Chapter 2. The Electoral Process
Que. 6. Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the sentences.
(1) The election commissioner is appointed by the …………….
(a) President
(b) Prime Minister
(c) Speaker of LokSabha
(d) Vice President
(2) ……………was appointed as the first Chief Election Commissioner of independent India.
(a) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(b) T. N. Sheshan
(c) Sukumar Sen
(d) Neela Satyanarayan
(3) Constituencies are created by ………….… committee of the Election Commission
(a) selection
(b) delimitation
(c) voting
(d) timetable
(4) ……………. was the first voter of India.
(a) Sham Sharan Negi
(b) Sukumar Sen
(c) T. N. Sheshan
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
Que.7. State whether the following statements are true or false. Give reasons for your answers.
(1) The Election Commission lays down the code of conduct during elections.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reasons:
1. To control malpractices during elections and to ensure free and fair elections in India, the Election Commission has laid down the ‘Model Code of Conduct’.
ii. This code is a unique document which explains the rules that are to be followed by the government, political parties and voters before elections and during elections. The government also cannot violate these rules.
(2) Under special circumstances the Election Commission holds re-elections in a particular constituency for a second time.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reasons:
i. This happens if the elected government loses its majority before completing its term in the Parliament or if the parties of the coalition government withdraw their support that results in the loss of majority support for the government. Also, if no alternative government is possible then under such circumstances, Midterm elections are held by the Election Commission before the completion of the term.
ii. Sometimes By-elections are conducted in the constituency, if an elected representative in Lok Sabha, Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) or local self-government resigns or if there is a vacant seat on account of his/her death.
(3) The state government decides as to when and in how many stages the elections would be held in a particular state.
Ans. The above statement is False.
Reasons:
i. In India, Election Commission is central to the process of elections.
ii. It is under the direction and control of Election Commission that the whole process of election right from the declaration of the date of elections to the announcement of results is carried out.
Thus, the above statement is false.
(4) The facility of VVPAT in EVM machines ensures to stop malpractices in elections.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reasons:
i. An expert committee established on 8 October 2010 by election commission decided to add the Voter Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) in EVM machine.
ii. This facility enables voters to easily verify whether the vote casted by them is registered properly or not.
Therefore, VVPAT in EVM machines ends malpractices in election.
Que. 8. (A) Explain the following concepts.
(1) Reorganising the constituencies
Ans.
(i) Lok Sabha consists of 543 members.
(ii) Every member represents one constituency. This means that there are 543 constituencies of Lok Sabha.
(iii) These constituencies are created by the Delimitation Commission of the Election Commission.
(iv) The Delimitation Commission does not succumb to any pressure while restructuring the constituencies.
(2) Journey from the ballot box to EVM machine
Ans.
(i) After independence, the first election was conducted between 1951 and 1952. This was the beginning of the shaping of democracy through electoral reforms.
(ii) Earlier, ballot boxes were used for the purpose of voting.
(iii) It was later, in the decade of 1990s, EVM (Electronic Voting Machine) came to be used. An EVM is a simple electronic device which is used to record votes in place of ballot papers and boxes.
(iv) The voter can choose the option of ‘NOTA’ (None of the above) available on the EVM when he does not want to vote for any candidate.
(v) Disabled people (Divyang) find it easy to vote through EVM.
(vi) Due to EVM, it is possible to declare the results easily and it has also made the process eco-friendly.
(3) Midterm elections
Ans.
(i) Before completion of term, the elections hold by the Election Commission are called midterm election.
(ii) The Election Commission holds midterm elections under following circumstances:
a. If the elected government loses its majority before completing its term in the Parliament.
b. If the parties of the coalition government withdraw their support resulting in the loss of majority support for the government.
c. If no alternative government is possible.
(4) By-elections
Ans.
(i) Sometimes elections are conducted in the constituency by Election Commission under special circumstances as follows:
a. If an elected representative in Lok Sabha, Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) or local self-government resigns. or
b. If there is a vacant seat on account of his/her death.
(ii) Under both the above circumstances, the elections are held for the vacant seat. This is called a by-election.
(B) Complete the activity.
(1) Complete the following picture:
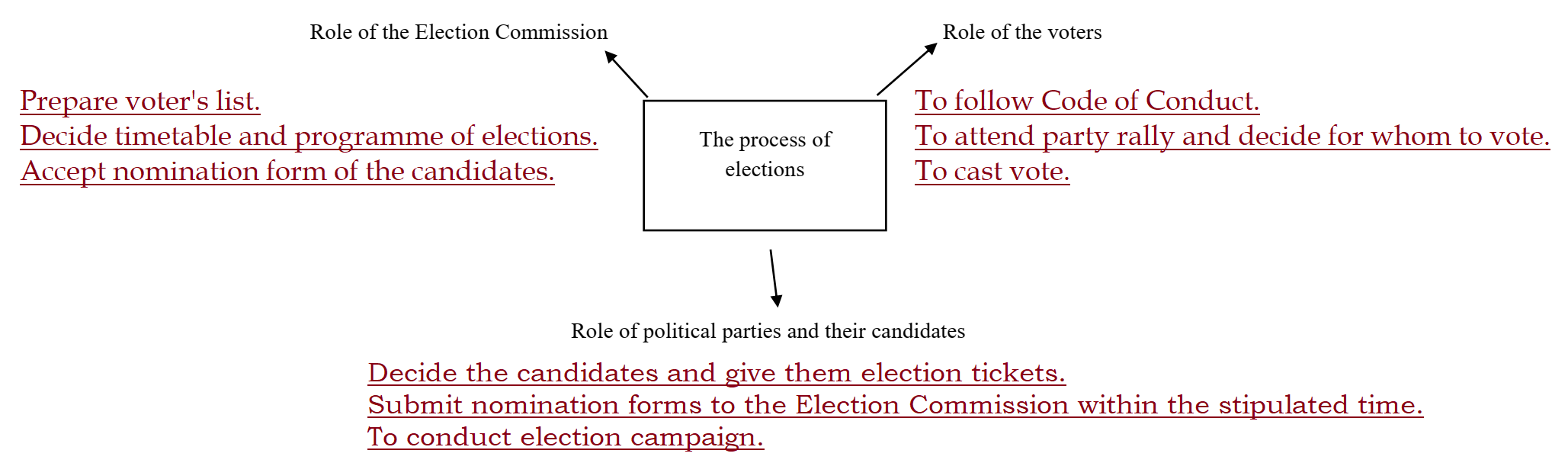
Ans.
(2) Complete the flow-chart:
Ans.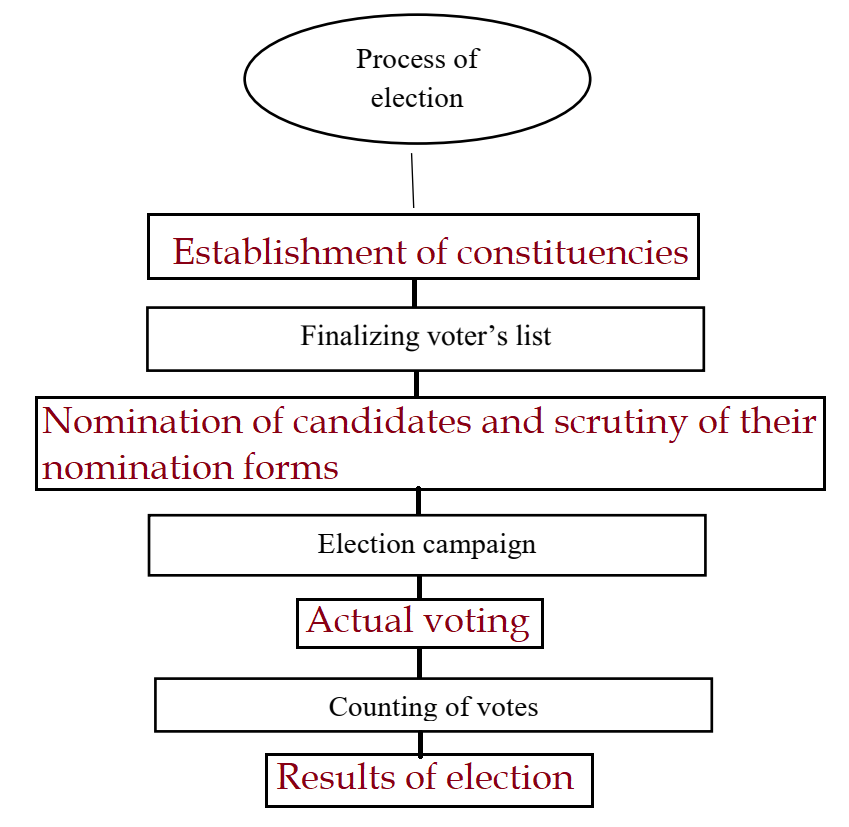
Q.9. Answer in brief.
(1) Explain the functions of the Election Commission.
Ans. The functions of the Election Commission are :
(1) Prepare the voters’ list.
(2) Decide election timetable and the entire process of holding elections.
(3) Scrutinize the applications of the candidates.
(4) Conduct free and fair elections and do all the work related to it.
(5) Give recognition and also derecognize political parties.
(6) Resolve all the disputes and complaints regarding elections.
(2) Write some additional information about the post of the Election Commissioner.
Ans. (1) The Election Commission in India has one Chief Election Commissioner and two other Commissioners.
(2) All the commissioners are appointed by the President.
(3) The Chief Election Commissioner of India is usually a member of the Indian Civil Services or Indian Administrative Services.
(4) The responsibility of conducting free and fair elections to the Parliament and State Legislatures lies with the Election Commissioner.
(5) In order to safeguard the independence of the Election Commissioner, he cannot be easily removed from the post for any political reasons.
(3) Explain the meaning of the Code of Conduct.
Ans. (1) After the announcement of elections till the declaration of results, the Election Commission enforces the Code of Conduct.
(2) It explains the rules to be followed by the government, political parties candidates and voters before and during elections.
(3) Code of conduct is adopted to control malpractices during elections. It is to ensures free and fair elections.
(4) State the challenges in conducting free and fair elections.
Ans. The following challenges are faced by the Election Commission to conduct free and fair elections :
(1) Managing the large geographical landscape and huge electoral population.
(2) To stop misuse of money and muscle power during elections.
(3) Barring candidates with criminal background from contesting elections.
(4) To conduct elections successful in politically criminalised environment.
(5) Conducting elections in spite of increasing instances of violence and making them a success.