apana Bazaar
2) Producer’s Co-operatives : Producer’s Cooperatives are voluntary associations of small producers and artisans who join hands to face competition and increase production. These
societies are of two types
a) Industrial Service Co-operatives : In this type, the society undertakes to supply raw materials, tools and machinery to the members. The producers work independently
and sell their industrial output to the co-operative society. The output of members is marketed by the society.
b) Manufacturing Co-operatives : In this type, producer members are treated as employees of the society and are paid wages for their work. The society provides
raw material and equipment to every member.
The members produce goods at a common place or in their houses. The society sells the output in the market and its profits is distributed among the members.
3) Marketing Co-operatives : These are voluntary associations of independent producers who want to sell their output at remunerative prices. The output of different members is
pooled and sold through a centralized agency to eliminate middlemen. The sale proceeds are distributed among the members in the ratio of their outputs.
4) Co-operative Farming Societies : These are voluntary associations of small farmers who join together to obtain the economies of large scale farming. In India farmers are
economically weak and their land- holdings are small.
In their individual capacity, they are unable to use modern tools, seeds, fertilizers, etc. They pool their lands and do farming collectively with the help of modern technology to
maximize agricultural output.
4) State any four merits of Joint Hindu Family Business.
Ans : Merits :
1) Easy Formation : Joint hindu family business is easy to start as registration and agreement is not required for its formation. There is no restriction on minimum and maximum numbers of members. It comes into existence as per Hindu Law.
2) Protection of Co-parceners Interest : Co-parceners have right to demand partition. KARTA takes utmost care of their interest
3) Quick and Prompt Decision : The KARTA is senior most family member. KARTA has experience and knowledge of the family business. KARTA takes all business decisions.
KARTA can take right and quick decisions at the right time on the basis of his experience.
4) On The Job Training : The members of joint hindu family business get training of the business skill automatically. They also observe the management of KARTA. They learn many business tactics.
5) Co-parcener’s Liability : The liability of co-parceners is limited up to the extent of their share in the Joint Hindu Family Business. Hence the personal property of co-parcener is not used for the payment of joint hindu family business liability.
5) State any four demerits of Joint Stock Company.
Ans : i) Rigid Formation : Registration of joint stock company is compulsory. It requires number of legal documents. It is necessary to pay heavy registration charges. A public company cannot start its actual business without getting Commencement Certificate. Hence, procedure of formation is complicated, expensive and time consuming.
ii) Lack of Secrecy : In order to protect the interest of investor, it is compulsory to publish books of accounts every year. All the important documents of joint stock company are
available for inspection at registered office. The competitors can take undue advantage of internal information of a joint stock company. Hence, there is no secrecy in joint stock
company.
iii) Delay in Decision Making process : As an owner of the company, every shareholder has right to participate in management of the company. Therefore, all important business decisions are taken in the share holders meetings. The procedure of conducting the meeting is very lengthy and time consuming. It is necessary to prepare notice of meeting, copy of agenda, proxy forms etc. All these documents must be sent minimum 21 days before the meeting. Therefore there is always delay in decision making.
iv) No Personal Contact : There are large number of employees in joint stock company. Employees feel that their efforts should be appreciated by their superiors. But it is not possible in a large organization like joint stock company. The employees are demotivated to work hard. Similarly, Manager and Directors of the company are not able to establish personal contact with their customers. Customers likes & dislikes are not taken into consideration many times.
v) Reckless Speculation : Company is managed by directors. Few unscrupulous directors use confidential information for reckless speculations and their personal gains. This results in sudden fluctuation in the prices of shares in Stock Exchange. It adversely affects public confidence.
Q.6 Justify the following statements.
1) The Liability of a ‘Sole trader’ is Unlimited.
Ans : Sole Trader has unlimited liability. Unlimited liability implies that, there is no distinction between personal property and business property of sole trader. If business assets are not sufficient to pay off liabilities of business then personal properties of sole trader may be attached to business properties.
2) Karta is the sole manager of ‘Joint Hindu Family Business’.
Ans : The Karta is the eldest or senior most person in the family business. A Karta has unlimited liability. He has the entire decision making power and he is not binding on the views of the co-parceners. Thus, Karta is the sole manager of the Joint Hindu Family business.
3) The main objective of co-operative society is to provide services to its members.
Ans : The Co-operative Society is a voluntary association of persons formed for the purpose of promoting the interest of its members. It is different from all other organizations. The main objective of a co-operative organization is not to make a profit but to give service to its members. The co-operative society is formed for the welfare of the people. Co-operative societies are rightly called a service oriented organization. Maximization of profit is not the aim. Thus, the main objective of Co-operative society is to provide services to its members
4) A Joint Stock Company can raise huge capital.
Ans : A joint stock company issues shares to the public. The face value of shares is comparatively low. So it can collect huge amount of capital. It can also accept deposits from the public and issue debentures to raise funds.
5) The liability of Co-parceners is limited in ‘Joint Hindu Family Business’.
Ans : The liability of co-parceners is limited up to the extent of their share in the Joint Hindu Family Business. Hence the personal property of co-parcener is not used for the payment of joint hindu family business liability.
6) Sole proprietorship is useful for small business.
Ans : Sole trading concern is owned by only one person. He uses his own skill and intelligence for his business. Sole trader brings capital from his own savings. He may borrow from friends and relatives. However, the capital collected is limited. He alone takes decisions of the business. Therefore, the managerial ability is also limited. Because of limited capital and limited managerial ability, it is not possible to expand the business beyond a certain limit. Thus, a sole proprietorship is useful for a small business where limited capital and less managerial ability is needed.
7) Co-operative society follows democratic principles.
Ans : Each member of co-operative society enjoys equal voting right. The principle of voting is ‘One member – one vote’. The number of shareholders are large. They are scattered over the region. Thus shareholders elect their representatives. They are called as ‘Managing Committee’ members. They look after the day-to-day management of the society.
8) There is separation of ownership and management in Joint Stock Company.
Ans : Shareholders are the owners of joint stock company. They elect their representatives to look after day to day business activities. These representatives are called as ‘Directors’. The directors appoint professional managers and other employees for the day to day working of the company. These employees work on salary basis. Therefore, the ownership of Joint Stock Company is with shareholder and the management is in the hands of directors. So there is separation of ownership and management.
9) Shares of Private limited company are not freely transferable.
Ans : The total share capital of a company is divided into small shares. To become the member of the company it is compulsory to purchase a share. The shares of public limited company are freely transferable. It means a shareholder can buy or sell shares without permission of the company. The shares of private limited company are not freely transferable.
10) All partners are joint owners of partnership firm.
Ans : The partnership firm is jointly owned by the partners. The partners have to use the partnership property only for business purpose and not for personal use.
11) Active partners take active part in day to day management of partnership firm.
Ans : An active partner is one who takes active participation in the day-to-day working of the business. Active partner may act in different capacities such as manager, organizer, adviser and controller of all the affairs of the firm. Active partner contributes to capital, shares profits or losses and has unlimited, joint and several liability. He is also known as working partner, ordinary partner etc. This partner may get some extra benefits for his services rendered other than share in the profit.
Q.7 Attempt the following.
1) Explain various types of Co-operative Society.
Ans : 1) Consumers Co-operative societies : Consumer’s Cooperatives are formed by the consumers to obtain their daily requirements at reasonable prices. These societies protect lower and middle class people from the exploitation. The profits of the society are distributed among members in the ratio of purchases made by them during the year. e.g. Super Bazaar, Apana Bazaar
2) Producer’s Co-operatives : Producer’s Cooperatives are voluntary associations of small producers and artisans who join hands to face competition and increase production. These
societies are of two types
a) Industrial Service Co-operatives: In this type, the society undertakes to supply raw materials, tools and machinery to the members. The producers work independently and sell their industrial output to the co-operative society. The output of members is marketed by the society.
b) Manufacturing Co-operatives : In this type, producer members are treated as employees of the society and are paid wages for their work. The society provides raw material and equipment to every member. The members produce goods at a common place or in their houses. The society sells the output in the market and its profits is distributed among the members.
3) Marketing Co-operatives : These are voluntary associations of independent producers who want to sell their output at remunerative prices. The output of different members is pooled and sold through a centralized agency to eliminate middlemen. The sale proceeds are distributed among the members in the ratio of their outputs.
4) Co-operative Farming Societies : These are voluntary associations of small farmers who join together to obtain the economies of large scale farming. In India farmers are economically weak and their land- holdings are small. In their individual capacity, they are unable to use modern tools, seeds, fertilizers, etc. They pool their lands and do farming collectively with the help of modern technology to maximize agricultural output.
5) Housing Co-operatives : These societies are formed by low and middle income group people in urban areas to have a house of their own. Housing cooperatives are of different types. Some societies acquire land and give the plots to the members for constructing their own houses. Other societies themselves construct houses and allot them to the members who make payment in installments. They also arrange loans from Financial Institutions and Government Agencies.
6) Credit Co-operatives : These societies are formed by poor people to provide financial help and to develop the habit of savings among members. They help to protect members from exploitation of money lenders who charge exorbitant interest from borrowers. Credit cooperatives are found in both urban and rural areas.
2) Explain the features of Joint Stock Company.
Ans : 1) Voluntary Association : Person of any caste, religion can become the member of Joint stock company. There is no restriction regarding number of shares purchased by one person. After the death, shares of any shareholder, are transferred to his nominees. There is no restriction on transfer of shares.
2) Registration : Registration is compulsory according to the Companies Act, 2013. An application in prescribed format must be submitted to the Registrar of Company. Necessary registration fees are paid by the promoters. ‘A Certificate of Registration.’ (Incorporation Certificate) is issued to the company after registration. A private limited company can immediately start its business after getting Incorporation Certificate. A public limited company must obtain ‘Certificate of Commencement of Business’(Trading Certificate) to start its business.
3) Registered Office : The address of registered office of company is mentioned in Memorandum of Association. All the important document of a company are kept in the registered office. e.g. Register of shareholders, Annual Reports, Minutes Book, Memorandum and Articles of Association, Prospectus, Statutory Report etc.
4) Artificial Legal Person : A company is an artificial person created by law. It can enter into contract with third parties after registration. e.g. It can buy or sell asset, borrow money, open an account in bank etc. Therefore, only law can create joint stock company and only law can wind up it.
5) Separate Legal Status : There is a separate legal existence of joint stock company. It is a separate legal entity apart from its members.
6) Common Seal : A company is an artificial person. It does not have a physical existence like a human being. Therefore it is necessary to make provision for the signature of the company. Every joint stock company has a common seal. It is used as a signature of joint stock company. A seal has name of the company engraved on it. It is considered as the important property of the company. Therefore, a seal is kept in the custody of company secretary. A seal is affixed on all important documents of the company but the document must be signed by a company secretary and by minimum two directors.
7) Limited Liability : The liability of all shareholders is limited up to the extent of unpaid face value of shares held by them. Therefore, private property of shareholders is not used for the payment of company’s liabilities.
8) Transferability of Shares : The total share capital of a company is divided into small shares. To become the member of the company it is compulsory to purchase a share. The shares of public limited company are freely transferable. It means a shareholder can buy or sell shares without permission of the company. The shares of private limited company are not freely transferable.
3) Describe the features of Co-operative Society.
Ans : 1) Voluntary Association and Open Membership : Any person can become the member of co-operative society. There is no discrimination on the basis of caste, religion, gender etc. for membership
2) Democratic Principle : The management of co-operative society is based on democracy. All the decisions are taken on majority basis. ‘One Member One Vote’ is the rule for voting. According to the rules and regulations of Co-operative Society Act, meetings are arranged by the society.
3) Management : The management of co-operative society is in the hands of Managing Committee of members. They are elected representatives of shareholders. All the important business decisions are taken by managing committee members. The committee members look after day-to-day administration of society.
4) Registration : Registration of co-operative society is compulsory. Every co-operative society must follow rules and regulations of Indian Co-operative Society’s Act 1912 and the respective State Co-operative Society’s Act. Minimum 10 members are required for registration of co-operative society. There are number of legal documents required for registration.
5) Separate Legal Status : After registration, every co-operative society is considered as a separate legal entity before the law. Therefore it can enter into the contract, purchase
property, open a bank account in it’s name etc. The shareholders and managing committee members are not responsible for the transactions of co-operative society. But they are answerable to the court on behalf of the society.
6) Limited Liability : The shareholders of co-operative society have limited liability. It is limited up to the unpaid value of the share purchased by them. Therefore, their private property is not used for payment of society’s liability.
7) Number of Members : Minimum 10 members are required for the formation of co-operative society. There is no limit for maximum number of members as per Co-operative Society’s Act.
8) Equal Voting Rights : Every member gets equal rights in co-operative society as a shareholder. In co-operative society membership is open to all. All members have equal
voting rights irrespective of number of shares held by them.
9) Service Motive : A Co-operative society provides various services to its members. Its main objective is to provide services to the society. Goods are available at lowest rates for its members. In a co-operative bank, loan and overdraft facility is available at the lowest interest rates for its shareholders only.
Q.8 Answer the following.
1) Explain features of Sole Trading Concern.
Ans : 1) Individual Ownership : There is only one owner in sole trading concern. He invests all the capital required for the business. He owns all the assets of the business. He also remains responsible for all the liabilities of the business.
2) No Sharing of Profit and Risk : A proprietor is a single owner of the business. There is nobody to share his profits or losses. He enjoy the profit of the business as well as he bears all risks alone.
3) Self-employment : A sole trading concern is the best suitable form for self-employment. Any unemployed person can start business with small capital and earn for his livelihood. He gets a source of income by starting his own business.
4) Local Market Operations : Large amount of capital and expert managerial ability is required for large scale business. A sole trader has limited capital and limited managerial ability. Hence, generally a sole trader operates in local market.
5) No separate Legal Status : A sole trading concern does not enjoy separate legal status. In the eyes of Law, the sole trader and his business are considered one and the same.
6) Minimum Government Regulations : There is no separate act or law to govern the activities of sole trading concern. The registration of sole trading concern is not compulsory. Rigid legal formalities are not required for formation. Only the tax laws and labour laws have to be followed.
7) Unlimited Liability : Sole Trader has unlimited liability. Unlimited liability implies that, there is no distinction between personal property and business property of sole trader. If business assets are not sufficient to pay off liabilities of business then personal properties of sole trader may be attached to business properties.
2) Explain different types of Partnership.
Ans : A) General Partnership : In General Partnership, every partner has equal rights. General partnership comes into existence according to provisions of ‘Indian Partnership Act, 1932’.
1) Partnership at will : When there is no provision in partnership agreement regarding time period for partnership then it is known as ‘Partnership at will’. Such partnership can be easily dissolved. Any partner can give notice of his intension to leave partnership at any time.
2) Partnership for Particular Period : When Partnership is formed for a specific time such partnership is known as ‘Partnership for Particular Period’. For e.g., 6 months, 1 year. Such Partnership firm dissolves after expiry of particular period.
3) Partnership for Particular Venture : When partnership firm is formed for particular venture or business, such partnership is known as ‘Partnership for Particular Venture’. For example, construction of dams, roads or bridges, selling of seasonal products etc.
B) Limited Liability Partnership : Limited liability partnership comes into existence as per the provisions of ‘Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008’. There are two kinds of partner as follows:
• Designated Partner : Every Limited liability partnership should have at least two Designated Partners. Among two partners one partner must be the resident of India.
• General Partner : In limited liability partnership all other partners are General Partners. The Limited Liability Partnership offers some personal liability protection to the participants. Individual partners in limited liability partnership are not personally responsible for the wrongful acts of other partners, or for the debts or obligations of the business.
3) Explain different types of Partners.
Ans :
1) Active Partner : An active partner is one who takes active participation in the day-to-day working of the business. Active partner may act in different capacities such as manager, organizer, adviser and controller of all the affairs of the firm. Active partner contributes to capital, shares profits or losses and has unlimited, joint and several liability. He is also known as working partner, ordinary partner etc. This partner may get some extra benefits for his services rendered other than share in the profit.
2) Dormant Partner : A dormant partner is one who contributes capital, shares profits and contributes to the losses of the business but does not take part in the working of the concern. A person may have money to invest but they may not be able to devote time for the business such a person becomes a dormant partner. Dormant partner also known as a sleeping partner and these partners are liable for the liabilities of the business like other partners. He cannot bind the business, i.e. firm, to third party, by his acts.
3) Nominal Partner : A nominal partner is one who only lends his name to the firm. He neither contributes to capital nor shares profits of the business. Due to his presence in firm, the business may get more credit in the market or may promote its sales. A nominal partner is liable to those third parties who give credit to the firm on the assumption of that person being a partner in the firm.
4) Secret Partner : The partner who is not known to third parties is termed as Secret partner. His membership in the firm is kept secret from outsiders. Secret partner contributes to capital, shares profits of the firm, assumes unlimited liability and he is liable for the losses of the business. He can take part in the working of the business.
5) Partner in profits only : When a partner agrees to share only profits of the firm and would not be liable for its losses, he is know as partner in profits only. Such partners share capital of the firm and may not take active participation in the management of the firm. However, such partners are liable for all debts of the firm.
6) Sub – Partner : When a partner agrees to share their own profit derived from the firm with a third person is known as sub – partner. A Sub-partner cannot represent himself as a partner in the original firm.
7) Partner with Limited Liability : This type of partner exists in a limited partnership. The liability of the partner is limited to the extent of capital contributed by him in the firm. He is a special partner and generally does not take active part in the working of the firm.
8) Quasi Partner : Quasi Partner is partner in partnership firm who retired from firm but left his capital with the firm. Quasi partner does not take active participation in the firm but shares profit of the firm. Such partner is liable for the debts of the firm. Many times such partners receives certain rate of interest on his capital.
4) Explain the five features of Joint Stock Company.
Ans :
1) Voluntary Association : Person of any caste, religion can become the member of Joint stock company. There is no restriction regarding number of shares purchased by one person. After the death, shares of any shareholder, are transferred to his nominees. There is no restriction on transfer of shares.
2) Registration : Registration is compulsory according to the Companies Act, 2013. An application in prescribed format must be submitted to the Registrar of Company. Necessary registration fees are paid by the promoters. ‘A Certificate of Registration.’ (Incorporation Certificate) is issued to the company after registration. A private limited company can immediately start its business after getting Incorporation Certificate. A public limited company must obtain ‘Certificate of Commencement of Business’(Trading Certificate) to start its business.
3) Registered Office : The address of registered office of company is mentioned in Memorandum of Association. All the important document of a company are kept in the registered office. e.g. Register of shareholders, Annual Reports, Minutes Book, Memorandum and Articles of Association, Prospectus, Statutory Report etc.
4) Artificial Legal Person : A company is an artificial person created by law. It can enter into contract with third parties after registration. e.g. It can buy or sell asset, borrow money, open an account in bank etc. Therefore, only law can create joint stock company and only law can wind up it.
5) Separate Legal Status : There is a separate legal existence of joint stock company. It is a separate legal entity apart from its members.
5) Explain the merits of Co-operative Society.
Ans : 1) Democratic Management : Each member of co-operative society enjoys equal voting right. The principle of voting is ‘One member – one vote’. The number of shareholders are large. They are scattered over the region. Thus shareholders elect their representatives. They are called as ‘Managing Committee’ members. They look after the day-to-day management of the society.
2) Open Membership : The membership of co-operative society is voluntary and open to all. i.e. any person of any caste, creed, religion etc. can purchase shares of co-operative society and become the member of it. There is no compulsion to join or to leave the organization.
3) Less Operating Expenses : The cost of operation is low in co-operative society. No middlemen are involved. There are no advertisement expenses. Managing committee members provide honorary services. Various concessions, reliefs and privileges related to registration fees, stamp duty, income tax etc. are given by Government.
4) Limited Liability : The liability of the shareholders of co-operative society is limited. It is limited up to the extent of unpaid amount on shares held by them. Thus, member’s private property cannot be used even if the assets of the society are insufficient to pay the debts of the third party.
5) Tax Concession : Co-operative society plays an important role in the economic and social development of the country. The government gives many concessions to them, like exemption of payment of income-tax up to a certain limit. This helps to increase the profit of the society.
6) Self – Financing and Charity : As per the latest amendment act of co-operative society, a society can pay maximum 15% dividend to its members. Therefore, remaining surplus is used as self-financing. Some amount of profit is utilized for charity purpose, social activities and for the growth of co-operative society.
6) Explain the demerits of Partnership firm.
Ans : 1) Problem of Continuity : The partnership business may face problem of continuity unless provided for continuation of business in the event of death, insolvency or insanity to any partner in the partnership firm. If partnership agreement does not have provision of continuation of partnership business in case of death, insolvency and insanity, business is liable for dissolution.
2) Absence of Legal Status : In partnership business, there is no separate legal existence of partnership firm. In the eyes of law both are same. Law does not make any distinction between partners and firm. So there is absence of separate legal status for partnership firm. In the event of death, insolvency or insanity partnership firm is liable for dissolution.
3) Disputes : Disputes are common in partnership business as more than one individuals are involved in various activities. Some partners may or may not agree on some points which leads to disputes among partners. Sometimes disputes may lead to the dissolution of the firm.
4) Non – Transferability of Interest : No partner of business can transfer his share in business to the outsider without the consent of all partners in the firm. In general, there is non-transferability of interest in partnership business.
5) Limitations on number of Partners : The Indian Partnership Act limits maximum number of partners. No partnership firm can go beyond maximum prescribed limits of 50 partners.
This restricts maximum number of partners admitted in business. Such restrictions may affect partnership firm while capital contribution and even in case of management of partnership business.
6) Difficulty in Admission of Partner : In partnership business, there is often difficulty in admission of new partner. Admission of new partner may affect profit sharing ratio of existing partners. Therefore existing partner may object admission of new partners in business. Existing partners may not have full faith on incoming partner. This leads to difficulty in admission of new partner.
7) Unlimited Liability : Unlimited liability arises when the assets of the firm are not sufficient to pay off claims of the creditors. The private property of the partners is attached to satisfy such claims.
8) Risk of Implied Authority : There is often risk of implied authority in partnership business. Partners may take undue advantage of managing business on behalf of others which leads
to risk of implied authority. For Example, partners may sign some agreements in his own capacity which may be against the interest of the firm or partners may take loans or advances without consent of other partners.
9) Limited Capital : In partnership business, there is less capital as compared to joint stock company. There are restrictions on number of members which leads to limited capital raising capacity of business. Limited capital restricts the expansion of business.
10) Problem of Secrecy : Though books of accounts and financial matters relating to business are not required to be published, partnership firm lacks business secrecy. Some partners may share confidential information of business to competitors or third parties for getting financial benefits from them.
7) Explain the merits of Joint Stock Company.
Ans : 1) Large amount of Capital : A joint stock company issues shares to the public. The face value of shares is comparatively low. So it can collect huge amount of capital. It can also accept deposits from the public and issue debentures to raise funds.
2) Professional Management : Management of the company is in the hands of directors. They are elected representatives of shareholders. Due to large financial resources, a company can appoint highly qualified professionals, by paying attractive salary. So the knowledge of experts is used for day to day management of the company.
3) More Scope for expansion : A joint stock company collects large amount of capital. Attractive salaries are paid to professional managers. Proper authorities are given to take business decisions. Shareholders are interested in getting highest rate of dividend. As a result, company can undertake big and risky projects.
4) Public Confidence : A joint stock company enjoys public confidence. There is less interference of Government. Every Joint Stock Company in India is governed as per the provisions of ‘The Companies Act 2013’. As per the Act the company has to get its annual accounts audited by a practing Chartered Accountant.
5) Relief in Taxation : A joint stock company plays important role in the economic development of the country. It requires to pay taxes by flat rate. Certain exemptions and concessions are given to the joint stock companies, which opens branches in economically backward regions for e.g. tax holidays up to 5 years.
6) Expert Services : A joint stock company can appoint experts for managing business activities like Legal Advisers, Management Experts, Auditors, Consultants etc.
7) Perpetual Succession : A joint stock company enjoys continuous and stable life. The death, retirement, insolvency or insanity of its members does not result into dissolution of the Company.
8) Limited Liability : The liability of a member of a company is limited to the extent of the unpaid amount of shares held by him Shareholders are not liable for the debts of the company & there is no need to use their personal property for the purpose.
8) Explain the features of partnership firm.
Ans : 1) Agreement : Partnership is an outcome of an agreement between two or more persons who are conducting partnership business for earning profit. The agreement between partners may be oral or written. It is always advisable to have written agreement between all partners.
2) Joint Ownership : The partnership firm is jointly owned by the partners. The partners have to use the partnership property only for business purpose and not for personal use.
3) Joint Management : Every partner has right to take active participation in the management of the business. However, one or more partners may agree to manage business on behalf of other partners in the firm.
4) Lawful Business : Every partnership firm must undertake lawful business only. The partnership should not engage in any business which is forbidden by law of land. The partnership firm cannot be formed to carry out any unlawful business. e.g. partnership formed to smuggle goods, sale of illegal arms etc.
5) Liability : The liability of each partner is unlimited, joint and several. Unlimited liability arises when the assets of the firm are not sufficient to pay off claims of the
creditors. The private properties of the partners are attached to satisfy such claims. Joint liability indicates that each and every partner is jointly liable with other partners for the debt of the firm, whether incurred by himself or by other partners as agents of the firm Several liability indicates that each and every partner is individually and separately liable for the debts of the firm, whether incurred by himself or by other partners as agents of the firm.
6) Number of Partners : A Partnership firm must have minimum two persons at any time during the entire life of the partnership firm. Maximum partners permitted are 50.
7) Principal – Agent Relationship : Every partner is the joint owner of the business and partners take part in the management of the firm. Thus, every partner assumes two roles in business –
A) to each other within firm they are acting as ‘Principal’ B) while dealing with outsider or while representing firm they act as an ‘Agent’ of the firm.
8) Restriction on Transfer of Interest : No partner of firm can transfer or sell their interest or share in the firm to outsider without the prior consent of all other partners in the firm.
9) Registration : Registration of partnership is not mandatory as per the provisions of Indian Partnership Act, 1932. However, in Maharashtra (from April, 1985) and in some other state
registration of partnership is compulsory as per their respective state provisions. If Partners so desire, they can register their firm with the ‘Registrar of Firms’ of their respective States. The firm as well as partners enjoys several benefits after registration of the firm.
10) Sharing of profits and losses : The partners agree to share profits and losses among themselves in certain proportions. Such profit-loss sharing depends upon amount of capital introduced, services offered, goodwill of the partner and other terms of agreement. If agreement is silent on profit-loss sharing then all partners are assumed as equal partners.
11) Termination of Partner : A partner may resign on his own by giving notice to other partners in writing. The partners may also be removed from the firm for fraudulent activities.
12) Dissolution : The firm can be dissolved at any time, if the partners agree to do so. The partnership firm gets automatically dissolved in case of death, insolvency or insanity of any one of the partners unless provided in the partnership agreement about continued existence of the firm in such situations. The partnership firm automatically gets dissolved when total number of partners in the firm is reduced to one partner.
9) Explain the types of co-operative societies.
Ans : 1) Consumers Co-operative societies : Consumer’s Cooperatives are formed by the consumers to obtain their daily requirements at reasonable prices. These societies protect lower and middle class people from the exploitation. The profits of the society are distributed among members in the ratio of purchases made by them during the year. e.g. Super Bazaar, Apana Bazaar
2) Producer’s Co-operatives : Producer’s Cooperatives are voluntary associations of small producers and artisans who join hands to face competition and increase production. These
societies are of two types
a) Industrial Service Co-operatives : In this type, the society undertakes to supply raw materials, tools and machinery to the members. The producers work independently
and sell their industrial output to the co-operative society. The output of members is marketed by the society.
b) Manufacturing Co-operatives : In this type, producer members are treated as employees of the society and are paid wages for their work. The society provides
raw material and equipment to every member. The members produce goods at a common place or in their houses. The society sells the output in the market and its profits is distributed among the members.
3) Marketing Co-operatives : These are voluntary associations of independent producers who want to sell their output at remunerative prices. The output of different members is
pooled and sold through a centralized agency to eliminate middlemen. The sale proceeds are distributed among the members in the ratio of their outputs.
4) Co-operative Farming Societies : These are voluntary associations of small farmers who join together to obtain the economies of large scale farming. In India farmers are
economically weak and their land- holdings are small. In their individual capacity, they are unable to use modern tools, seeds, fertilizers, etc. They pool their lands and do farming collectively with the help of modern technology to maximize agricultural output.
5) Housing Co-operatives : These societies are formed by low and middle income group people in urban areas to have a house of their own. Housing cooperatives are of different types. Some societies acquire land and give the plots to the members for constructing their own houses. Other societies themselves construct houses and allot them to the members who make payment in installments. They also arrange loans from Financial Institutions and Government Agencies.
6) Credit Co-operatives : These societies are formed by poor people to provide financial help and to develop the habit of savings among members. They help to protect members
from exploitation of money lenders who charge exorbitant interest from borrowers. Credit cooperatives are found in both urban and rural areas.
10) Explain the demerits of Joint Stock Company.
Ans : i) Rigid Formation : Registration of joint stock company is compulsory. It requires number of legal documents. It is necessary to pay heavy registration charges. A public company cannot start its actual business without getting Commencement Certificate. Hence, procedure of formation is complicated, expensive and time consuming.
ii) Lack of Secrecy : In order to protect the interest of investor, it is compulsory to publish books of accounts every year. All the important documents of joint stock company are available for inspection at registered office. The competitors can take undue advantage of internal information of a joint stock company. Hence, there is no secrecy in joint stock company.
iii) Delay in Decision Making process : As an owner of the company, every shareholder has right to participate in management of the company. Therefore, all important business decisions are taken in the share holders meetings. The procedure of conducting the meeting is very lengthy and time consuming. It is necessary to prepare notice of meeting, copy of agenda, proxy forms etc. All these documents must be sent minimum 21 days before the meeting. Therefore there is always delay in decision making.
iv) No Personal Contact : There are large number of employees in joint stock company. Employees feel that their efforts should be appreciated by their superiors. But it is not possible in a large organization like joint stock company. The employees are demotivated to work hard. Similarly, Manager and Directors of the company are not able to establish personal contact with their customers. Customers likes & dislikes are not taken into consideration many times.
v) High Cost of Management : A joint stock company is a commercial organization. It is ready to spend huge amount for the advertisement. The manager gets best salary and other benefits. It requires huge amount for operational expenses. So the cost of management is very high in joint stock company.
vi) Reckless Speculation : Company is managed by directors. Few unscrupulous directors use confidential information for reckless speculations and their personal gains. This results in sudden fluctuation in the prices of shares in Stock Exchange. It adversely affects public confidence.