Imprtant Questions Asked in SSC Board Exams From This Lesson ⇒ Click here
Text Book Solution ↓
1. Identify me.
(a) I am diploblastic & acoelomate. Which phylum do I belong to?
Ans. Cnidaria or Coeleterata.
(b) My body is radially symmetrical. Water vascular system is present in my body. I am referred as fish though I am not. What is my name?
Ans. Starfish.
(c) I live in your small intestine. Pseudocoelom is present in my thread like body. In which phylum will you include me?
Ans. Ascaris, phylum Aschelminthes.
(d) Though I am multicellular, there are no tissues in my body. What is the name of my phylum?
Ans. Sponge, Porifera.
2. Write the characters of each of the following animals with the help of classification chart.
Bath sponge, grasshopper, rohu, penguin, frog, lizard, elephant, jellyfish.
Ans. Bath sponge:
(i) It belongs to phylum porifera. (ii) It bears numberous pores on its body called ostia and oscula.
(iii) It has special type of cell-collar cells. (iv) It has good ability of regeneration. (v) It is always attached to substratum and hence do not show locomotion. (vi) Its body is supported by spicules or spongin fibres.
Ans. Grasshopper :
(i) Grasshopper belongs to phylum Arthropoda. (ii) Body is covered with chitinous exoskeleton. (iii) Body is divided into head, thorax and abdomen. (iv) There are two pairs of wings and three pairs of jointed appendages for locomotion. (v) It is bilaterally symmetrical.
Ans. Rohu :
(i) Rohu belongs to class pisces. (ii) It is found in fresh water. (iii) It is a bony fish. (iv) Skin shows presence of scales. (v) Respiration occurs with gills.
Ans. Penguin:
(i) This animal belongs to class Aves. (ii) They are found at the south pole, i.e. at Antarctica, which is a cold region (iii) Exoskeleton shows feathers. (iv) Penguin is warm-blooded. (v) They are adapted to a cold region life. (vi) Penguin is oviparous. (vii) Neck is present between head and trunk.
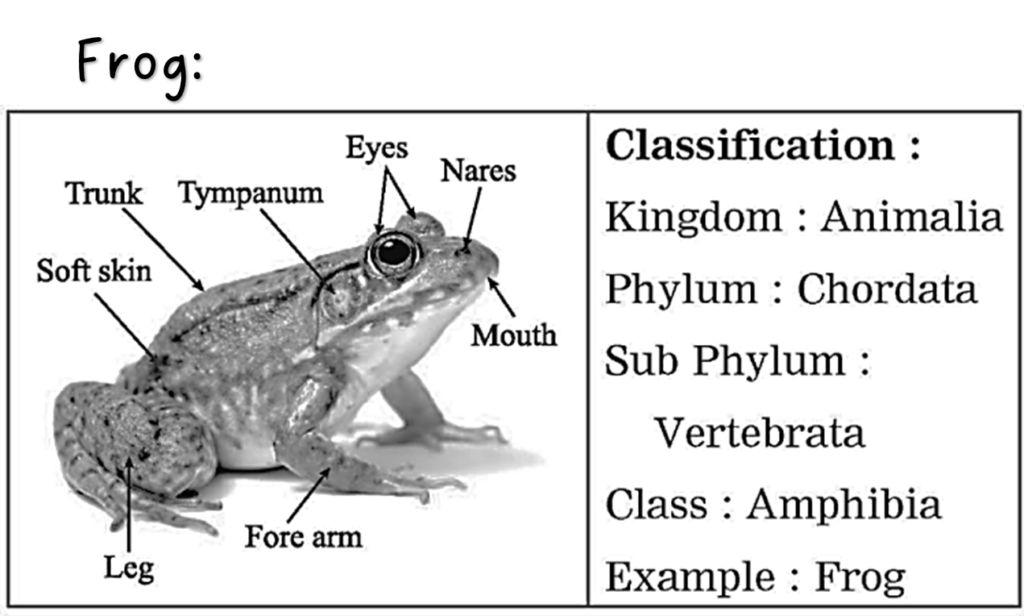
Ans. Frog:
(i) Frog belongs to class Amphibia. (ii) Can live in water as well as on land during adult life. (iii) Skin is without any exoskeleton and is usually kept moist for respiration. (iv) They have two pairs of appendages. Digits are without claws. (v) External ear is absent but tympanum is present.
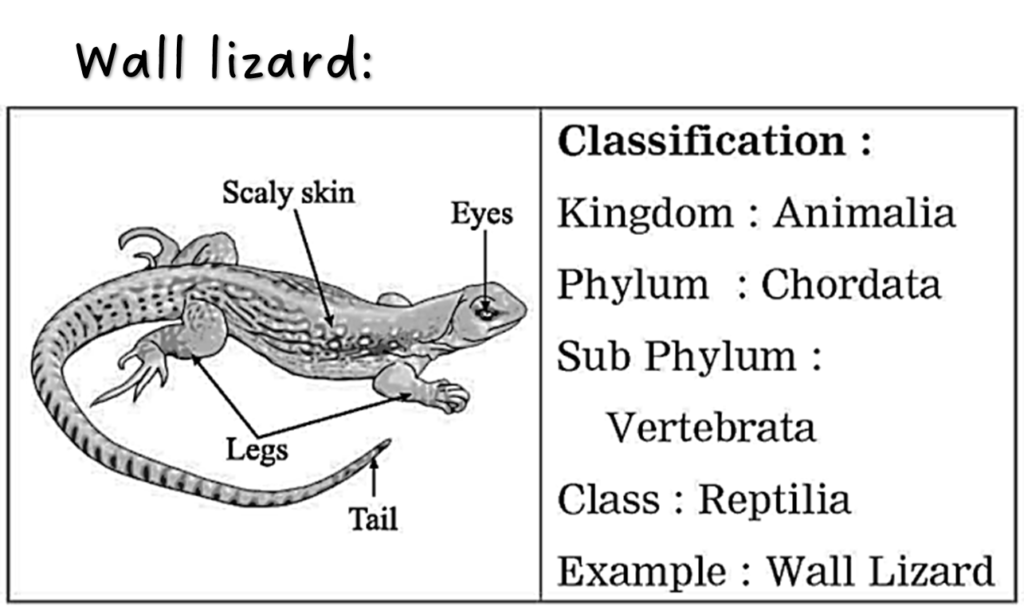
Ans. Lizard:
(i) It belongs to class Reptilia. (ii) It is cold-blooded (Poikilotherm) (iii) It shows creeping movement as body cannot be lifted up. (iv) Neck is present between head and trunk. (v) External ear is absent.
Ans. Elephant:
(i) Elephant belongs to class mammalia. (ii) Body shows differentiation into head, neck, trunk and tail. (iii) Mammary glands are present. (iv) The heart is four chambered. (v) Largest terrestrial mammal. (vi) It is warm-blooded. (vii) Body is divided into head, neck, trunk and tail.
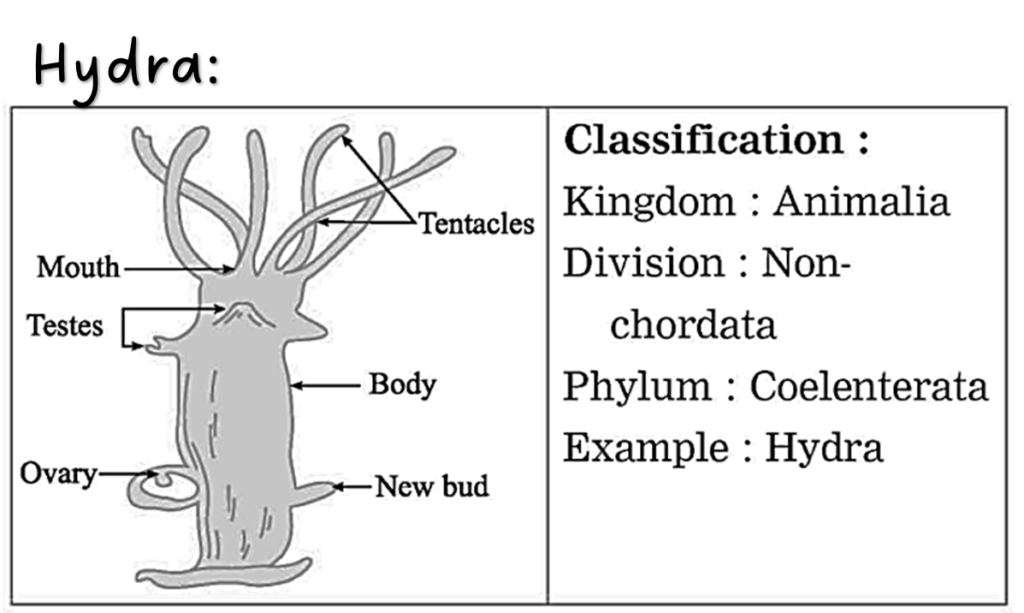
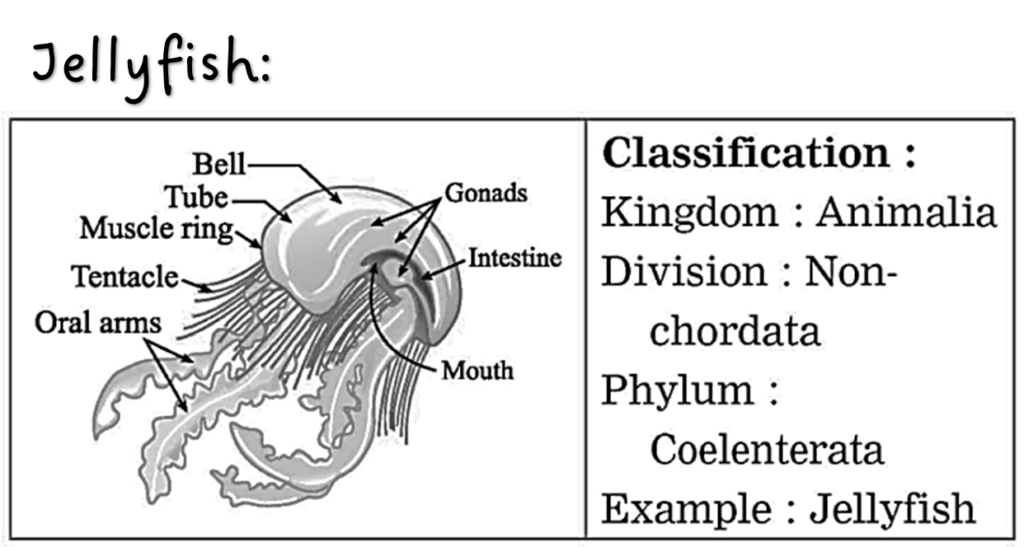
Ans. Jellyfish:
(i) Jelly fish belongs to Phylum Coelenterata. (ii) Cnidoblast bearing tentacles are present around the mouth. Tentacles are useful for capturing the prey whereas cnidoblasts inject the toxin in the body of the prey. (iii) Body is umbrella shaped, hence called Medusa. (iv) It is diploblastic, and shows radial symmetry.
3. Write in brief about progressive changes in animal classification.
Ans. There were different methods of classification of animals.
(1) The first classification method was given by the Greek philosopher Aristotle. He took into account the criteria like body size, habits and habitats of the animals. This method was called artificial method of classification. (2) The same artificial method was used by other scientists such as Theophrastus, Pliny, John Ray, Linnaeus, etc. (3) Further due to advances in science the references were changed and there were some new methods of classification proposed. (4) The system of classification called ‘Natural system of classification’ was then proposed. This system of classification was based on criteria such as body organization, types of cells, chromosomes, bio-chemical properties, etc. (5) Later, Dobzhansky and Meyer gave the system of classification based on evolution. (6) In 1977, Carl Woese has also proposed the three domain system of animal classification.
4. What is the exact difference between grades of organization and symmetry? explain win examples.
Ans. I. Grades of organization :
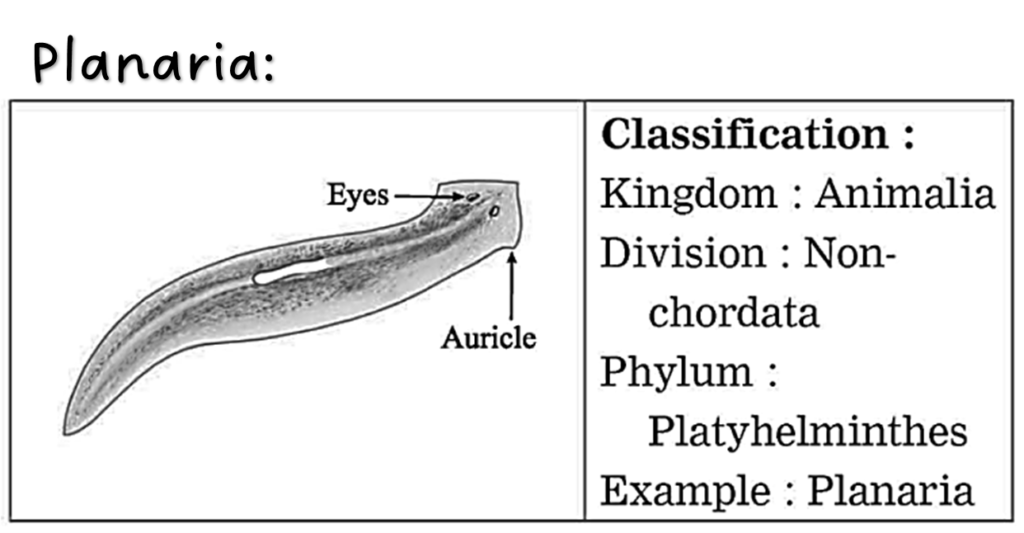
(1) The grades of organization mean the way an organism has different body formation. (2) Unicellular organisms like amoeba have a single cell in the body and hence the organization in its body is called protoplasmic grade of organization. (3) Some organisms have only cells in their body which is called cellular grade of organization, e.g. Poriferans. (4) Some have tissues e.g. Coelenterates. They are said to have tissue grade organization. Some have organs, they are said to have organization-organ grade, e.g. Platyhelminthes. All other higher animals have organ-system grade organization.
II Symmetry;
(1) Symmetry on the other hand shows the base of the body formation. (2) The symmetry can be understood by taking an imaginary cut through the animal body. (3) Based on the symmetry there can be three types. (4) In asymmetric animals, there is no symmetry in any plane, e.g. Amoeba. (5) The bilateral symmetry is the one in which an imaginary axis can pass through only one median plane to divide the body into two equal halves. Most of the animals have bilateral symmetry and hence their organs are arranged in symmetric way on both the sides. (6) The imaginary cut passing through the central axis but any plane of body can give more than one equal half. The organs of such animals are arranged in a radius of an imaginary circle, e.g. Cnidarians and some chinoderms. Both grades of organization and symmetry are the bases for classifying animals into different phyla.
5. Answer in brief.
(a) Give scientific classification of shark upto class.
Ans.
Kingdom : Animalia
Sub kingdom : Metazoa
Phylum : Chordata
Subphylum : Vertebrata
Class : Pisces
(b) Write four distinguishing characters of phylum- Echinodermata.
Ans. (i) The body is rough with calcareous spines. (ii) Body show radial symmetry in adult stage. (iii) They are exclusively marine animals. (iv) Locomotion with tube feet.
(c) Distinguish between butterfly and bat with the help of four distinguishing properties.
Ans. Butterfly:
(i) Butterfly belongs to Non-chordates. (ii) Butterfly belongs to Phylum Arthropoda. (iii) It belongs to Class Insecta. (iv) Exoskeleton is chitinous.
Bat:
(i) Bats are Chordates. (ii) Bat belongs to phylum Chordata. (iii) It belongs to Class Mammalia. (iv) Exoskeleton is covered with hair.
(d) To which phylum does Cockroach belong? Justify your answer with scientific reasons.
Ans. (i) Cockroach belongs to the phylum Arthropoda and class Insecta. (ii) Scientific reasons: (a) The body is covered by chitinous exoskeleton. (b) Jointed appendages present, three pairs of walking legs and two pairs of membranous wings. (c) Body is eucoelomate, triploblastic, bilaterally segmented and segmented. (d) Respiration by spiracles and tracheal tubes.
6. Give scientific reasons.
(a) Though tortoise lives on land as well as in water, it cannot be included in class- Amphibia.
Ans. (i) The animals which not only live in water but also on land and respire in both climatic conditions are called Amphibians. (ii) Tortoise respires through lungs but does not have a structure to respire in water. (iii) It is adapted for locomotion in water. (iv) Also, tortoise lays eggs with hard shells which is a characteristic of reptiles. (v) Tortoise has a neck, whereas neck is absent in amphibian. Therefore, tortoise is not an amphibian.
(b) Our body irritates if it comes in contact with jelly fish. (Sep.’21)
Ans. (i) Jelly fish has tentacles with cnidoblasts around mouth. (ii) The toxin released from the cnidoblasts comes in contact with the body of a person touching it. (iii) Due to this, there is an itching effect and irritation.
(c) All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
Ans. (i) In some chordates, the notochord is present only in the tail region of larvae. (ii) In some other chordates, notochord is present throughout the body length. (iii) In some chordates, the notochord is replaced by vertebral column. (iv) Due to this, all chordates do not get classified in the same group. (v) Hence, all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
(d) Balanoglossus is connecting link between non-chordates & chordates. (Nov ’20)
Ans. (i) Balanoglossus belongs to Hemichordata meaning half-chordates. (ii) The body shows proboscis, collar and trunk. (iii) Its characteristic features resemble with Nonchordates as well as chordates. (iv) Thus, this animal shows characteristics of both the groups and hence, it is a considered as a connecting link between non-chordates and chordates.
(e) Body temperature of reptiles in not constant.
Ans. (i) Reptiles are cold blooded animals or poikilotherms. (ii) The body temperature of cold blooded animals changes with the surrounding temperature. (iii) Reptilians have different habitat which have different temperatures. (iv) In order to adapt to different situations, the body temperatures of reptiles at different locations differ. Hence, their body temperature is not constant.
7. Answer the following questions by choosing correct option.
(a) Which special cells are present in the body of sponges (Porifera)?
1. Collar cells. 2. Cnidoblasts. 3. Germ cells. 4. Ectodermal cells.
Ans. Collar cells.
(b) Which of the following animals’ body shows bilateral symmetry?
1. Star fish. 2. Jelly fish. 3. Earthworm. 4. Sponge.
Ans. Earthworm.
(c) Which of the following animals can regenerate it’s broken body part?
1. Cockroach. 2. Frog. 3. Sparrow. 4. Star fish.
Ans. Star fish.
(d) Bat is included in which class?
1. Amphibia. 2. Reptilia. 3. Aves. 4. Mammalia.
Ans. Mammalia.
Ans.


10. Sketch, label and classify
Hydra, Jellyfish, Planaria, Round worm, Butterfly, Earthworm, Octopus, Star fish, Shark, Frog, Wall lizard, Pig.
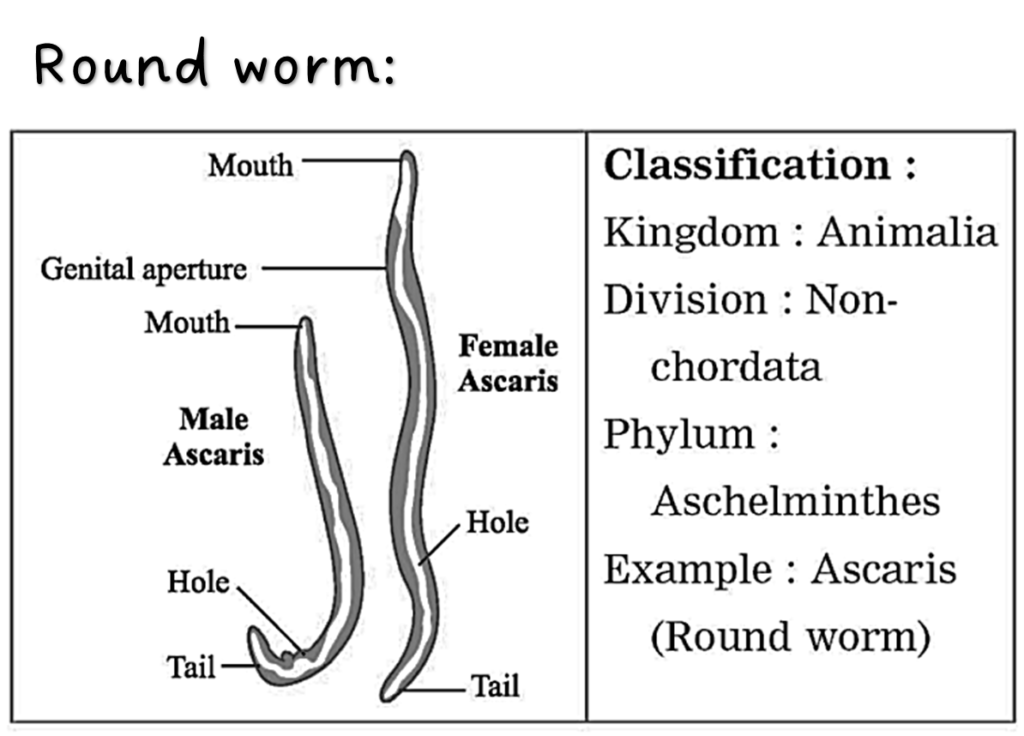
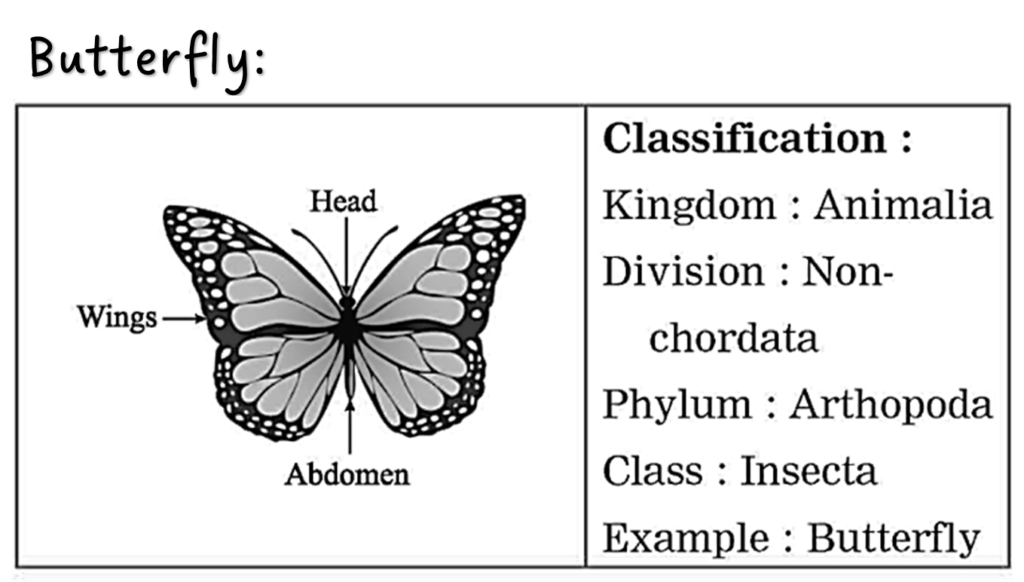


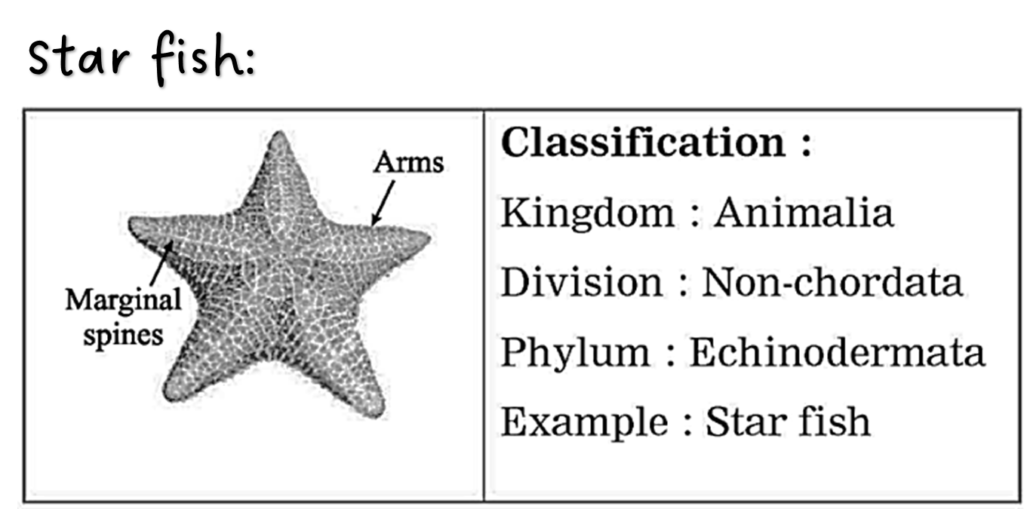
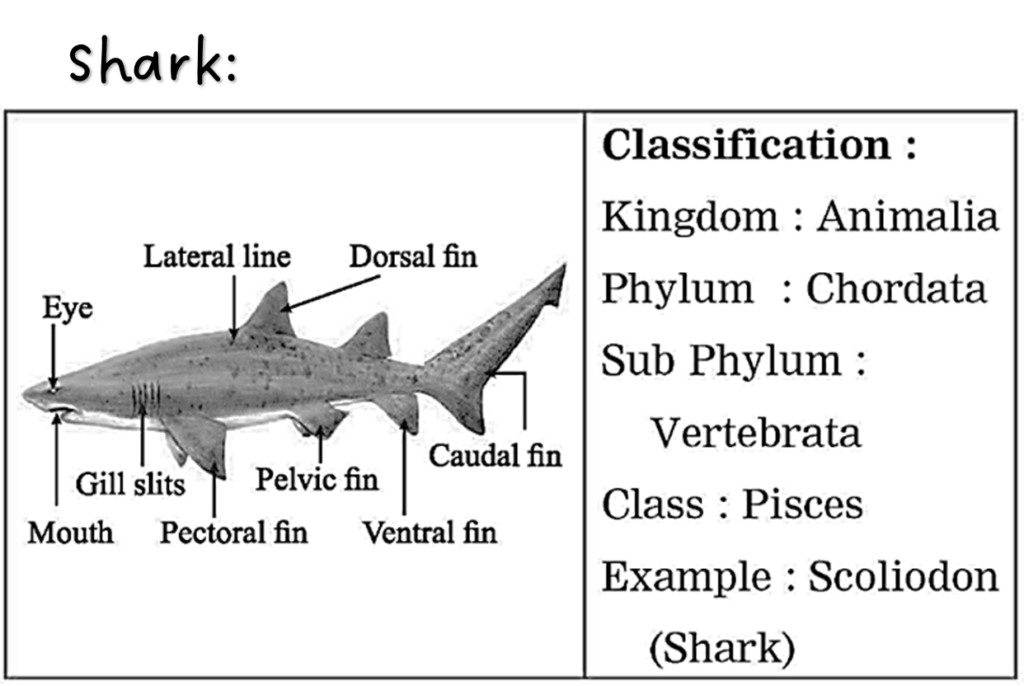

11. Label the following.
Ans.