Chapter 3. Political Parties
(1) When people come together and participate in electoral process, to acquire political power, such organizations are called……………
(a) Government
(b) Society
(c) Political parties
(d) Social Organizations
(2) National Conference is a party in ……………… State.
(a) Orissa
(b) Assam
(c) Bihar
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
(3) Justice Party a non-Brahmin movement was transformed into …………… Political Party.
(a) Assam Gan Parishad
(b) Shiv Sena
(c) Dravid Munnetra Kazhagam
(d) Jammu and Kashmir National Conference
(4) To achieve power is the main objective of …………….
(a) Social organizations
(b) Political parties
(c) Cultural organizations
(d) Students’ organizations
Que.7. State whether the following statements are true or false. Give reasons for your answers.
(1) Political parties act as a link between government and people.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reason:
(i) The political parties convey the demands and complaints of the people to the government.
(ii) Information about various government policies and schemes are conveyed to the people by the political parties.
(iii) People’s reaction to the policies and their expectations are conveyed to the government too by the parties.
In this way, political parties act as a link between government and the people.
(2) Political parties are social organizations.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reasons:
(i) As social organisations actively take the initiative in resolving social problems, political parties also, in the similar manner, strive to resolve the problems of people. It has some
proposed policies and programmes for promoting collective good.
(ii) However, there is a difference in the goals and style of working of the political parties and other organisations.
Hence, we can say that political parties are social organisations.
(3) Coalition politics leads to instability.
Ans. The above statement is False.
Reasons:
(i) As no single party got majority after the elections held in 1989, coalition government came to power at the centre and the states.
(ii) Parties had to set aside their policies and programmes and concentrate on a common agenda to run the government.
(iii) Though the experiment failed in 1977, in the following years, the National Democratic Alliance and the Democratic Front government ruled at the centre and state level effectively.
(4) Shiromani Akali Dal is a national party.
Ans. The above statement is False.
Reasons:
(1) The number of seats secured in Parliament and Legislative Assembly or percentage of votes secured.
(2) Shiromani Akali Dal does not meet the criteria listed above.
(3) As its influence is limited to the state of Punjab and not in any other state.
The Election Commission has given recognition to it as regional party.
Que. 8. (A) Explain the following concepts.
(1) Regionalism
Ans.
(i) India is a vast country with great physical diversity. People belonging to different region have their own language, culture and traditions.
(ii) Along with these, we find diversity in literature, education, history and movements.
(iii) Each one feels an affinity towards their language, traditions and region. This affinity gradually develops into the identity consciousness and gives rise to excessive regional pride.
(iv) People start giving preference only to their language and region.
This is known as Regionalism.
(2) National Parties
Ans.
(i) National party is a political party which satisfies either of the following two conditions :
(a) It secures minimum 6% of the valid votes in four or more states in the earlier Lok Sabha or State Assembly elections and minimum 4 members should be elected in the Loksabha from any state or states in the earlier elections OR
(b) The candidates of a party should be elected from minimum 2% constituencies out of the total Loksabha constituencies and the candidates should be elected from atleast 3 states.
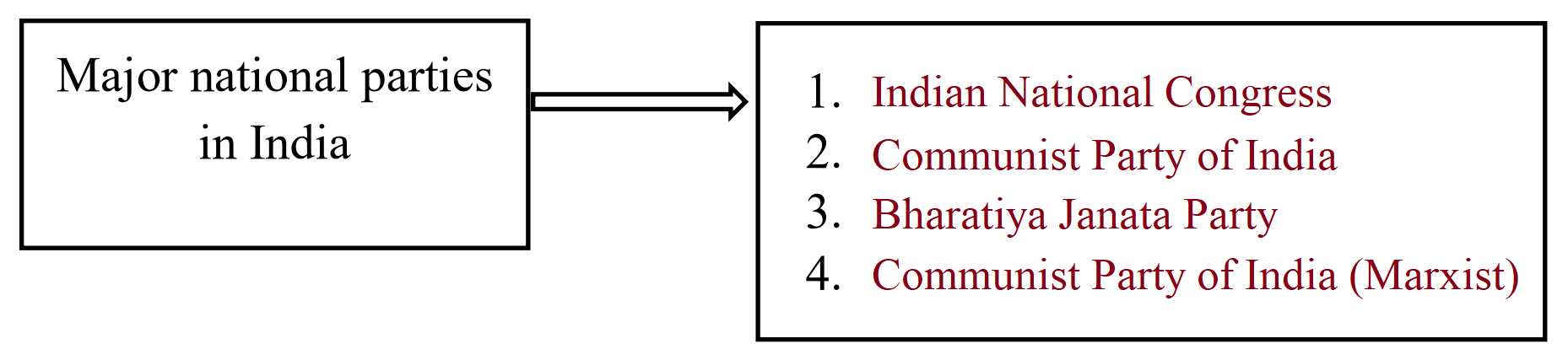
(ii) Some of the national parties in India are Indian National Congress, Communist Party of India, Bharatiya Janata Party, Communist Party of India (Marxist), Bahujan Samaj Party, Nationalist Congress Party and All India Trinamool Congress Party.
(3) Regional Parties
Ans.
(i) The groups who have a proud feeling about the different identity of their region and who compete to capture power to bring about regional development are ‘Regional Parties’.
(ii) The influence of such parties are limited to their region. They give importance to regional problems.
(iii) Development of one’s own region is the prime objective of these parties. Sometimes they demand for independent state or autonomy.
(iv) They influence the national politics because of their dominance in the region. They have passed through various phases, from separatism to autonomy and then merged with mainstream national politics.
(B) Complete the activity.
(1) Complete the time-line (political parties and their establishment years):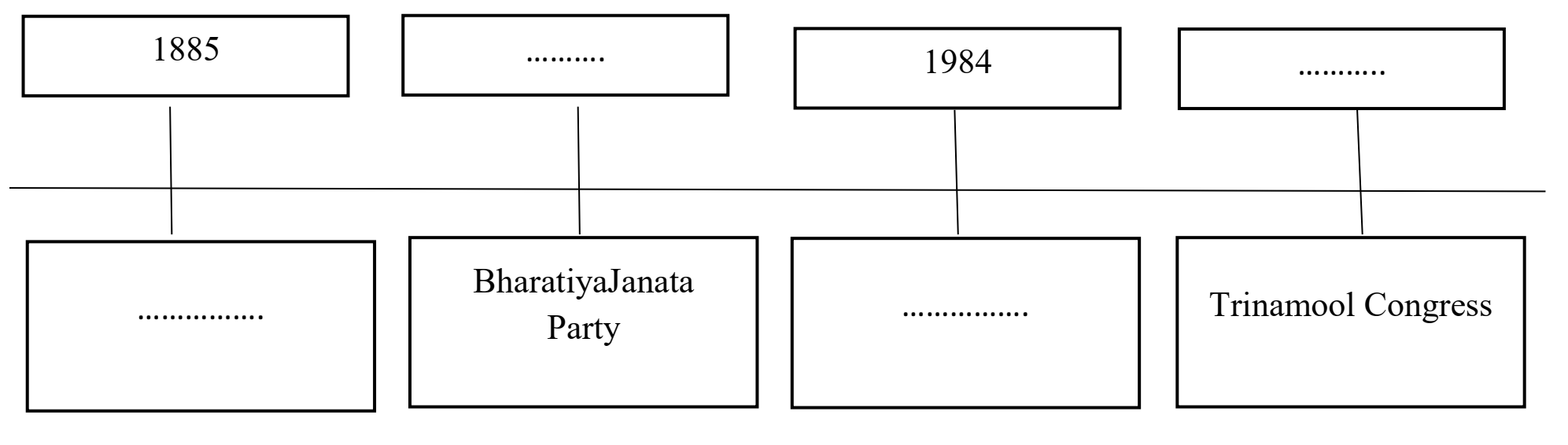 Ans.
Ans.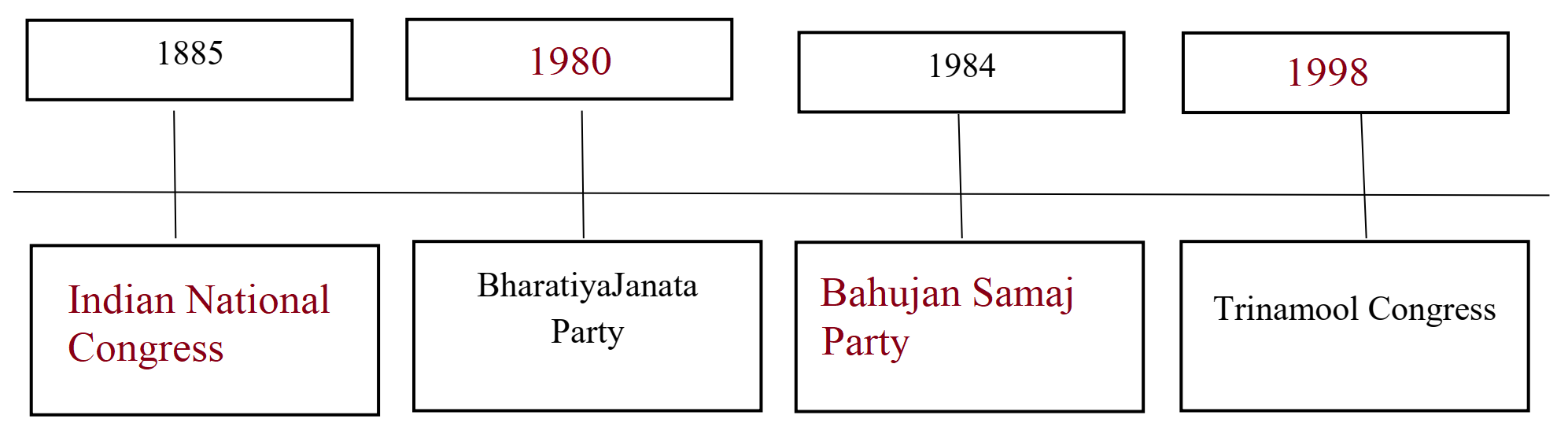
(2) Complete the following chart: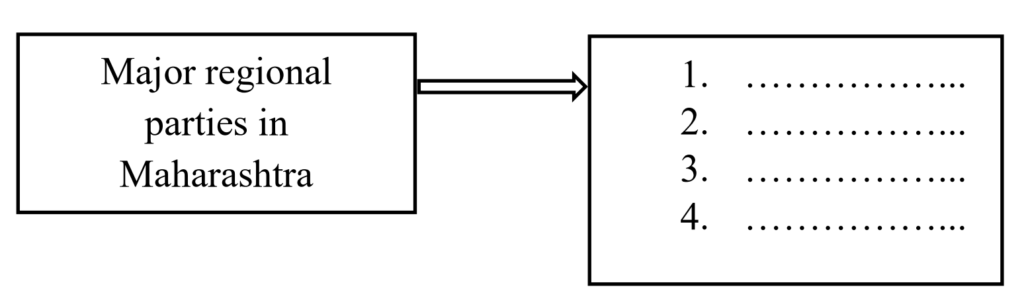
Ans.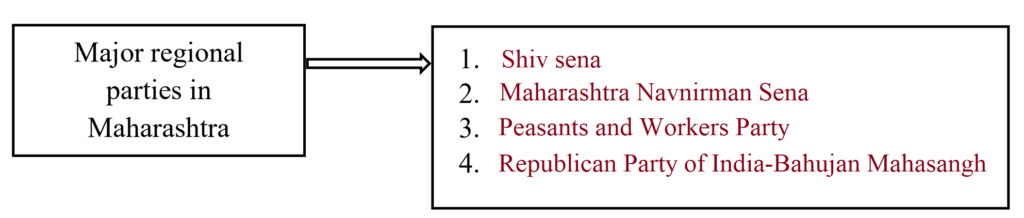
(3) Complete the following chart:
Ans.
Que. 9. Answer in brief
(1) What are the major characteristics of political parties?
Ans. The main characteristics of political parties are as follows :
(i) Political parties aim at securing power by contesting elections.
(ii) Every political party has some ideology.
(iii) Every party has an agenda. It is based on the party’s ideology.
(iv) The party that gets majority seats in election forms the government and the one that does not secure the majority act as opposition parties.
(v) Political parties are a link between the people and the government and work to gain the support of the people.
(2) What changes have been taken place in the nature of political parties in India?
Ans. The following changes were seen in the party system in India :
(i) Indian National Congress was the only dominant party in states and at the centre after independence.
(ii) All other parties came together and formed coalition in 1977 and defeated the Congress. For the first time in history the two party system got importance over one party system.
(iii) One party system came to an end after the 1989 elections.
(iv) Regional parties got importance and coalition government was formed at the centre and in the states.
(3) State the difference between an ideology and an agenda.
Ans.
