Exercises
1. Choose the correct option.
(i) [L1 M 1 T-2 ] is the dimensional formula for
(A) velocity
(B) acceleration
(C) force
(D) work
(ii) The error in the measurement of the sides of a rectangle is 1%. The error in the measurement of its area is
(A) 1 %
(B) 1/2%
(C) 2%
(D) None of the above
(iii) Light year is a unit of
(A) time
(B) mass
(C) distance
(D) luminosity
(iv) Dimensions of kinetic energy are the same as that of
(A) force
(B) acceleration
(C) work
(D) pressure
(v) Which of the following is not a fundamental unit?
(A) cm
(B) kg
(C) centigrade
(D) volt
2. Answer the following questions.
(i)
Ans.
(ii)
Ans.
(iii) Define absolute error, mean absolute error, relative error and percentage error.
Ans.
♦ Absolute error:
The magnitude of the difference between mean value and each individual value is called absolute error in the observations.
♦ Mean absolute error:
The arithmetic mean of all the absolute errors is called mean absolute error in the measurement of the physical quantity.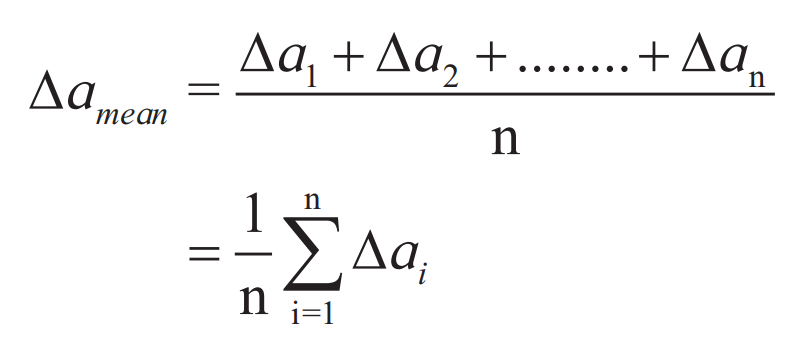
♦ Relative error:
The ratio of mean absolute error to its arithmetic mean value is called relative error.
♦ Percentage error:
When relative error is represented as percentage it is called percentage error.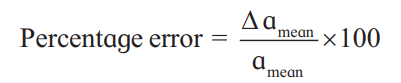
(iv) Describe what is meant by significant figures and order of magnitude.
Ans.
(i) The number of digits in a measurement about which we are certain, plus one additional digit, the first one about which we are not certain is known as significant figures or significant digits. The larger the number of significant figures obtained in a measurement, the greater is the accuracy of the measurement. If one uses the instrument of smaller least count, the number of significant digits increases.
(ii) The magnitude of any physical quantity can be expressed as A×10n where ‘A’ is a number such that 0.5 ≤ A<5 and ‘n’ is an integer called the order of magnitude.
example: radius of Earth = 6400 km = 0.64×107 m. The order of magnitude is 7