Q.1 Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence.
1) _________ is the link between producer and retailer.
a) Consumer b) Wholesaler c) Manufacturer
Answer : Wholesaler
2) Price charged by retailers is generally _______
a) higher b) lower c) fixed
Answer : higher
3) A Wholesaler invest ___________ capital in the business.
a) small b) large c) less
Answer : large
4) Retailer is the_________ link in the chain of distribution.
a) first b) last c) second
Answer : last
5) Retailers supply information to the ________ through Wholesalers.
a) manufacturer b) government c) consumers
Answer : manufacturer
6)Major items __________ are chemicals, crude oil and petroleum products, edible oils, electronic goods, gold and silver, pearl and precious stone.
a) exported by India b) not exported by India c) imported by India
Answer : imported by India
7) For customs clearance the _________ is prepared by the exporter.
a) carting Order b) letter of Credit c) shipping Bill
Answer : shipping Bill
8)___________ carry goods on their head in baskets or containers.
a) Hawkers b) Peddlers c) Cheap Jacks
Answer : Peddlers
9) ________ open their shops on market days i.e. on fixed days.
a) Street traders b) Market Traders c) Peddlers
Answer : Market Traders
10) _________ retailers deal in particular goods.
a) General Stores b) Speciality shop retailers c) Second hand goods shops
Answer : Speciality shop retailers
11) _______ is known as a self-service store.
a) Department store b) Supermarket c) Multiple store
Answer : Supermarkets
Q.2. Match the pairs.
1)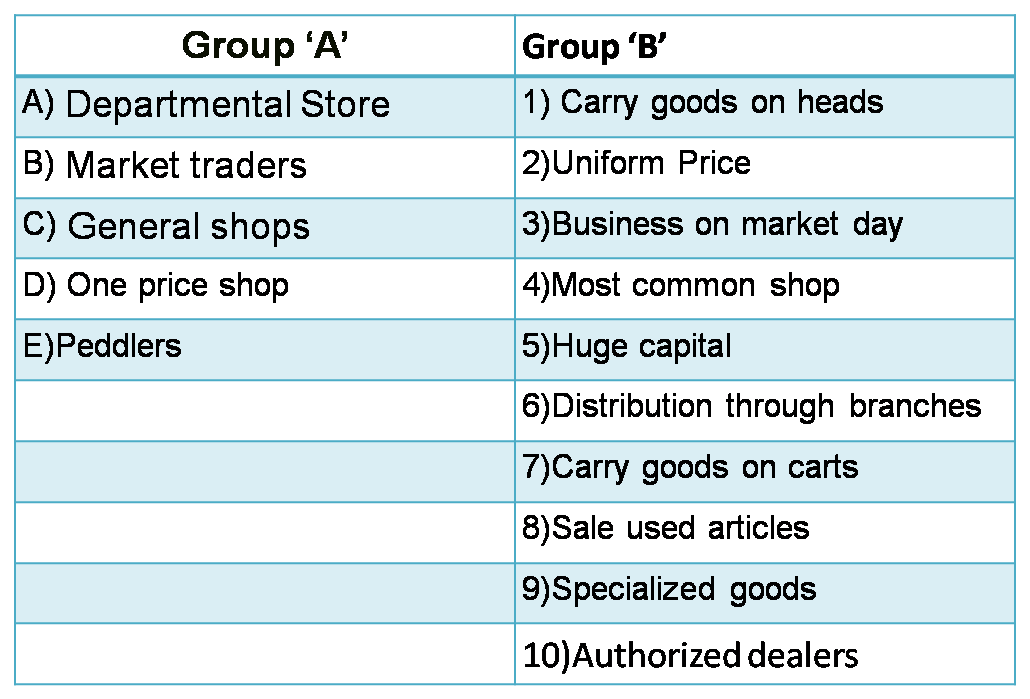
Answer :
2)
Answer :
C) Give one word/phrase/term, For the following sentences.
1) A person who moves daily from place to place to sell goods.
Answer : Itinerant retailor
2) The middleman between wholesaler and consumer.
Answer : Retailor
3) A retail shop which operates through branches.
Answer : Chain stores
4) A shop where all goods are available at same price.
Answer : One price shop
5) A retailer who displays his goods on the road.
Answer : Street traders
6) An order placed by an importer for the supply of certain goods.
Answer : Indent
D) State True or False.
1) Wholesaler keeps large stock of goods.
Answer : True
2) Wholesaler deals in small quantity.
Answer : False
3) A retailer has no direct contact with consumers.
Answer : False
4) Super market shops offer home delivery facilities to customer.
Answer : False
5) Departmental store located out of the city.
Answer : False
6) Customers cannot bargain in one price shop.
Answer : False
7) Letter of Credit is required for obtaining export license.
Answer : True
8) Buying goods from other country is known as export trade.
Answer : False
9) Maintaining high quality is necessary to sustain in export business.
Answer : True
E) Find the odd one.
1) General Stores, Hawkers, Cheap Jacks, Peddlers.
Answer : General Stores
2) Departmental Stores, Chain Stores, Market Trader, One Price Shop.
Answer : Market Trader
3) Specialty Shops, Secondhand goods shops, Malls, Authorized Dealers.
Answer : Malls
F) Complete the sentences.
1) The original form of trade was Barter.
2) Trade establishes a link between producers and consumers.
3) The wholesaler provides valuable services to manufactures and retailers.
4) The wholesaler purchases a large quantity of goods from the manufacturers.
5) The wholesaler bears the risk of price and market fluctuations.
6) The wholesaler provides financial support to retailers by way of credit facility.
7) The retailer is the connecting link between the wholesaler and consumers.
8) Super Market is a large retail organization which mainly sells wide variety of food and grocery items on the basis of ‘self-service’.
9) Chain Stores are retail stores owned by a single organization.
10) The shop where the prices of all products or goods are same is known as one price shop.
11) A modern shopping mall is an American term.
12) The Letter of Credit is the safest method of payment in export trade.
G) Select the correct option.
1) Wholesaler deals in (small / large) quantity.
Answer : large
2) Departmental store located (in / out of) the city.
Answer : in
3) Customer cannot bargain in (General stores / one price shop).
Answer : one price shop
4) Retailer operates in (global / local) markets.
Answer : local
5) Departmental store is a (large / small) scale retail shop.
Answer : Large
6) Supermarket shop requires (limited / larges) capital.
Answer : Large
7) Chain stores are retail store owned by (many / single) organization.
Answer : single
8) The shop where the prices of all the products or goods are (different / same) is known as one price shop.
Answer : same
I) Correct the underlined word and rewrite the following sentences.
1) When the trade activities are conducted between two or more countries, it is called as internal trade.
Answer : When the trade activities are conducted between two or more countries, it is called as external trade.
2) Export trade refers to the purchase of good and services from foreign country.
Answer : Import trade refers to the purchase of good and services from foreign country
3) The price charged in departmental stores is comparatively less.
Answer : The price charged in departmental stores is comparatively high.
4) Wholesaler requires less capital.
Answer : Retailer requires less capital.
5) Tariff rates of various countries affect the internal trade.
Answer : Tariff rates of various countries affect the external trade.
J) Arrange in proper order.
1) Retailer, consumer, producer, wholesaler
Answer : c) Producer d) Wholesaler a) Retailer b) Consumer
2) International market, local market, national market, state market
Answer : b) Local Market d) State Market c) National Market a) International Market
3) Import stage, Pre-import stage, Post-import stage, preliminary stage
Answer : d) Preliminary Stage b) Pre-import Stage a) Import Stage c) Post-import Stage
Q.2 Explain the following terms/concepts.
A) Wholesale Trade
Answer : (1) When goods are purchased in large quantities from the manufacturer or producer for the purpose of resale to retailers, it is known as wholesale trade. The person who is engaged in wholesale trade is known as a wholesaler. Wholesaler buy goods from manufacturers and sell it to retailers so wholesaler is buyer as well as seller. (2) The Wholesaler may perform different functions in the process of distribution of goods and services. It enables the producers to reach the consumers.
2) Retail Trade
Answer : (1) When goods are sold relatively in small quantity to the ultimate consumer by wholesaler or distributor or dealer is known as Retail Trade. (2) The person who is engaged in retail trade is known as retailer.
3) Foreign Trade
Answer : (1) Trade carried on between two or more foreign countries is called foreign trade. (2) Foreign trade depends as political relations between two countries. (3) Procedure of foreign trade is complex, difficult and lengthy.
4) Letter of Credit
Answer : (1) The exporter requests importer to issue a letter of credit in his favour. The receipt of ‘letter of credit’ from importer’s bank will clear the foreign exchange and other restrictions. (2) It is generally demanded by the exporter country.
5) One Price Shop
Answer : (1) The shop where the prices of all the products or goods are same is known as One Price shop. (2) This shop sells a large variety of goods of daily use at low prices. The products irrespective of their size and quality are sold at one common uniform price. The price are fixed in advance. Goods like gift articles, watches, shampoos, hair products, household articles, crockery, etc. (3) e.g. shops selling goods for Rs. 49/-, Rs. 99/-, Rs. 199/-
6) Departmental Store
Answer : (1) A departmental store is a large scale retail shop having different departments (sections) under one roof. Each section deals in a particular type of goods, All the departments are organized and managed by one management. (2) It sells a large variety of goods. i.e. food, toys, dresses etc. e.g. Shoppers Stop.
7) General Store
Answer : (1)General store Retailers sell goods which are required by people for their day to day needs like food grains, soaps, stationery, medicines, oils, toffees, biscuits, plastic goods, footwear, umbrella, pens etc. (2) These shops are generally situated near residential areas of the city or town. (3) They provide home delivery of goods. (4) They have variety of goods in each item. They buy the goods from wholesalers or buy directly from manufacturers.
8) Mall
Answer : (1) A Mall is a large enclosed shopping complex containing various stores, businesses and restaurants. (2) A modern shopping mall is an American term in which one or more buildings form a complex. (3) It is modern type of shop which enables customer to buy different products from one unit to other units of mall. (4) Now a days, the popularity of mall is increasing because of variety of things available at one place. e.g. Phoenix Mall, Inorbit Mall.
Q.3 Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
(1) Sonupant purchases his grocery material every month from nearest Nandulal grocery shop and he purchases wheat, rice and pulses in bulk for whole year from Gorhe and Son’s, Market yard.
1) Who is wholesaler?
Answer : Gorhe and son’s Market yard.
2) Who is retailer?
Answer : Nandulal grocery shop is the retailer.
3) Any one difference between wholesaler and retailer
Answer : Goods are sold to retailer for the purpose of sale by wholesaler.
Goods are sold to customer for consumption by the retailer.
(2) Anurag is selling goods to Japan. Kavita is buying goods from USA where as Ganesh is buying raw material from South Africa and after processing it sells finished goods to Malaysia.
1) Who is exporter?
Answer : Anurag is the exporter.
2) Who is importer?
Answer :Kavita is an importer.
3) What is Entrepot Trade?
Answer : Entrepot trade is re-exporting of the goods to another country, with or without processing or re-packaging e.g. Ganesh buying raw materials from South Africa and processing it and selling it to Malaysia.
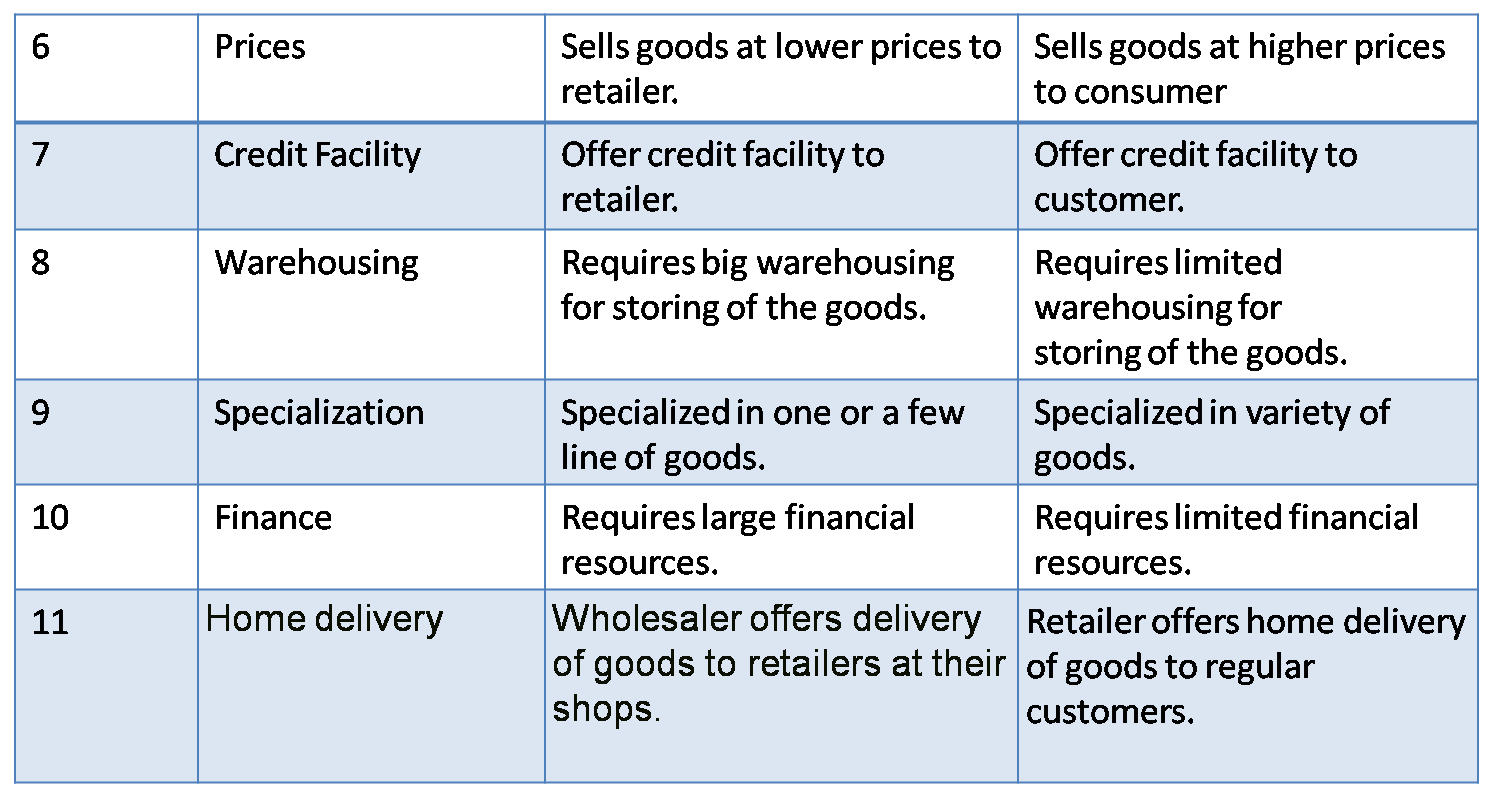
Q.4 Distinguish between.
1) Wholesaler and Retailer.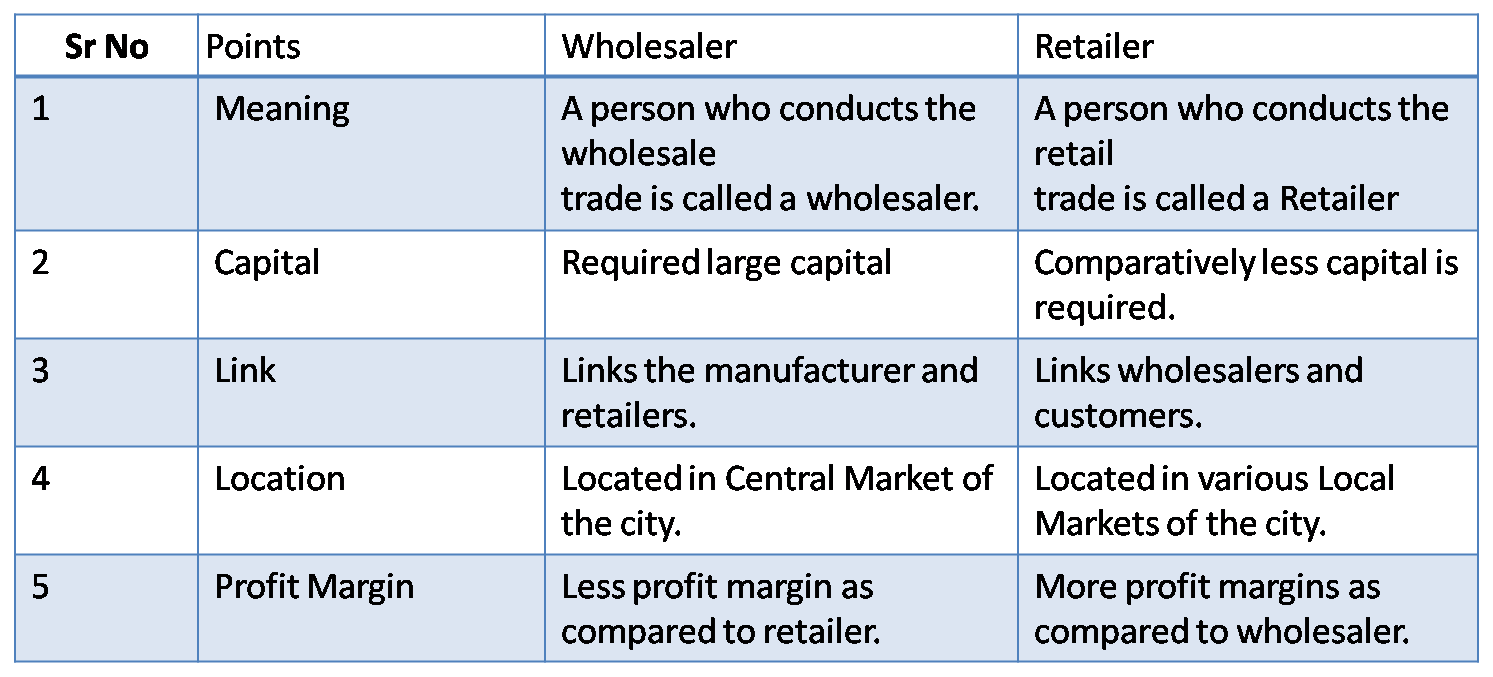
2) Itinerant Retailers and Non-Itinerant 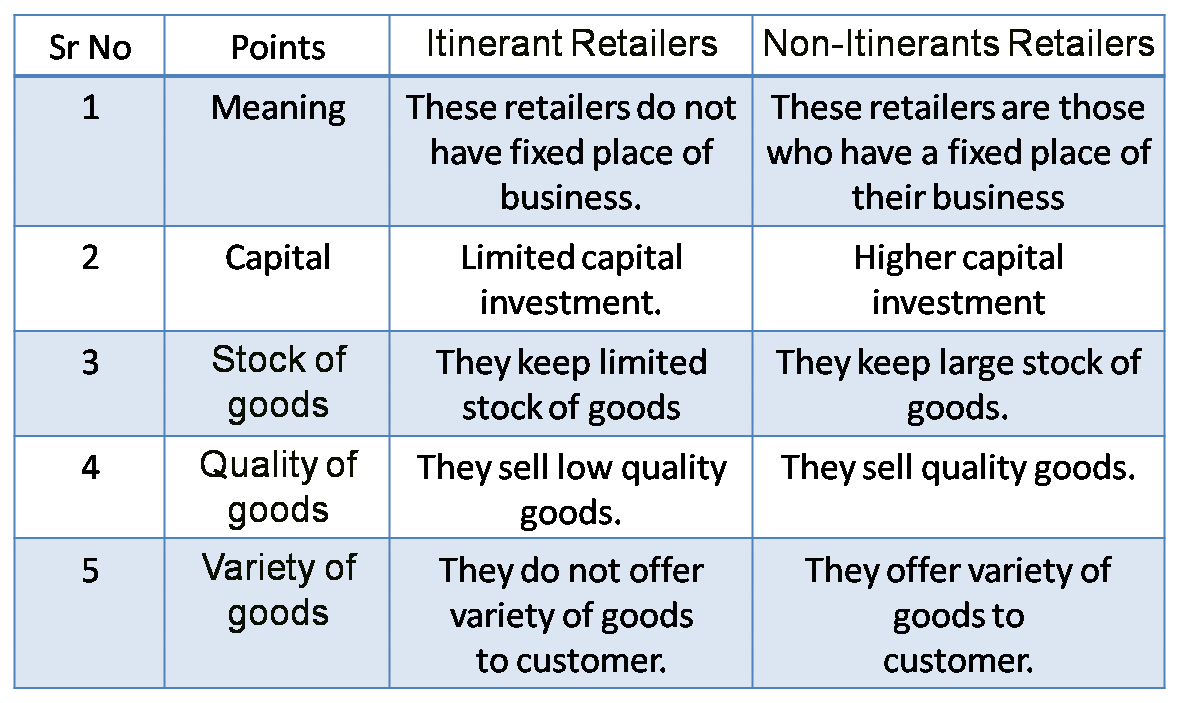
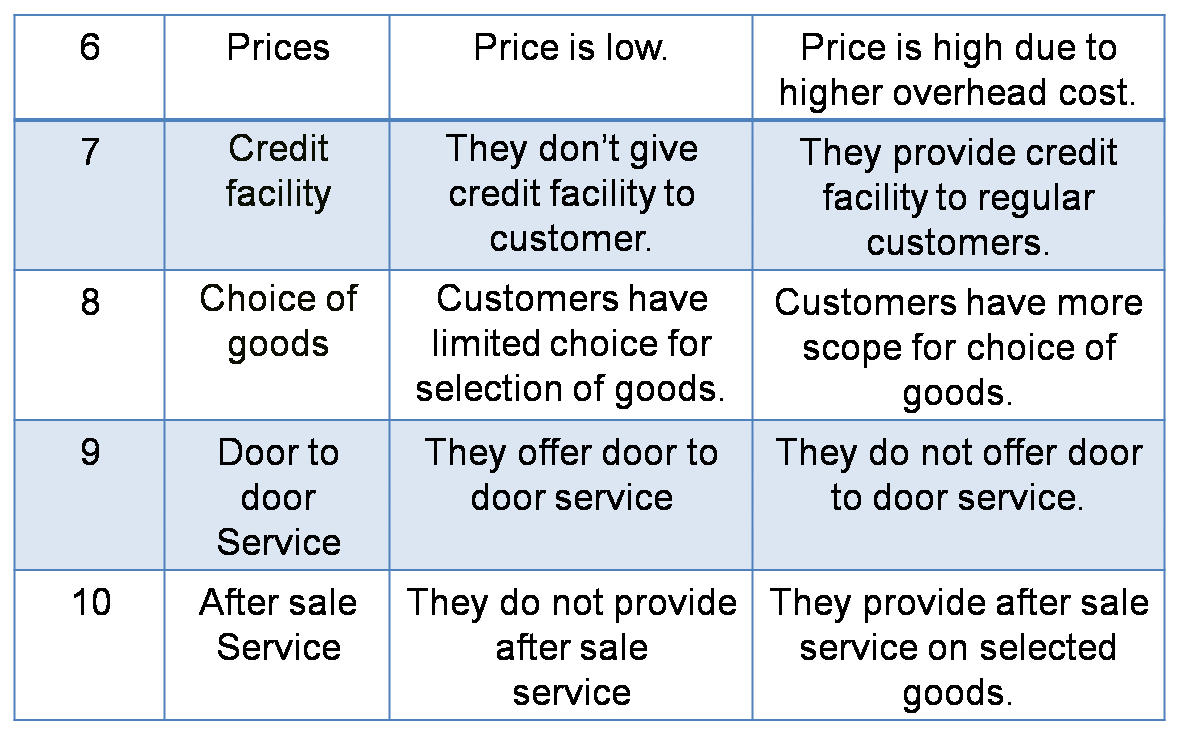
3) General stores and Specialty stores.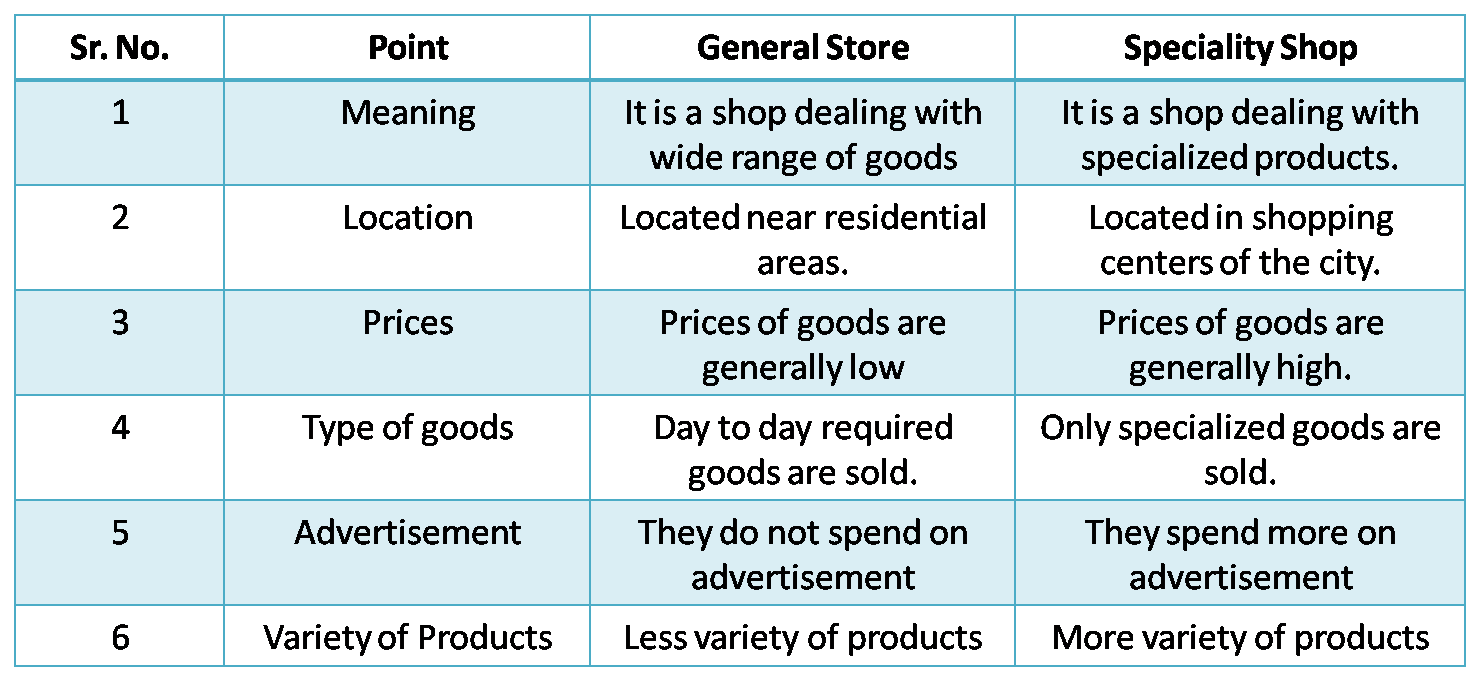
4) Departmental stores and Chain store.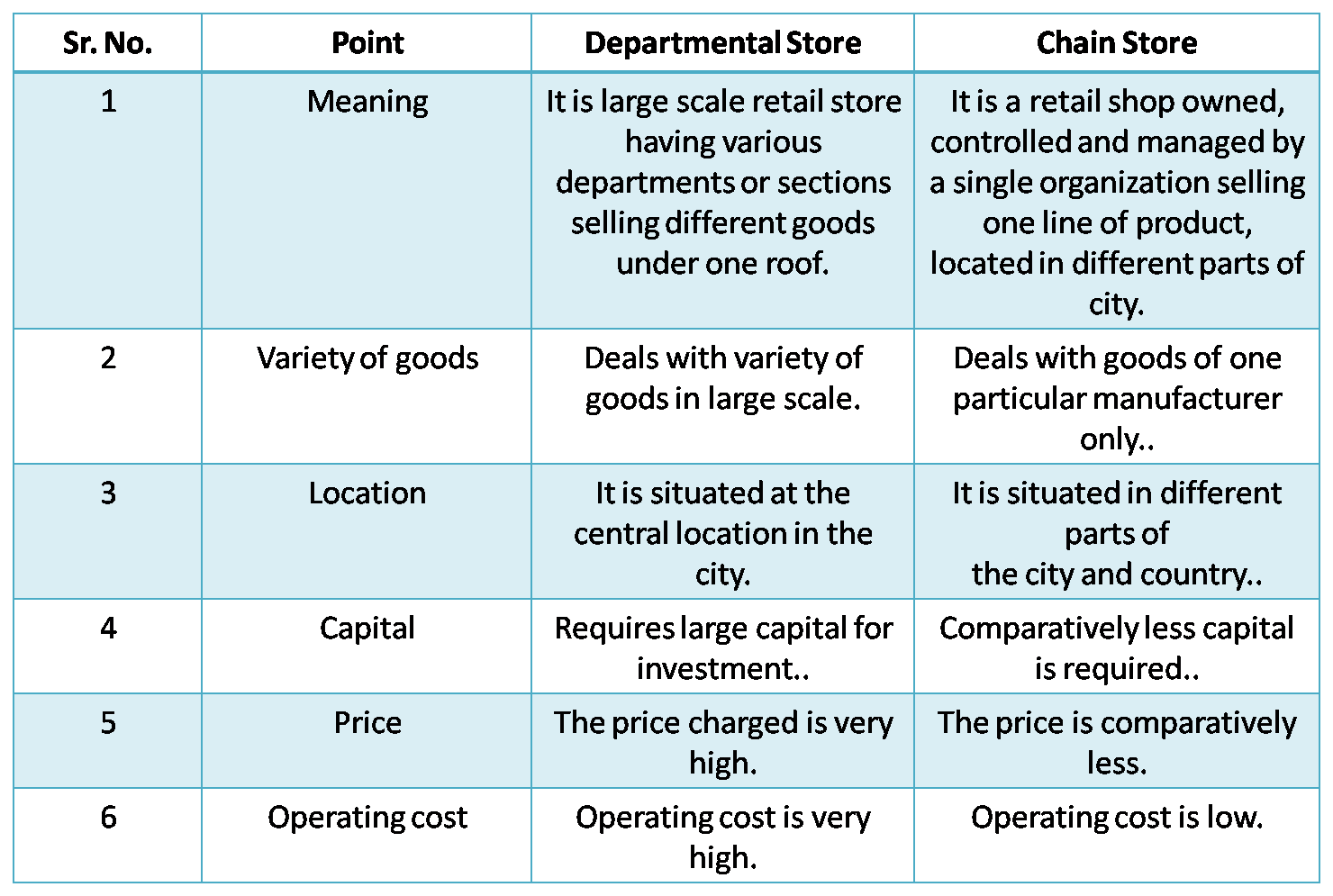
5) Import Trade and Export Trade.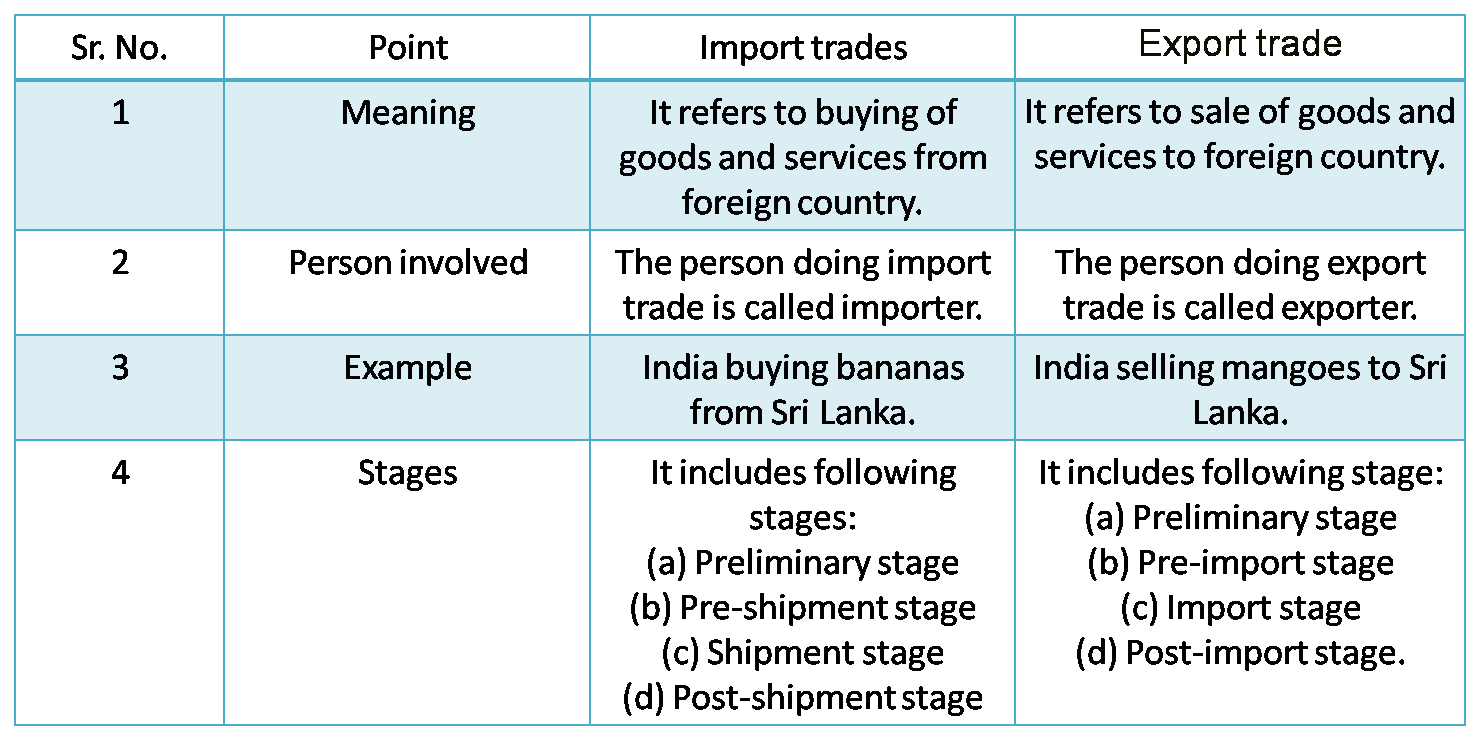
Q.5 Answer in brief.
1) State any four features of one price shop.
Answer : 1) Uniform Price : All the goods whether big or small in size are sold goods at one standard fixed price. There is no scope for bargaining.
2) Low Price : Usually the price of the goods is reasonable and low.
3) Variety of Goods : These shops usually deal in variety of small sized goods. There is a wide scope of choice of goods e.g. stationery, toys, fun games, play cards, cosmetics etc.
4) Location : These shops are located in busy centers of the city such as busy trade streets near railway stations, bus stops, etc. Sometimes this shop is temporarily set up in fairs or
exhibitions.
5) Cash Sales : In this shop goods are sold on cash basis only. No credit facility is given to customers and so there is no risk of bad debts.
2) State any four services of wholesalers to manufacturers.
Answer :
Services of Wholesalers to Manufacturers.
(1) Provide Finance: Wholesaler provides advance to the manufacturers so they can do bulk production. Manufacturer can maintain continuous flow of production.
(2) Collecting Order and Distribution of Goods: Wholesaler collects small orders of goods from the retailers then he collects the goods from manufacturer and distributes it to retailers.
(3) Goods Sale on Large Scale: Wholesaler sells goods to the retailers on large scale on behalf of manufacturers.
(4) Economy in Production: Large scale of production is made possible because production of goods is done continuously by the manufacturer.
(5) Market Information: Wholesaler provides latest information of market condition to manufacturer. On the basis of this information manufacturer changes his production policies and regulates production activities.
(6) Storage: The wholesaler provides storage facilities for the manufacturers’ product of goods. This helps them to fill up the time gap between production and consumption of goods.
3) Write any four services of retailers to consumers.
Answer :
Services of Retailers to Consumers:
1) Variety of Goods: Retailer keep different brands of goods which helps the customer to choose.
2) After Sales Services: After sales services are given for a particular period, which is known as guarantee period for costly and durable goods such as refrigerators, TV. etc. Such services create confidence in minds of consumers for further purchases.
3) Regular Supply of Goods: Retailer stocks the goods sufficiently which are required by the customers and customers purchases the goods whenever needed.
4) Credit Facilities: Retailers provides credit facility to customer which helps him to grow up sales also it is convenient for the customers to purchase goods.
5) Home Delivery: Retailer provides home delivery service to the customers which helps him to maintain permanent relationship with the customers.
4) State any two types of small scale fixed shop retailer.
Answer :
1) General Stores : General store Retailers sell goods which are required by people for their day to day needs like food grains, soaps, stationery, medicines, oils, toffees, biscuits,
plastic goods, footwear, umbrella, pens etc. These shops are generally situated near residential areas of the city or town. They provide home delivery of goods. They have variety of goods in each item. They buy the goods from wholesalers or buy directly from
manufacturers.
2) Second hand Goods Shop : These retailers purchase and sell used goods e.g. They deal in books, furniture, TV. Set, clothes, cars etc. After repairing the goods and setting them in
working conditions, the goods are sold to the consumers. Generally consumers from weak financial background purchase goods from them. As prices of these goods are cheap, they
lack quality, durability and guarantee.
5) Explain preliminary stage of Import procedure.
Answer :
A) Preliminary Stage
1) Registration : The Importer has to get himself registered with various authorities as follows:
i) Directorate General Foreign Trade to obtain Import-Export Certificate Number.
ii) Income Tax authority to obtain Permanent Account Number.
iii) Formalities regarding GST.
2) Negotiation : The importer must hold negotiation with overseas suppliers regarding-
i) Price of goods
ii) Delivery schedule
iii) Credit Period
iv) Terms and Condition regarding sale, payment and delivery.
6) Explain post-shipment stage of Export procedure.
Answer :
1) Shipment Advice : The exporter sends shipment advice to the importer informing him about dispatch of goods. He also sends copy of packaging list, commercial invoice and
non-negotiable copy of loading along with advice letter.
2) Presentation of Documents : The exporter submits all necessary documents to the bank for negotiation and realization of export proceeds.
3) Realization of Export Incentive : The exporter makes an arrangement to obtain export incentive from the concerned authorities. The incentive includes duty drawbacks, refund
of GST, if paid etc.
4) Follow-Up : Exporter should always have follow up after export to find buyers reaction towards the goods.
Q.6 Justify the following statements.
1) Wholesaler sells goods in large quantities.
Answer :
1) Wholesaler buys goods in large quantities from the manufacturer and sells it to the retailers according to their orders.
2) Thus, wholesaler sells goods in large quantities.
2) Wholesaler maintains price stability.
Answer :
1) A wholesaler is both a buyer and a seller.
2) He is in a position to maintain price stability by balancing supply and demand factors.
3) By supplying regular goods to the retailer, he solves the risk of shortage and price fluctuation is reduced.
4) Thus, wholesaler maintains price stability.
3) Retailer provide home delivery of goods to customers.
Answer :
1) Retailer is a person who buys goods on smaller quantities.
2)Retailer provides home delivery of goods to customer at nominal cost or free of cost.
3) This helps them to improve relations with the customers and maintain permanent relations with the customers.
4) Thus, retailer provide home delivery of goods to customers.
4) Wholesaler performs various marketing functions.
Answer :
1) The wholesaler carries various marketing functions like warehousing, advertisings, sales promotion, etc. on behalf of the manufacturers.
2) They also perform various marketing functions like assembling, warehousing, transporting, grading, packing, advertising and financing.
3) These functions help the retailers and a manufacturers as they can concentrate on the production and selling activities.
4) Thus, wholesaler performs various marketing functions.
5) Authorized dealer do not have other product of other manufacturers.
Answer :
1) An authorized dealer only deals with one line of products from one-manufacturers.
2) They do not have products of other manufacturers.
3) They promote the goods by providing window display, advertising and also having attractive schemes for selling the goods.
4) Thus, authorized dealer do not have other product of other manufacturers.
6) General stores are generally situated near residential areas.
Answer :
1) General Stores are found in residential areas and offer shopping convenience to the customers.
2) They deal in wide variety of goods.
3) They deal with day to day useful goods.
4) Thus, general stores are generally situated near residential areas.
7) Departmental store has centralized management system.
Answer :
1) Departmental stores are generally established by joint stock companies.
2) Various departments which look like specialized shops are controlled and managed by single management.
3) The management of departmental store is centralized.
4) All departmental store is centralized.
5) All departments are independent but they are centrally owned managed are controlled.
6) Thus, departmental store has centralized management system.
8) Packing plays an important role in selling product in the supermarket.
Answer :
1) Packing plays an important role in selling products in the supermarket.
2) Goods are duly packed by giving details of quantity, quality, weight, price, Contents, date of manufacturing and date of expiry.
3) This is helpful in handling the goods and also makes the goods more attractive and durable.
4) Thus, packing plays an important role in selling product in the supermarket.
9) Chain store sell a limited range of goods.
Answer :
1) Each branch of a chain store deals in the same commodity or in the same line of products.
2) This enables the store to give better guidelines to the customers,
3) Thus, chain store sell a limited range of goods.
10) There is no scope for bargaining in one price shop.
Answer :
1) The goods are priced at one price which is fixed.
2) There is a fixed and uniform price.
3) The price are fixed in advance, so there is no scope for bargaining.
4) Thus, there is no scope for bargaining in one price shop.
Q.7 Answer the following
1) What are the main features of wholesaler?
Answer :
(A) Meaning :
1) Wholesalers are those who engage themselves in wholesale trade.
2) It is concerned with the buying of goods in large quantities from producers and reselling the same in small quantities to the retailers.
3) Wholesaler is a connecting link between producers on one hand and retailers on the other.
B) Definition :
1) According to Philip Kotler, “Wholesaling includes all activities involved in selling goods or services to those who buy for resale or for business use.”
C) Features of Wholesaler :
1) A Wholesaler purchases goods from the producer in large quantities.
2) Wholesaler has to take risk in the process of distribution.
3) A Wholesaler deals with one or few types of goods.
4) A large amount of capital is required in this business.
5) A wholesaler maintains price stability by balancing supply and demand factors.
6) The manufacturers can get direct information about market through wholesalers.
7) A Wholesaler sells the goods to the retailers as per their requirements.
8) A Wholesaler performs the marketing functions like assembling, warehousing,
transporting, grading, packing, advertising and financing.
2) Explain the services of retailers to wholesaler.
Answer :
1) Retailer is the link between the wholesaler and consumers who operates in local markets. He deals in wide variety of goods by investing limited capital.
Services to Wholesaler :
1) Connecting Link : The retailer is the connecting link between the wholesaler and consumer.
2) Helps to Distribute : Retailers help to quickly distribute goods. It becomes very important, in case of perishable goods like dairy products, fruits, vegetables, pulses etc.
3) Marketing : If the wholesaler is unable to carry out marketing function, retailers conduct them. Sometimes he handles transportation on his own. Sometimes he tries to solve shortages problem or advertises for better sale.
4) Provide Information : The retailer provides information about changing demands, preferences, likes and dislikes of consumers to the wholesaler.
5) Attract Consumers : The Retailers attract consumers by advertising the products. This activity directly helps the wholesaler to sell the product.
6) Create Demand : Through personal salesmanship retailer attracts consumer’s attention towards new goods and arrivals in the market. To create demand for new goods, the retailer puts new goods for window display.
3) Explain small scale fixed shop retailers.
Answer :
Small scale fixed retailer :
The Retailers who conduct their business operations on a small scale and deal in variety of goods are small scale shop retailers. They offer shopping convenience to the customers as they
are situated in the same locality e.g. General stores, medical store, laundry, etc.
Types of small scale fixed retailers
1) General Stores : General store Retailers sell goods which are required by people for their day to day needs like food grains, soaps, stationery, medicines, oils, toffees, biscuits,
plastic goods, footwear, umbrella, pens etc. These shops are generally situated near residential areas of the city or town. They provide home delivery of goods. They have variety of goods in each item. They buy the goods from wholesalers or buy directly from
manufacturers.
2) Second hand Goods Shop : These retailers purchase and sell used goods e.g. They deal in books, furniture, TV. Set, clothes, cars etc. After repairing the goods and setting them in
working conditions, the goods are sold to the consumers. Generally consumers from weak financial background purchase goods from them. As prices of these goods are cheap, they lack quality, durability and guarantee.
3) Authorized Dealer : These retailers have authorized dealership of particular manufacturer’s goods. They deal in goods like T. V. Sets, washing machines, automobiles, music systems etc. Authorized dealers try to maximize sale of goods, because they get good commission
from manufacturers. Authorized dealers do not have products of other manufactures, except for whom they are working as authorized dealers. They promote the goods by window display, advertisements and attractive schemes.
4) Speciality Shops : These retailers deal in particular line of goods. They keep a wide variety of item of same line of the product. e.g. A toy shop may keep only toys of different
types. Other examples of Speciality shop retailer are sports material, ready-made dresses, leather goods, plastic goods, watches, books etc. They offer goods at varying price range.
They provide a wide choice to the customers. They give advice to the customers as they have expert knowledge about the product.
4) Explain services of wholesalers.
Answer :
Wholesaler provides services to:
(A) Manufacturers and (B) Retailers
(A) Services of Wholesalers to Manufacturers:
(I) Finance Assistance : Wholesaler provides advance to the manufacturers, so they can do bulk production. Thus, manufacturer can maintain continuous flow of production.
(II) Collecting Order and Distribution of Goods: Wholesaler collects small orders of goods from the retailers then he collects the goods from manufacturer and distributes it to retailers.
(III) Large Purchase: Wholesaler purchases goods on large scale from the manufacturers and sells it to the retailers on behalf of the manufacturers.
(IV) Transportation: Wholesaler sometimes carry the transportation function of manufacturer by himself. So cost and time of manufacturer is saved.
(V) Risk Bearing: He takes a risk of buying goods in big quantity and storing them. This may sometimes lead him to loss.
(VI) Provide Market Information: Wholesaler provides latest information of market condition to manufacturer. On the basis of this information manufacturer changes his production policies and regulates production activities.
(VII) Marketing Function: Wholesaler carries many marketing functions like warehousing, advertising, sales promotion, etc. on behalf of manufacturer.
(VIII) Storage: The wholesaler provides storage facilities for the products manufacture by the producers. This helps them to fill up the time gap between production and consumption of goods.
(B) Services of Wholesaler to Retailers :
1) Financial Support: Wholesaler provides credit facility, discount facility and financial assistance to their retailers.
2) Market Information: Wholesaler provides market information to retailers as he has link with various manufacturers. This information is very useful to retailers for purchase of goods.
3) Risk Bearing: Retailer holds limited stock of goods and avoids the risk of spoilage of goods. Retailer get protected from increase or decrease of prices of goods and fluctuation of demand.
4) Stock of Goods: Wholesaler stores the stock of goods for retailers, then retailer supply these goods to customers as per their demands.
5) Warehousing and Transport: Wholesaler provides the facility of storing of goods as well as transport facility to retailers. They also do home delivery of goods to retailers.
6) Regular Supply: Wholesaler assures regular supply of goods to the retailers. Risk of shortage of goods and price fluctuation is reduced.
7) Sales Promotion: Wholesaler provides promotional facility to the retailer. He advertises on behalf of retailers and this helps the retailers to increase the sales.
5) Explain different services of retailers.
Answer :
Retailers provides services to :
(A) Customers and (B) Wholesaler
(A) Services of Retailers to Customers:
1) Variety of Goods: Retailer keep different brands of goods which helps the customer to choose.
2) After Sales Services: After sales services are given for a particular period, which is known as guarantee period for costly and durable goods such as refrigerators, TV. etc. Such services create confidence in minds of consumers for further purchases.
3) Regular Supply of Goods: Retailer stocks the goods sufficiently which are required by the customers and customers purchases the goods whenever needed.
4) Credit Facilities: Retailers provides credit facility to customer which helps him to grow up sales and also it is convenient for the customers to purchase goods.
5) Home Delivery: Retailer provides home delivery service to the customers which helps him to maintain permanent relationship with the customers.
6) Information: Retailer is a link between manufacturer and consumer. He provides valuable information from the customers to the manufacturer so that he can modify the product as per the likes and dislikes of the customers. Complaints regarding defects in goods, improper functioning of the product, constant break down, etc. are passed on to the manufacturers.
7) Local Convenience: Retailers are generally located near residential areas. Hence, customers can buy the goods whenever they require.
8) Improves Standard of Living: Retailers help customers to increase their standard of living by making available all the latest types of goods produced.
9) Sale of Perishable Goods: Perishable goods like milk, meat, fish, vegetables, etc. require quick distribution. Hence, retailer provides this facility as per customers requirement.
(B) Services of Retailers to Wholesaler :
1) Connecting Link : The retailer is the connecting link between the wholesaler and consumer.
2) Helps to Distribute : Retailers help to quickly distribute goods. It becomes very important, in case of perishable goods like dairy products, fruits, vegetables, pulses etc.
3) Marketing : If the wholesaler is unable to carry out marketing function, retailers conduct them. Sometimes he handles transportation on his own. Sometimes he tries to solve shortages problem or advertises for better sale.
4) Provide Information : The retailer provides information about changing demands, preferences, likes and dislikes of consumers to the wholesaler.
5) Attract Consumers : The Retailers attract consumers by advertising the products. This activity directly helps the wholesaler to sell the product.
6) Create Demand : Through personal salesmanship retailer attracts consumer’s attention towards new goods and arrivals in the market. To create demand for new goods, the
retailer puts new goods for window display.
6) Define import trade. Explain its procedure in detail.
Answer :
Import trade refers to buying of goods and services from another country or countries i.e. a foreign country. The procedure of import trade varies from one country to another country depending upon the policy implemented in that country.
Import of goods and services is controlled by the government in most of the countries India follows the following import procedure, which is divided into four stages.
[A] 1st Stage: Preliminary Stage :
1) Registration : The Importer has to get himself registered with various authorities as
follows:
i) Directorate General Foreign Trade to obtain Import-Export Certificate Number.
ii) Income Tax authority to obtain Permanent Account Number.
iii) Formalities regarding GST. 2) Negotiation : The importer must hold negotiation with overseas suppliers regarding-
i) Price of goods
ii) Delivery schedule
iii) Credit Period
iv) Terms and Condition regarding sale, payment and delivery.
[B] 2nd Stage: Pre import Stage :
1) Quota Certificate : Certain items are subjected to quota restrictions. The Importer needs to obtain import quota certificate from government authorities.
2) Foreign Exchange Clearance : The Importer needs to obtain foreign exchange clearance from RBI. The Importer should forward the application for the same through his bank.
3) Order Placement : After obtaining foreign exchange clearances from RBI, the importer places an order with the overseas suppliers. This order is called as indent. The importer
negotiates the terms and conditions of the import contract and places the order.
4) Letter of Credit (LC): The exporter normally request for LC. The LC is an undertaking given by the importer’s bank guaranteeing the payment to the exporter on behalf of
importer. The LC is the safest method of payment in foreign trade. Therefore the importer has to obtain LC from his bank in favour of the exporter.
5) Clearing and Forwarding Agent (C & F Agents) : The importer has to appoint C& F agents to undertake various custom formalities and documentation work in respect of
import of goods.
6) Shipment Advice : The shipment advice enables the importer to make necessary arrangement for custom clearance and unloading of goods sent by the Exporter.
[C] Stage: Import Stage :
1) Receipt of Document : The importer receives the documents sent by the exporter through his bank. The documents include :
a) Bill of Lading b) Packing List c) Commercial Invoice d) Certificate of Origin e) Certificate of Inspection etc.
2) Bill of Entry : C & F agents prepare bill of entry which is required for custom clearance. The bill of entry give details about number of packages quality of goods, price of goods
etc.
3) Delivery Order : The C & F agent obtain delivery order from the shipping company. The shipping company gives the delivery order on payment of freight. Delivery order helps to unload the goods from vessel.
4) Custom Clearance : The purpose of custom clearance is to get the document certified from custom authority. The document includes bill of lading, bill of entry and packing list.
[D] 4th stage: Posts Import Stage :
1) Port Trust Dues : The C & F agents has to make payments of port trust dues.
2) Custom Duty : The C and F agent has to make payment to custom authorities in respect of importing goods.
3) Insurance Premium : The Importer has to make payment under FOB (Free on Board) contract.
4) Payment of Freight : The Importer has to make payment of freight under shipping contract.
5) Exporters Payment : The importer has to make payment to the exporter as per the terms of contract. The exporter draws a bills of exchange for the payment.
6) Follow up : The importer needs to take follow up in respect of import of goods. If there are any discrepancies importer should inform to the exporter.
7) What is export trade? Explain its procedure in detail.
Answer : Trade between two countries is called International Trade. It can be import or export trade. Export trade refers to selling of goods and services to other country or foreign countries Export procedure is as follows:
There are four stages which help in simplify the export procedure.
[A] Preliminary Stage: This is the first stage which includes the following steps.
1) Registration : The exporter has to get himself registered with various authorities as follows:
i) Directorate General of Foreign Trade to obtain Import-Export Certificate number.
ii) Income Tax authority to obtain Permanent Account Number.
iii) Other Authority like EPC (Export Promotion Council) and GST authority.
2) Appointment of agent :
After registration the exporter appoints agents or sales representative abroad to book orders. The exporter may also open sales office in foreign country.
[B] Pre-shipment Stage :
1) Receipt of Order : As soon as the order is received the exporter must verify and confirm the order. The exporter checks on the ‘Restriction on Import’ in Importer’s country.
2) Letter of Credit : The exporter requests importer to issue a letter of credit in his favour.
The receipt of ‘letter of credit’ from importer’s bank will clear the foreign exchange and other restrictions.
3) Preshipment Finance : The exporter obtain pre shipment finance from his banker to meet working capital requirement.
4) Production of Goods : The exporter has to produce goods as per buyer’s need. If the exporter is not a manufacturer then he will get the ordered goods from the local supplier.
5) Packaging : The goods must be properly packed because packing plays three important roles.
i) Protection of goods in transit
ii) Preservation of quality of goods
iii) Promotion of goods
6) ECGC Cover (Export Credit and Guarantee Corporation) : The exporter may obtain cover from ECGC. Such cover protects exporter against credit risk. e.g. If the importer fails to make the payment of bill, the exporter can be covered from ECGC to the extent of
90 % of the loss.
7) GST formalities (Goods and Services Tax) : The exporter needs to complete GST formalities regarding export trade.
8) Marine Insurance : The exporter has to obtain marine insurance under CIF (cost, insurance and freight) contract. He has to pay necessary insurance premium and obtain insurance policy.
9) C & F agents (Clearing and Forwarding) : In export trade C & F agents are known as custom house agents. These agents are responsible for forwarding the goods.
[C] Shipment Stage :
1) Processing of Document : Exporter prepares the shipping bill and gets all the documents processed at customs house.
2) Examination of Goods : The C&F agent obtain carting order from the PTA (Port Trust Authority) to cart the goods inside the docks.
3) Loading of Goods : After examining the goods CE (Customs Examiner) issues ‘Let Export’ order. The C&F agent then obtains ‘Let Ship Order’ from Custom Preventive Officer (CPO). The goods are then loaded on ship for which a Mate’s receipt’ is obtained.
The C&F agents approaches shipping companies and obtains a Bill of Lading.
[D] Post-shipment Stage :
1) Shipment Advice : The exporter sends shipment advice to the importer informing him about dispatch of goods. He also sends copy of packaging list, commercial invoice andnon-negotiable copy of loading along with advice letter.
2) Presentation of Documents : The exporter submits all necessary documents to the bank for negotiation and realization of export proceeds.
3) Realization of Export Incentive : The exporter makes an arrangement to obtain export incentive from the concerned authorities. The incentive includes duty drawbacks, refundof GST, if paid etc.
4) Follow-Up : Exporter should always have follow up after export to find buyers reaction towards the goods.