(1) Choose correct option
(A) The study of structure and arrangement of tissue is called as ___
(a) anatomy
(b) histology
(c) microbiology
(d) morphology
(B) ____ is a gland which is both exocrine and endocrine.
(a) Sebaceous
(b) Mammary
(c) Pancreas
(d) Pituitary
(C) ____ cell junction is mediated by integrin.
(a) Gap
(b) Hemidesmosomes
(c) Desmosomes
(d) Adherens
(D) The protein found in cartilage is _______.
(a) ossein
(b) haemoglobin
(c) chondrin
(d) renin
(E) Find the odd one out
(a) Thyroid gland
(b) Pituitary gland
(c) Adrenal gland
(d) Salivary gland
(2) Answer the following questions
(A) Identify and name the type of tissues in the following:
(a) Inner lining of the intestine
(b) Heart wall
(c) Skin
(d) Nerve cord
(e) Inner lining of the buccal cavity
Ans:
(a) Epithelial tissue (Columnar epithelium)
(b)Cardiac muscles (Muscular tissue)
(c) Epithelial tissue (Stratified epithelium)
(d) Nervous tissue
(B) Why do animals in cold regions have a layer of fat below their skin?
Ans:
(a)In adipose tissues, fats are stored in the form of droplets.
(b) The adipose tissue acts as good insulator and helps retain heat in the body. This helps in survival of animals in the colder regions.
Hence, animals in cold regions have a layer o f fat below their skin.
(C) What enables the ear pinna to be folded and twisted while the nose tip can’t be twisted?
Ans:
(a) The ear pinna (outer ear) is made up of a thin plate of elastic cartilage and is connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles. This elastic cartilage gives support and maintains the shape of pinna.
(b) The nose tip is made up of elastic cartilage. However, several bones and cartilage make up the bony-cartilaginous framework of the nose.
Hence, even though the tip of the nose is made up of elastic cartilage, it cannot be twisted like the ear pinna due to presence of bony-cartilaginous framework.
(D) Sharad touched a hot plate by mistake and took away his hand quickly. Can you recognize the tissue and its type responsible for it?
Ans:
(a) Nervous and muscular tissues are responsible for this action
(b) Nervous tissue recognizes the stimuli whereas muscular tissue allows responding to the stimuli.
(E) Priya got injured in an accident and hurt her long bone and later on she was also diagnosed with anaemia. What could be the probable reason?
Ans:
(a) The centre of long bones (diaphysis) contains bone marrow, which is a site of production of blood cells (red blood cells).
(b) Any severe injury to the bone marrow can affect rate of haematopoiesis (formation of blood cells).
(c) A low count of erythrocytes (red blood cells) is characterised as anaemia.
Hence, an injury to Priya’s long bone might have resulted in anaemia.
(F) Supriya stepped out into the bright street from a cinema theatre. In response, her eye pupil shrunk. Identify the muscle responsible for the same.
Ans: Smooth muscles (Involuntary muscles) are responsible for shrinking of eye pupil.
(3) Answer the following questions.
(A) What is cell junction? Describe different types of cell junctions.
Ans:
(i) Cell junctions: The epithelial cells are connected to each other laterally as well as to the basement membrane by junctional complexes called cell junctions.
(ii) The different types of cell junctions are as follows:
(a) Gap Junctions (GJs): These are intercellular connections that allow the passage of ions and small molecules between cells as well as exchange of chemical messages between cells.
(b) Adherens Junctions (AJs): They are involved in various signalling pathways and transcriptional regulations.
(c) Desmosomes (Ds): They provide mechanical strength to epithelial tissue, cardiac muscles and meninges.
(d) Hemidesmosomes (HDs): They allow the cells to strongly adhere to the underlying basement membrane. These junctions help maintain tissue homeostasis by signalling.
(e) Tight junctions (TJs): These junctions maintain cell polarity, prevent lateral diffusion of proteins and ions.
(B) With help of neat labelled diagram, describe the structure of areolar connective tissue.
Ans: Areolar tissue is a loose connective tissue found under the skin, between muscles, bones, around organs, blood vessels and peritoneum. It is composed of fibres and cells.
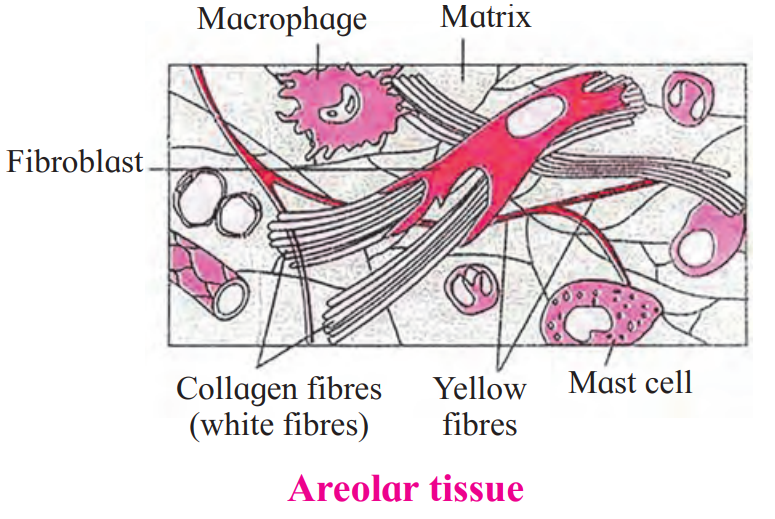
(i) The matrix of areolar tissues contains two types of fibres i.e. white fibres and yellow fibres.
(a) White fibres: They are made up of collagen and give tensile strength to the tissue.
(b) Yellow fibres: They are made up of elastin and are elastic in nature.
(ii) The four different types of cells present in this tissue are as follows:
(a) Fibroblast: Large flat cells having branching processes. They produce fibres as well as
polysaccharides that form the ground substance or matrix of the tissue.
(b) Mast cells: Oval cells that secrete heparin and histamine.
(c) Macrophages: Amoeboid, phagocytic cells.
(d) Adipocytes (Fat cells): These cells store fat and have eccentric nucleus.
(C) Describe the structure of multipolar neuron.
Ans: A neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous tissue. A neuron is made up of cyton or cell body and cytoplasmic extensions or processes.
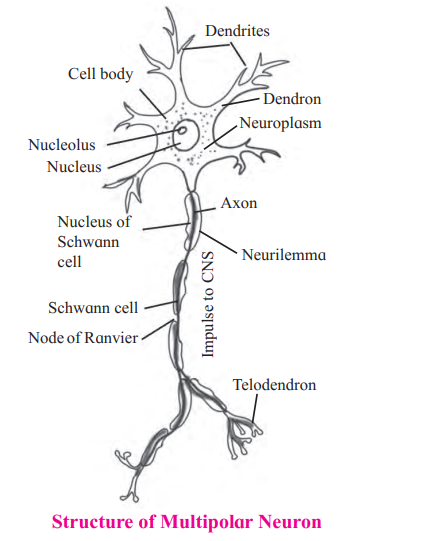
(a) Cyton:
The cyton or cell body contains granular cytoplasm called neuroplasm and a centrally placed nucleus
The neuroplasm contains mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, RER and Nissl’s granules.
(b) Cytoplasmic extensions or processes:
(i) Dendron: They are short, unbranched processes. The fine branches of a dendron are called dendrites. Dendrites carry an impulse towards the cyton.
(ii) Axon: It is a single, elongated and cylindrical process.
The axon is bound by the axolemma. The protoplasm or axoplasm contains large number of mitochondria and neurofibrils. The axon is enclosed in a fatty sheath called the myelin sheath and the outer covering of the myelin sheath is the neurilemma. Both the myelin sheath and the neurilemma are parts of the Schwann cell. The myelin sheath is absent at intervals along the axon at the Node of Ranvier. The fine branching structure at the end of the axon (terminal arborization) is called telodendron.
It is star shaped and gives out more than two processes. There is only one axon and remaining arc dendrons. Axon initiates from a funnel shaped area called axon-hillock.
(D) Distinguish between smooth muscles and skeletal muscles.
Ans :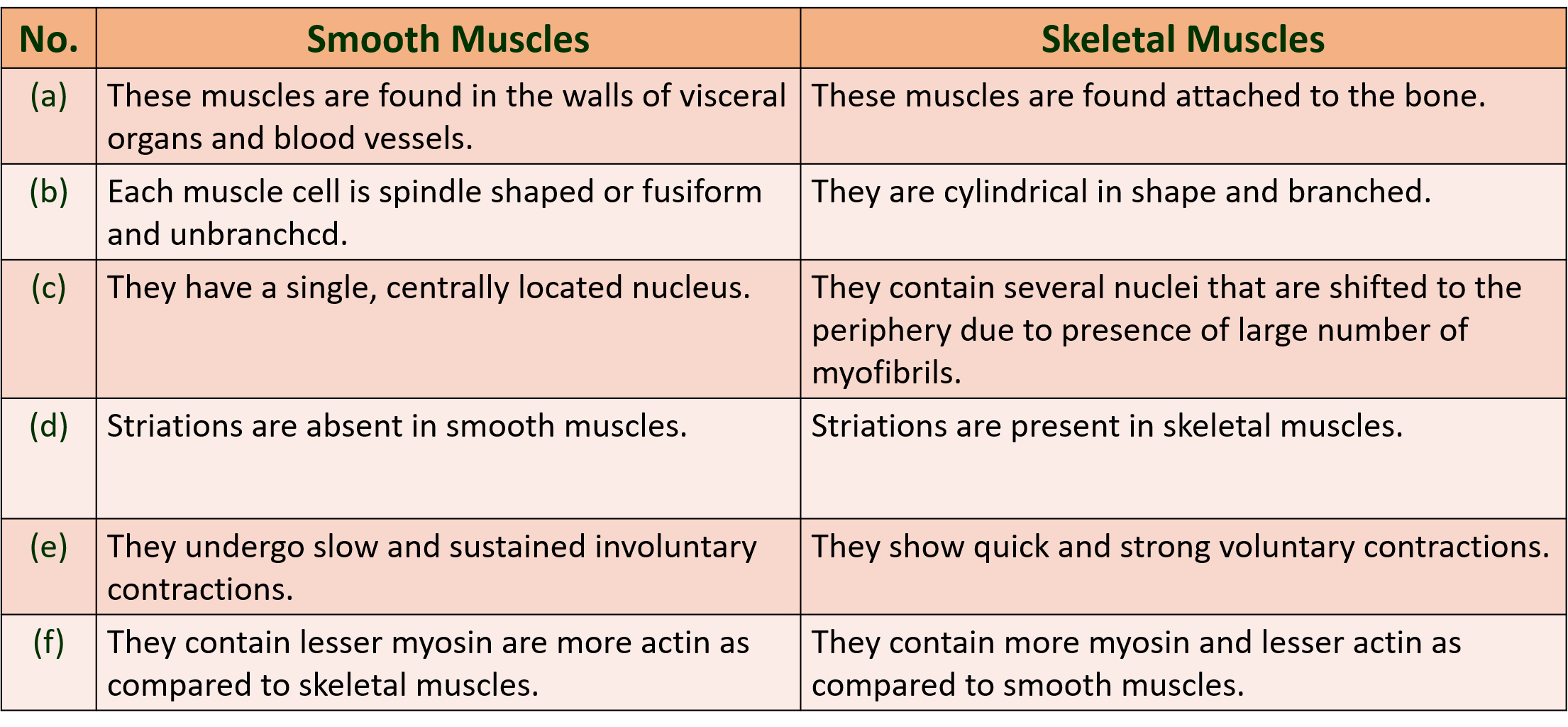
(4) Complete the following table
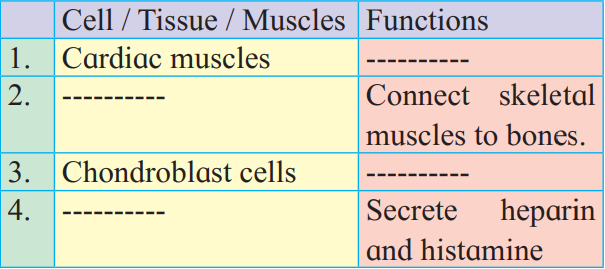
Ans: 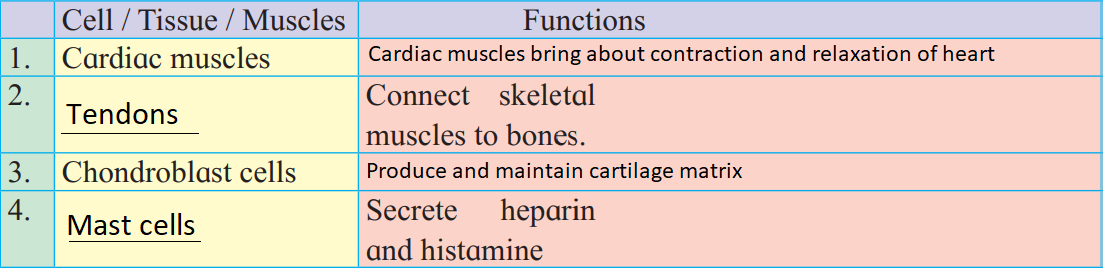
(5) Match the following.
‘A’ Group ‘B’ Group
(1) Muscle (a) Perichondrium
(2) Bone (b) Sarcolemma
(3) Nerve cell (c) Periosteum
(4) Cartilage (d) Neurilemma
Ans : (i-b), (ii-c), (iii-d), (iv-a)