Choose the correct alternative and write its alphabet against the subquestion number :
(1) ………………….. is a cold blooded animal. (March ’19)
(A) Bat (B) Snake (C) Rabbit (D) Elephant
Ans. (B) Snake
(2) Calcareous spines are present on the body of animal. (July ’19)
(A) fish (B) snail (C) sponge (D) starfish
Ans. (D) starfish
Find the correlation :
(1) Annelida : Earthworm : : Platyhelminthes : …………………… (March ’20)
Ans. Annelida : Earthworm : : Platyhelminthes : Planaria/Liverfluke
Distinguish Between :
Ans. [Students are requested to write in tabular (draw table) form]
Aves:
(1) Aves are totally adapted for the aerial mode of life. (2) Body is spindle shaped. Body is divisible into head, neck and trunk. (3) There are two pairs of limbs. The forelimbs are modified to form wings for flight. Digits have scales and claws. (4) Examples : Crow, Sparrow, Peacock, Parrot, Pigeon, Duck, Penguin, etc.
Mammalia:
(1) Mammals are adapted for terrestrial life. (2) Body is not spindle shaped. It is divisible into head, neck, trunk and tail. There arc two pairs of limbs. They are adapted for walking or running on the ground. (3) Digits have nails or hoofs. Few have claws. (4) Examples : Cat, Dog, Tiger, Lion, Elephant, Human, Kangaroo, Dolphin, Bat, etc.
Identify me :
(1) I am metamerically segmented, blood sucking, ectoparasite. I have suckers. Who am I and to what phylum do I belong to? OR Who am I? I have suckers. I am blood sucking. (July ’19)
Ans. Leech, Phylum Annelida.
(2) I have chitinous exoskeleton, I have three pairs of walking appendages, what phylum do I belong to? (Sept. ’21)
Ans. Phylum : Arthropoda; Class : Insecta.
4. Identify my class/phylum and give one example of it: (March ’19)
(a) I have mammary glands and exoskeleton in the form of hair.
(b) We form the highest number of animals on the planet. We have bilateral symmetry and our exoskeleton is in the form of chitin.
(c) I live in your small intestine, my body is long and thread like and pseudocoelomate.
Ans. (a) Class : Mammalia, Example : Cat, Dog, Man.
(b) Phylum : Arthropoda, Example : Prawn. Crab.
(c) Phylum : Aschelminthes, Example : Ascaris or round worm, Filarial worm.
Identify the class of given animals and write one characteristic of each animal : (July ’19) (5 Marks)
(1) Kangaroo (2) Penguin (3) Crocodile (4) Frog (5) Sea-horse.
Ans. (1) Kangaroo : Class Mammalia. It is a marsupial animal with pouch for development of offspring. Long hind limbs for jumping.
(2) Penguin : Class Aves. It is flightless bird. Body covered with thick feathery coat. Oviparous mode.
(3) Crocodile : Class Reptilia. It can swim in water but cannot respire in water. Body covered with exoskeleton of scaly plates.
(4) Frog : Class Amphibia. Shows aquatic as well as terrestrial mode. Can breathe with lungs and skin.
(5) Sea horse : Class Pisces. Bony fish. Highly modified body structure showing brood pouch for development of offspring gills for respiration, fins for swimming.
State any four benefits of animal classification. (March ’19)
Ans. (1) Studying the different animals becomes easy when they are placed under different groups. (2) The animal evolution becomes easier to follow after studying classification. (3) Relationship of the different animals with each other and with other groups can be understood clearly. (4) Habitat of each animal and its role in nature is understood by classification. (5) Various adaptations are understood by learning classification.
Name the largest phylum in animal kingdom. Write any two characters of that phylum. (3 marks) (Sept. ’21)
Ans. (1) Arthropoda is the largest phylum in animal kingdom. (2) Characteristics of Arthropoda : (a) Eucoelomate, triploblastic bilaterally symmetrical and segmented body. (b) Body covered over by chitinous exoskeleton. Jointed appendages present.
Name the locomotory organ of animal shown in the given figure : (Nov. ’20)

Ans. Tubefeet.
Identify and explain from the given figure different types of symmetry. (Nov. ’20)
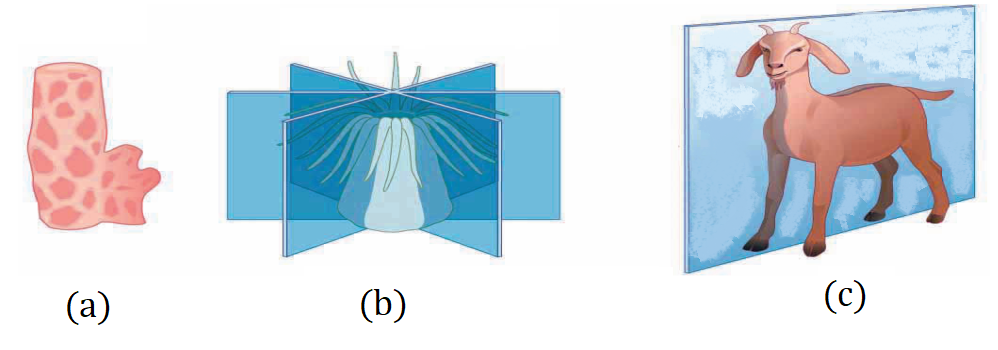
Ans. (a) Asymmetrical body : In asymmetrical body, there is no imaginary axis that can pass through body and divide it into two equal halves, e.g. Amoeba.
(b) Radial symmetry : In this type of body, if imaginary cut passes through central axis, in any plane of body, then it can give two equal halves.
(c) Bilateral symmetry : In such type of symmetry, there is only one imaginary axis that can pass through the body dividing it into two equal halves.
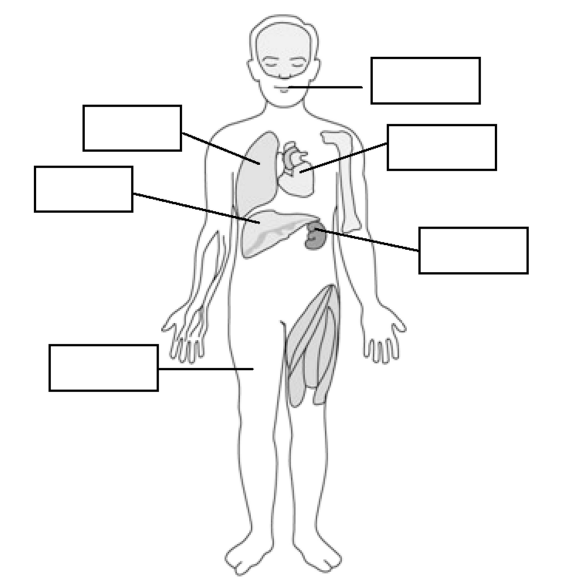
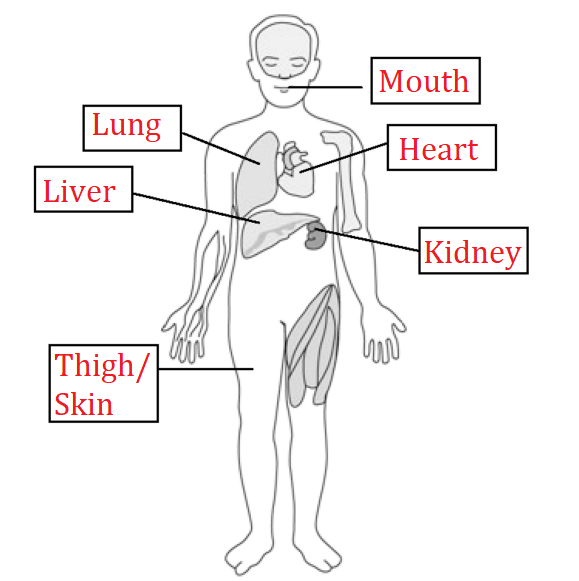
Label the body organization of human which has been shown in the following figure : (March ’20)