1. Choose correct option
A. Which of the following shows single stranded RNA and lacks protein coat?
a. Bacteriophage
b. Plant virus
c. Viroid
d. Animal virus
B. Causative agent of red tide is _____________.
a. Dinoflagellate
b. Euglenoid
c. Chrysophyte
d. Lichen
C. Select odd one out for Heterotrophic bacteria.
a. Nitrogen fixing bacteria
b. Lactobacilli
c. Methanogens
d. Cyanobacteria
D. Paramoecium : Ciliated Protist Plasmodium : ____________
a. Amoeboid protozoan
b. Ciliophora
c. Flagellate protozoan
d. Sporozoan
2. Answer the following
A. What are the salient features of monera?
Ans. Salient features of Kingdom Monera:
(1) Size: The organisms included in this kingdom are microscopic, unicellular and prokaryotic.
(2) Occurrence: These are omnipresent. They are found in all types of environment which are not generally inhabited by other living beings.
(3) Nucleus: These organisms do not have well defined nucleus. DNA exists as a simple double stranded circular single chromosome called as nucleoid. Apart from the nucleoid they often show presence of
extrachromosomal DNA which is small circular called plasmids.
(4) Cell wall: Cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan (also called murein) which is a polymer of sugars and amino acids.
(5) Membrane bound cell organelles: Membrane bound cell organelles like mitochondria, chloroplast, endoplasmic reticulum are absent. Ribosomes are present, which are smaller in size (70S) than in eukaryotic cells.
(6) Nutrition: Majority are heterotrophic, parasitic or saprophytic in nutrition. Few are autotrophic that can be either photoautotrophs or chemoautotrophs.
(7) Reproduction: The mode of reproduction is asexual or with the help of binary fission or budding. Very rarely, sexual reproduction occurs by conjugation method.
(8) Examples: Archaebacteria: e.g. Methanobacillus, Thiobacillus, etc. Eubacteria: e.g. Chlorobium, Chromatium, and Cyanobacteria e.g. Nostoc, Azotobacter, etc.
B. What will be the shape of bacillus and coccus type of bacteria?
Ans. The shape of bacillus type of bacteria is rod-shaped and coccus is spherical.
C. Why is binomial nomenclature important?
Ans. Binomial nomenclature is important because:
(1) The binomials are simple, meaningful and precise.
(2) They are standard since they do not change from place to place.
(3) These names avoid confusion and uncertainty created by local or vernacular names.
(4) The organisms are known by the same name throughout the world.
(5) The binomials are easy to understand and remember.
(6) It indicates phylogeny (evolutionary history) of organisms.
(7) It helps to understand inter-relationship between organisms.
3. Write short notes
A. Useful and harmful bacteria.
Ans:
(1) Useful bacteria:
Most of the bacteria act as a decomposer. They breakdown large molecules in simple molecules or minerals.
Examples of some useful bacteria:
Lactobacillus’. It helps in curdling of milk.
Azotobacter. It helps to fix nitrogen for plants.
Streptomyces: It is used in antibiotic production such as streptomycin.
Methanogens: These are used for production of methane (biogas) gas from dung.
Pseudomonas spp. and Alcanovorax borkumensis: These bacteria have the ability to destroy the pyridines
and other chemicals. Hence, used to clear the oil spills.
(2) Harmful bacteria:
This includes disease causing bacteria. They cause various diseases like typhoid, cholera, tuberculosis, tetanus, etc.
Examples of some harmful bacteria:
Salmonella typhi: It is a causative organism of typhoid.
Vibrio cholerae: It causes cholera.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis: It causes tuberculosis.
Clostridium tetani: It causes tetanus.
Clostridium spp.: It causes food poisoning.
Many forms of mycoplasma are pathogenic.
Agrobacterium , Erwinia, etc are the pathogenic bacteria causing plant diseases.
Animals and pets also suffer from bacterial infections caused by Brucella, Pastrurella, etc.
B. Five Kingdom system
Ans. Five kingdom system of classification was proposed by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. This system shows the phylogenetic relationship between the organisms.
The five kingdoms are: i. Kingdom Monera ii. Kingdom Protista iii. Kingdom Plantae iv. Kingdom Fungi v. Kingdom Animalia
C. Useful Fungi
Ans. Economic importance/Usefulness of fungi are as follows:
(1) Role of fungi in medicine:
a. Antibiotic penicillin is obtained from Penicillium.
b. Drugs like cyclosporine, immunosuppressant drugs, precursors of steroid hormones, etc are isolated
from fungi.
(2) Role of fungi in industries:
a. Yeast is used in bread making. It causes dough to rise and make the bread light and spongy. It is also
used in breweries or wine making industries. Sugars present in grapes are fermented by using yeast.
This results in production of alcohol which is used for making wine.
b. Lichen is a symbiotic association of algae and fungi are used in preparation of litmus paper which is
used as acid-base indicator.
(3) Role of fungi in food:
a. Fungi like mushrooms are consumed as a food. These are rich source of protein.
b. Fungi genus Penicillium helps in ripening of cheese.
(4) Role of fungi as biocontrol agents:
a. Fungi help to control growth of weeds.
b. Pathogenic fungi like Fusarium sp., Phytophthorapalmivora, Altemaria crassa, etc act as mycoherbicides.
4. Complete tree diagram in detail
Ans.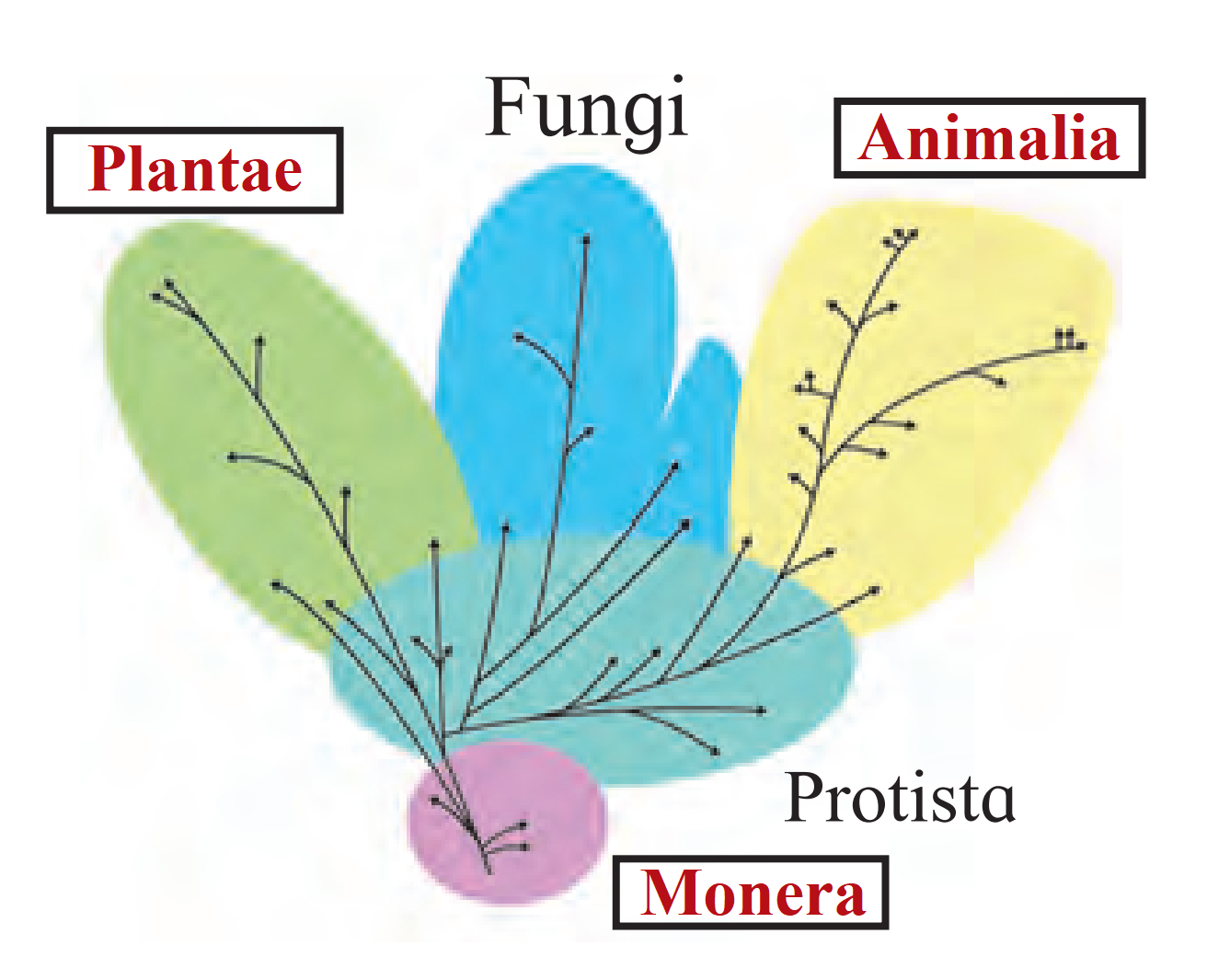
5. Draw neat labelled diagrams
A. Paramoecium
Ans.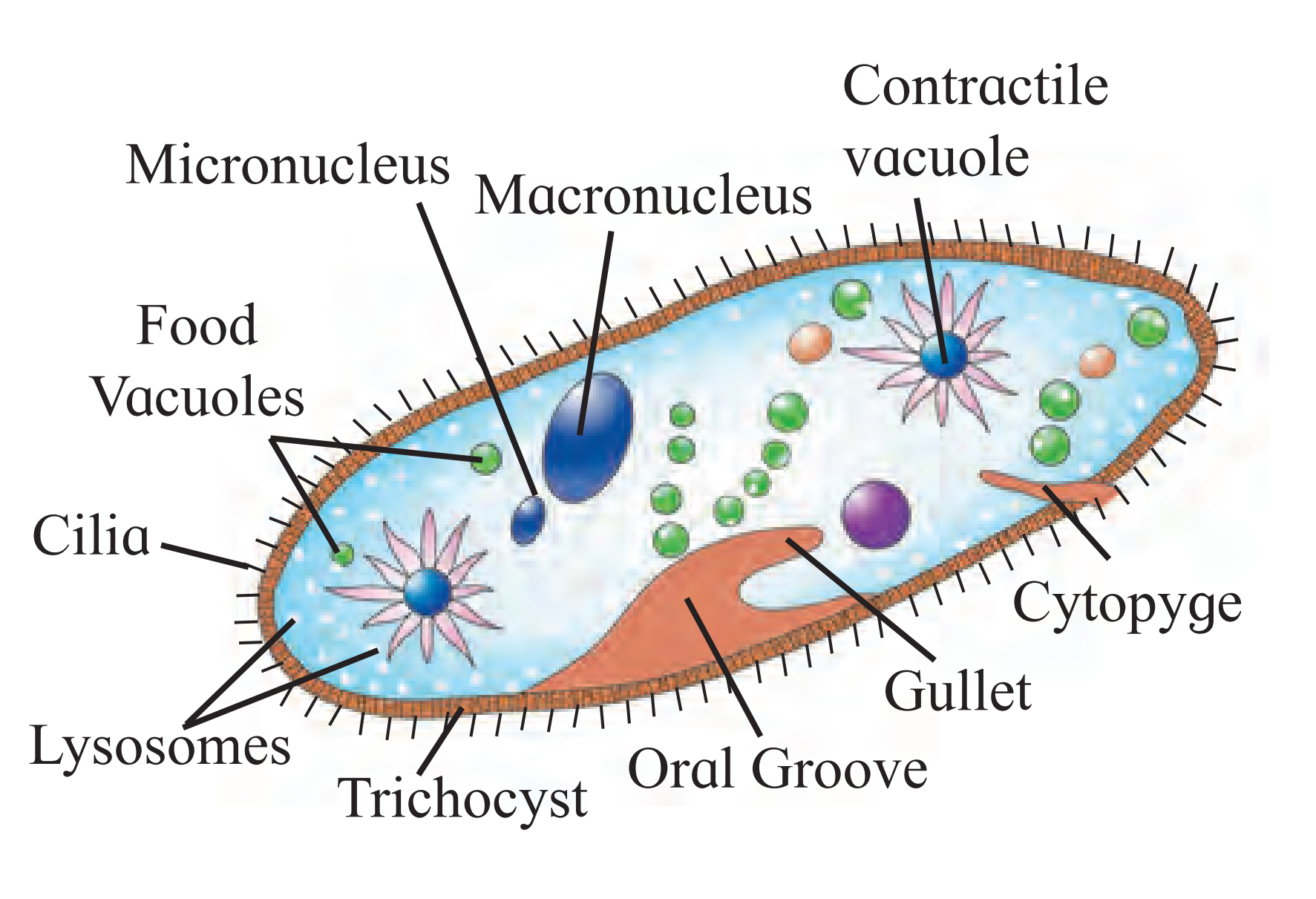
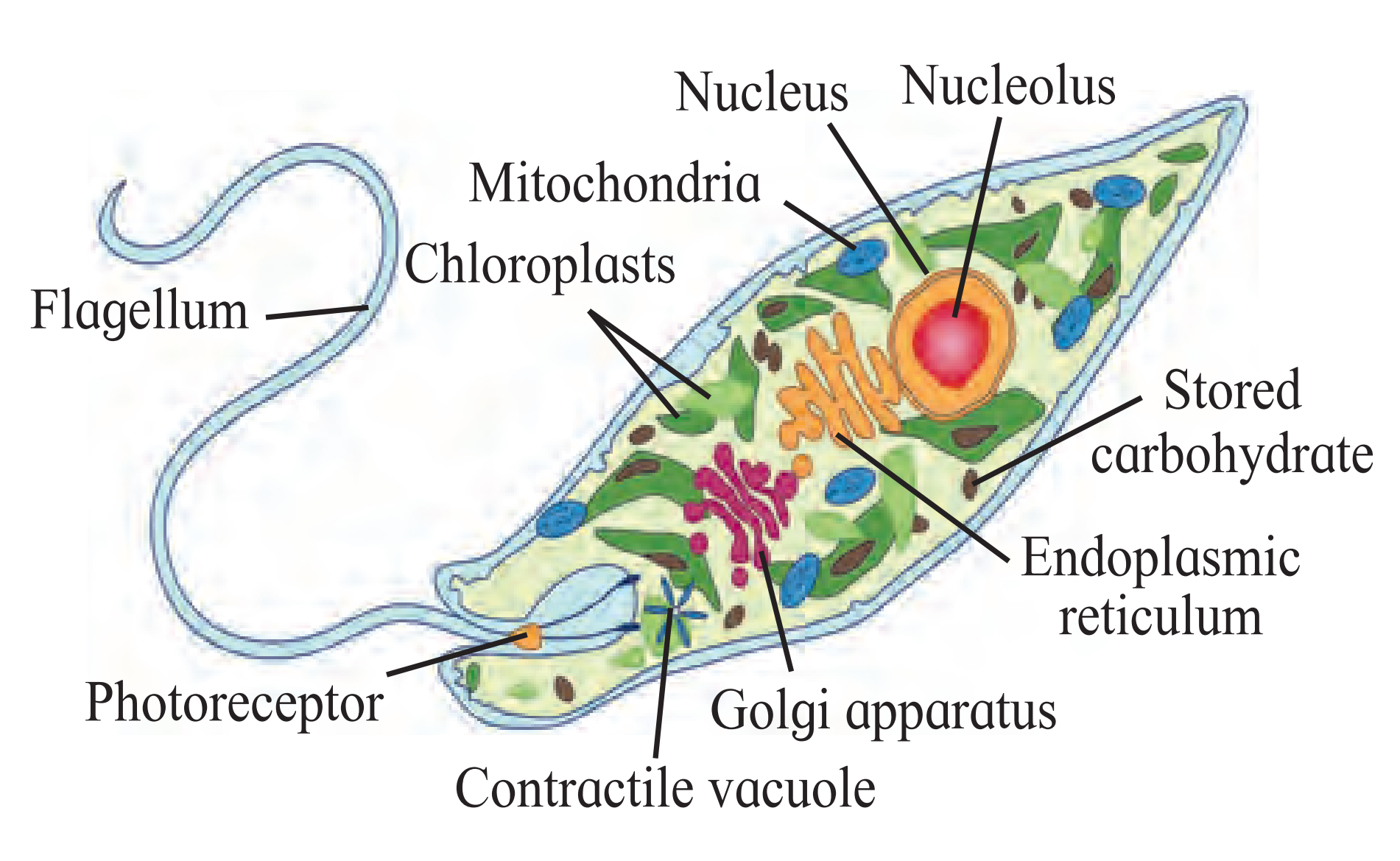
B. Euglena
Ans.
C. TMV
Ans.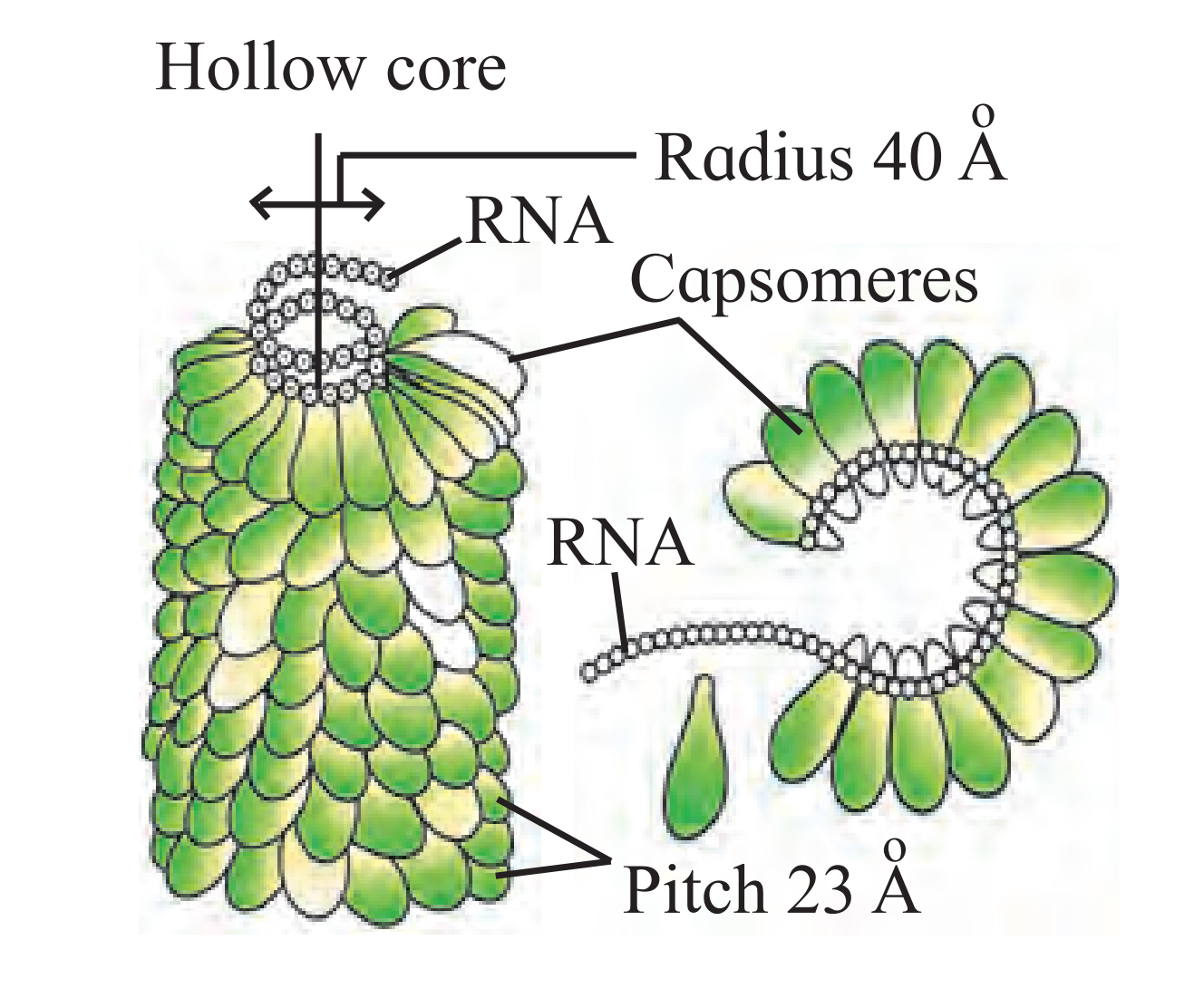
6. Complete chart and explain in your word.
Ans.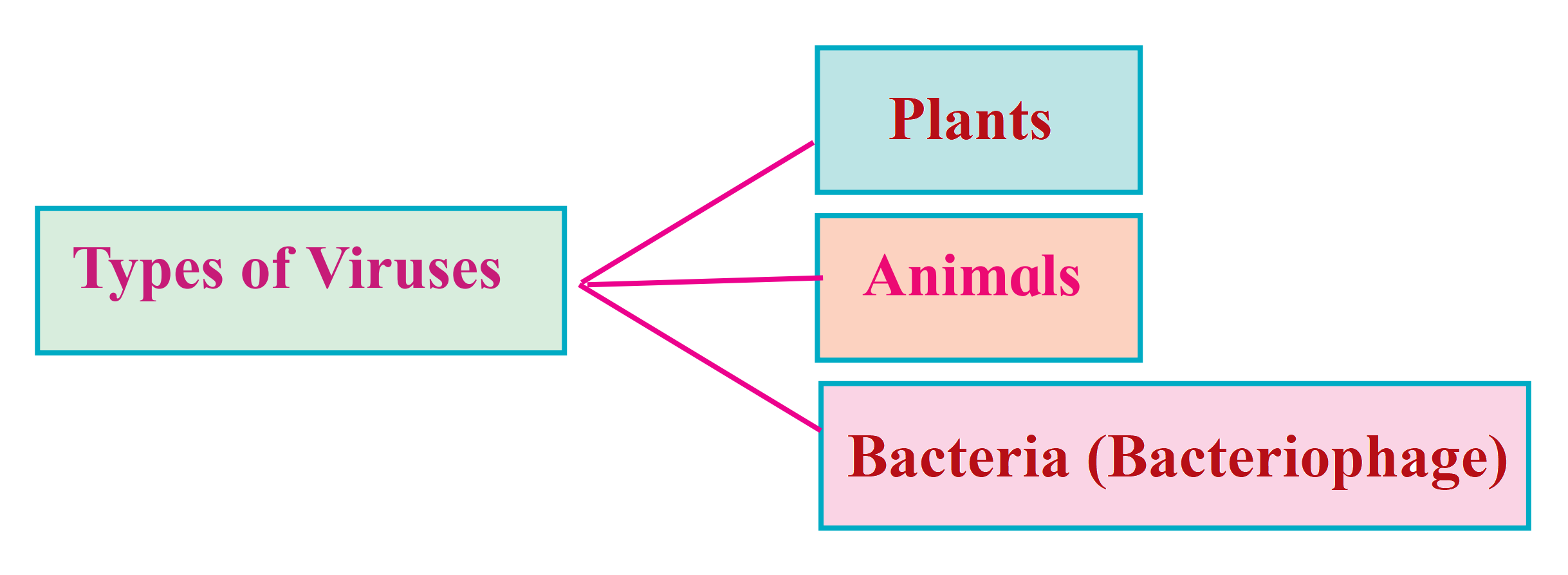
Depending upon the host, viruses are classified into three types as:
(1) Plant vims (2) Animal vims (3) Bacterial vims (Bacteriophage)
(1) Plant virus:
a. Generally, they are rod shaped or cylindrical with helical symmetry.
b. Majority of plant viruses have RNA as their genetic material. (Exception: Cauliflower Mosaic Vims
has double stranded DNA as genetic material)
c. Plant vimses cause disease in plants, e.g. Tobacco Mosaic Vims (TMV).
(2) Animal virus:
a. Generally, they are polyhedral in shape with radial symmetry.
b. They have either DNA or RNA as genetic material.
c. It causes disease to majority of animals including human beings, e.g. Influenza vims.
(3) Bacteriophage:
a. They have tadpole-like shape.
b. They infect bacteria and hence are called as bacteriophage.
c. Bacteriophages were discovered by Twort.
d. Bacteriophages have double stranded DNA as the genetic material.
e. Its body consists of head, collar and tail.
7. Identify the following diagrams, label them and write detail information in your words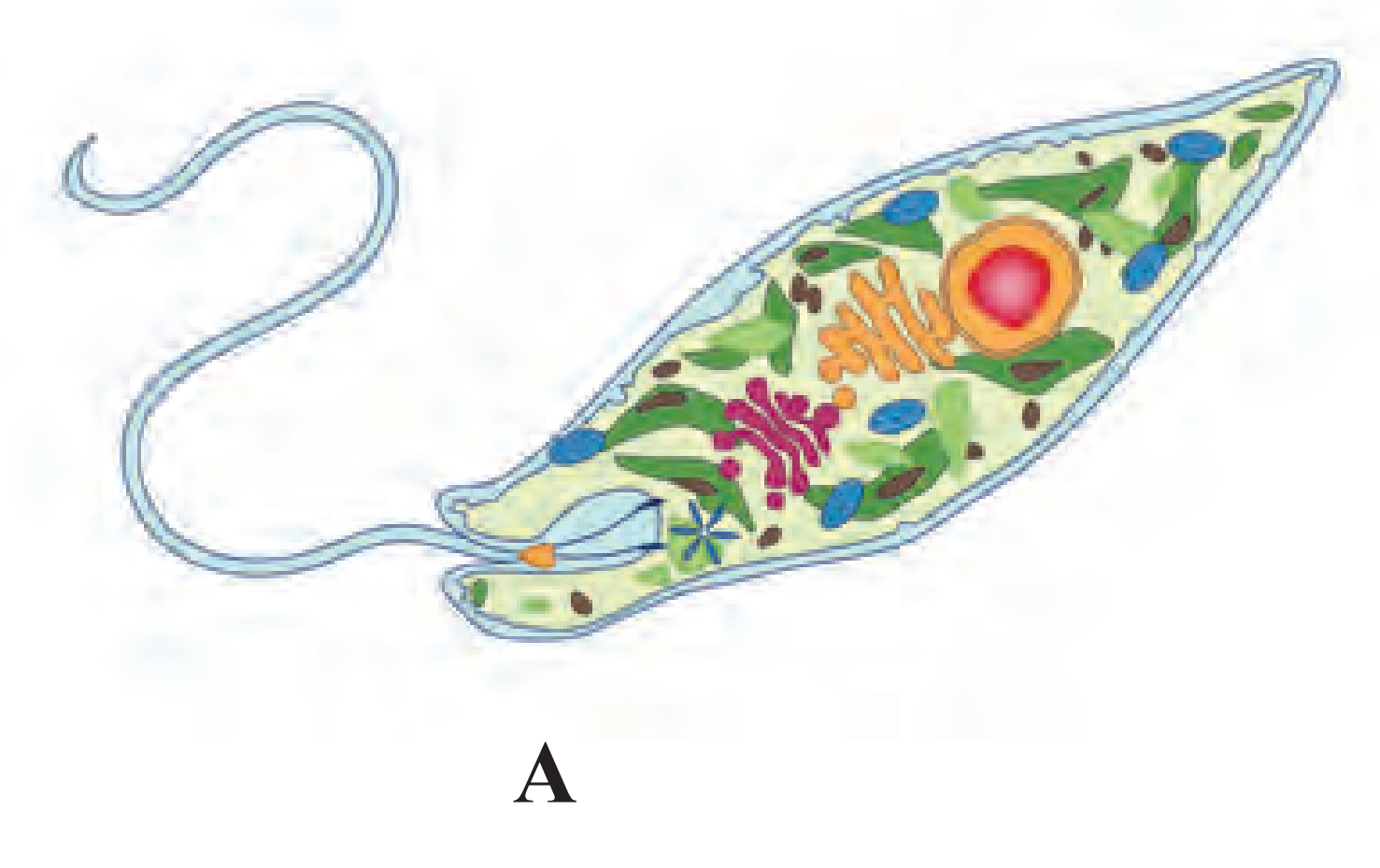
Ans.
(1) The given organism Is Euglena.
(2) It is flagellated Protista. It belongs to the group Euglenoids.
(3) Euglenoids are heterotrophlc flagellates, but also show autotrophic mode.
(4) It has two flagella one is short and the other is long.
(5) It can perform photosynthesis in the presence of light due to the presence of photoreceptors and photosynthetic pigments.
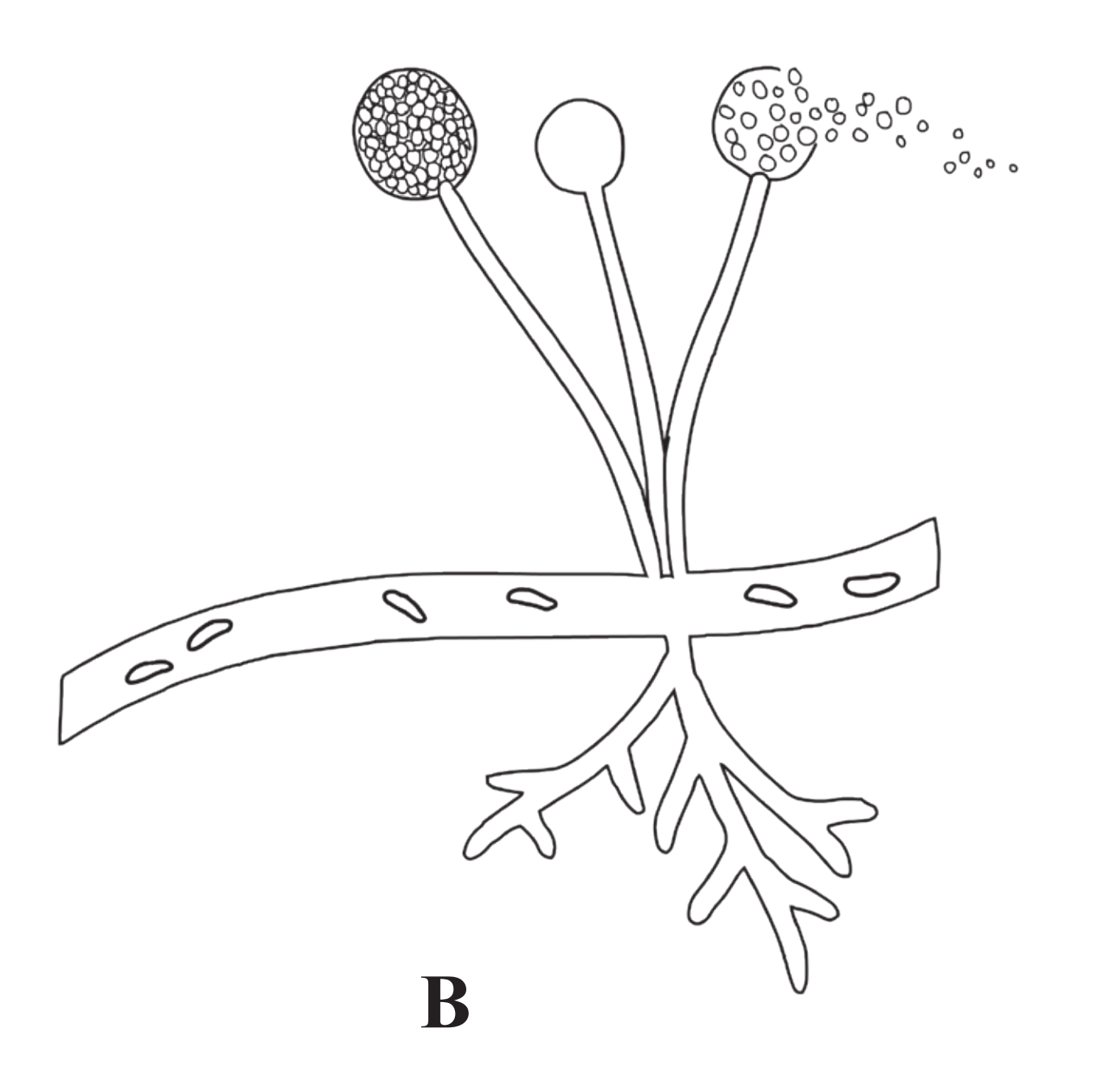
Ans.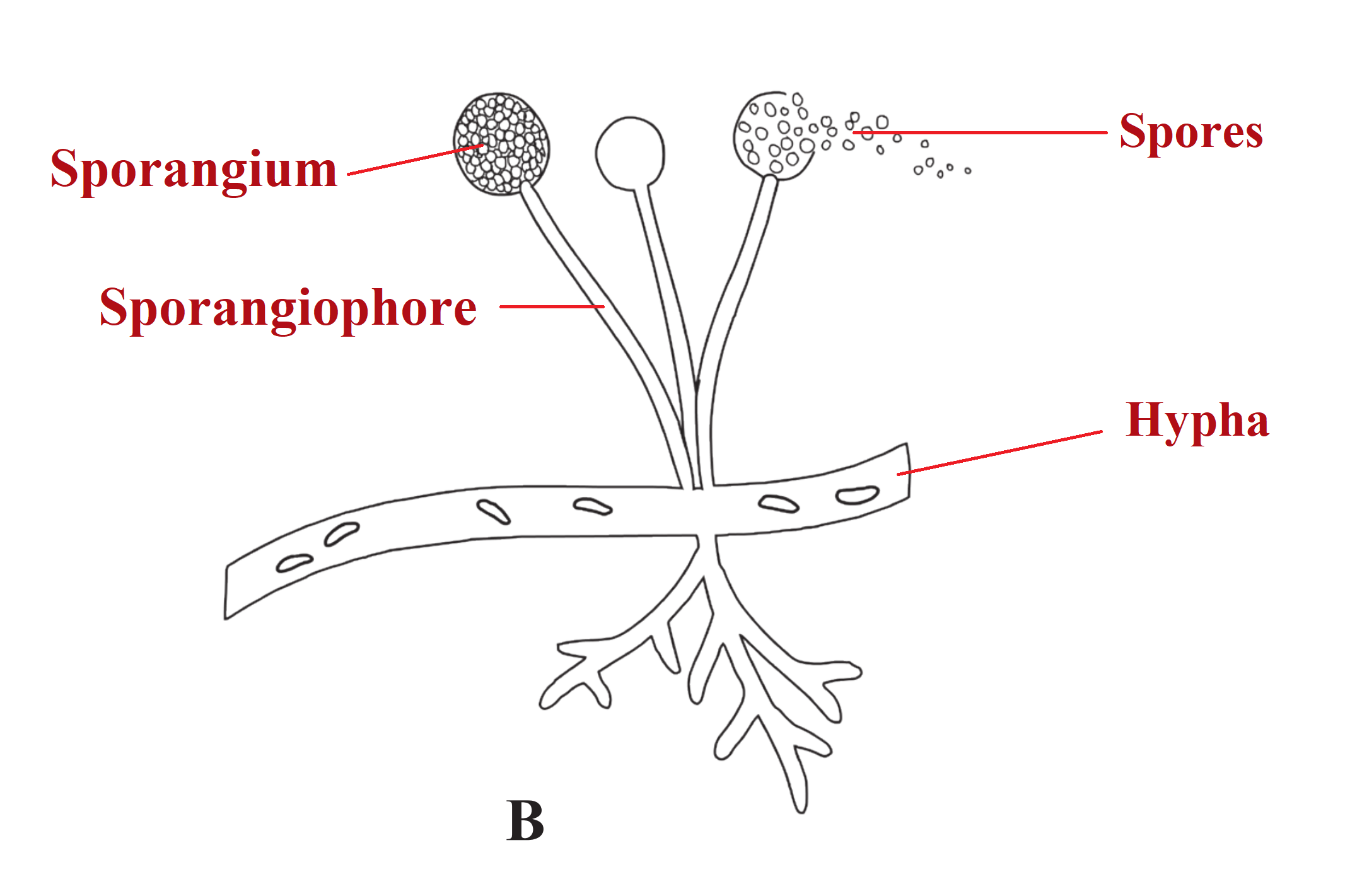
(1) The given diagram is of Mucor, which belongs to Kingdom Fungi and class Phycomycetes.
(2) They are decomposers and hence grow in damp, moist habitats on decaying organic matter.
(3) The body consists of hyphae which spread horizontally.
(4) On the hyphae sporangiophore are seen which bear sporangium at their tips.
(5) They liberate spores, which help in asexual reproduction.
Ans.
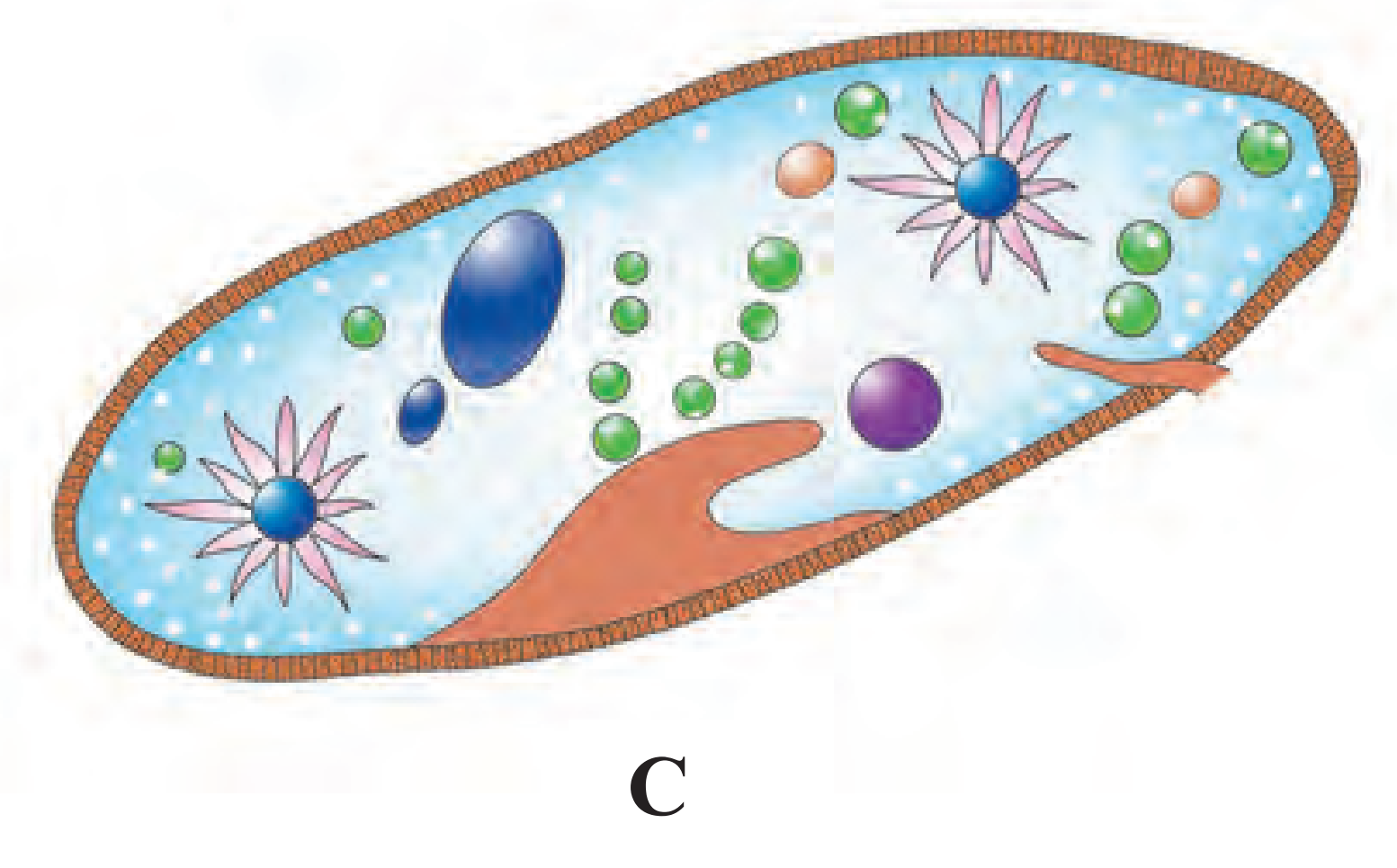
(1) The organism shown is Paramoecium.
(2) It belongs to Kingdom Protista. It is animal like Protista. Cilia are used for locomotion thus also called ciliate protozoan.
(3) There is gullet that opens on the cell surface.
(4) Two nuclei are present, one is bigger called macronucleus and other is smaller called micronucleus.
(5) Large contractile vacuoles are seen which help in osmoregulation.
Ans.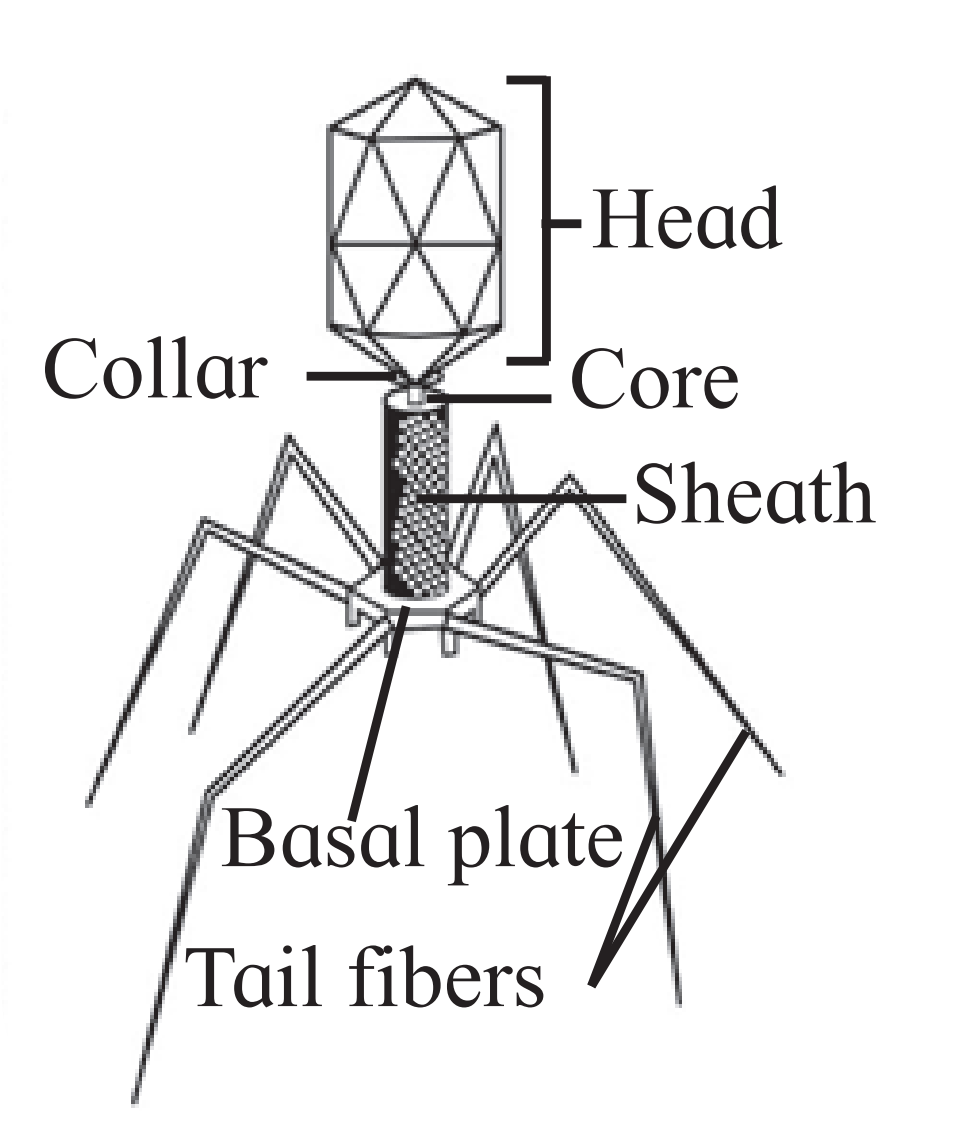
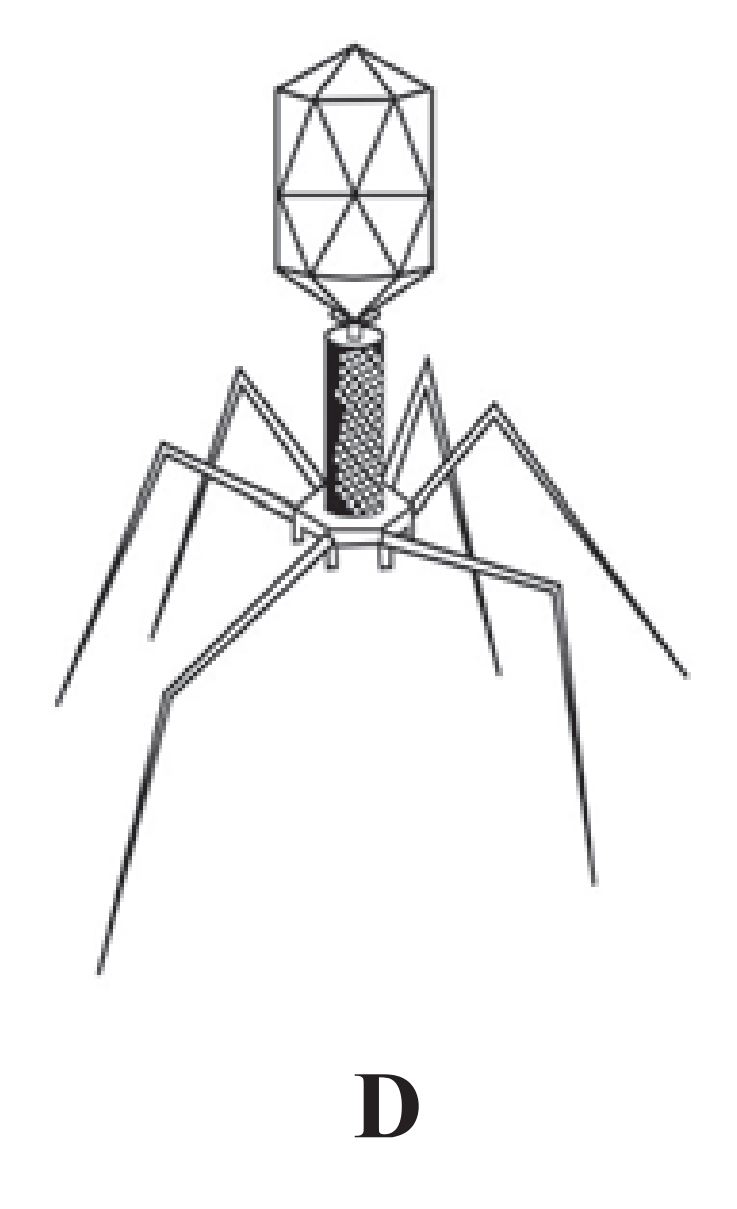
(1) This is bacteriophage. It is an acellular organism not included in any kingdom.
(2) This is a virus that infects the bacterial cells.
(3) They have a core of genetic material which is surrounded by capsid which is a protein coat.
(4) The structure consists of head, core and basal plate possessing tail fibres.
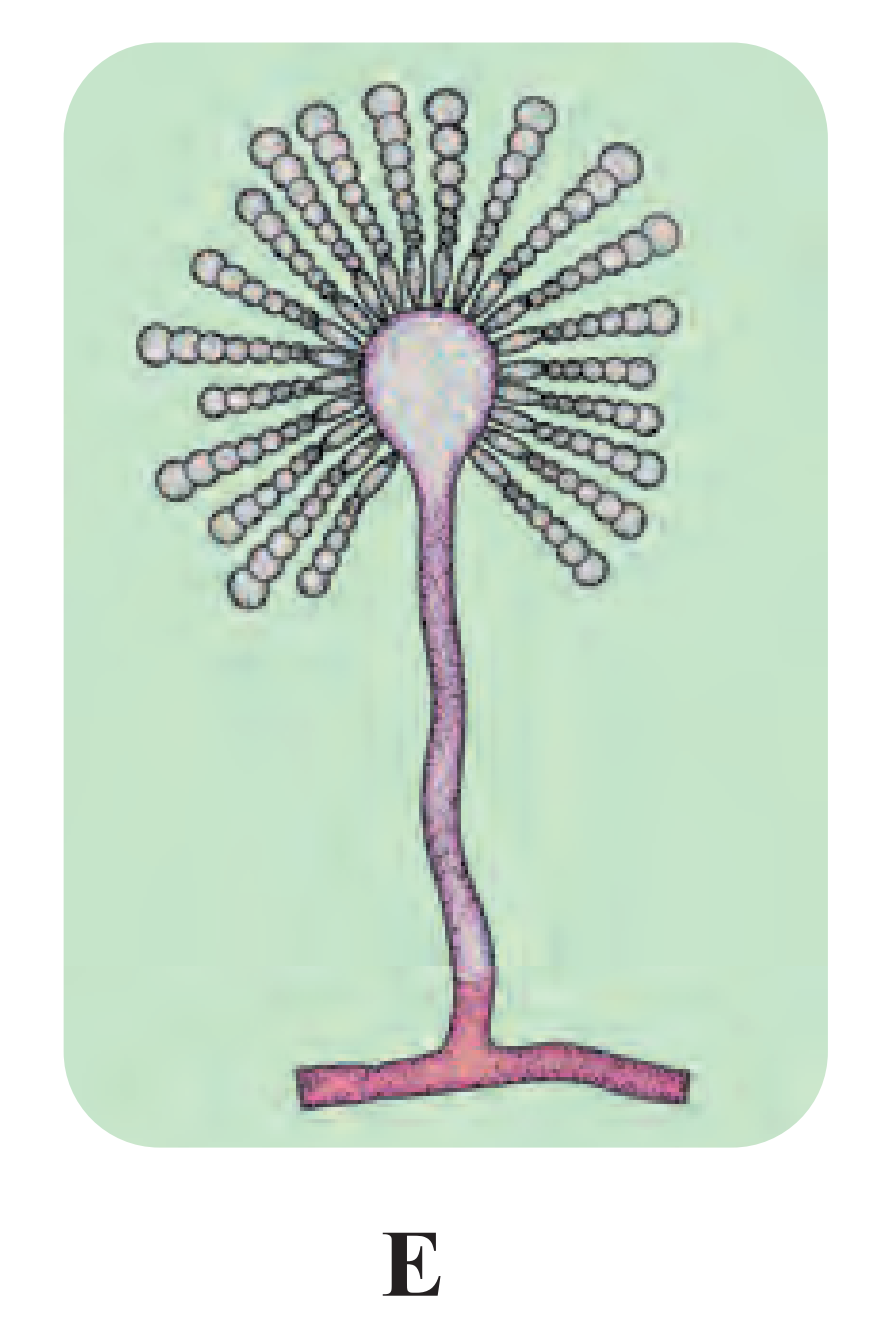
Ans.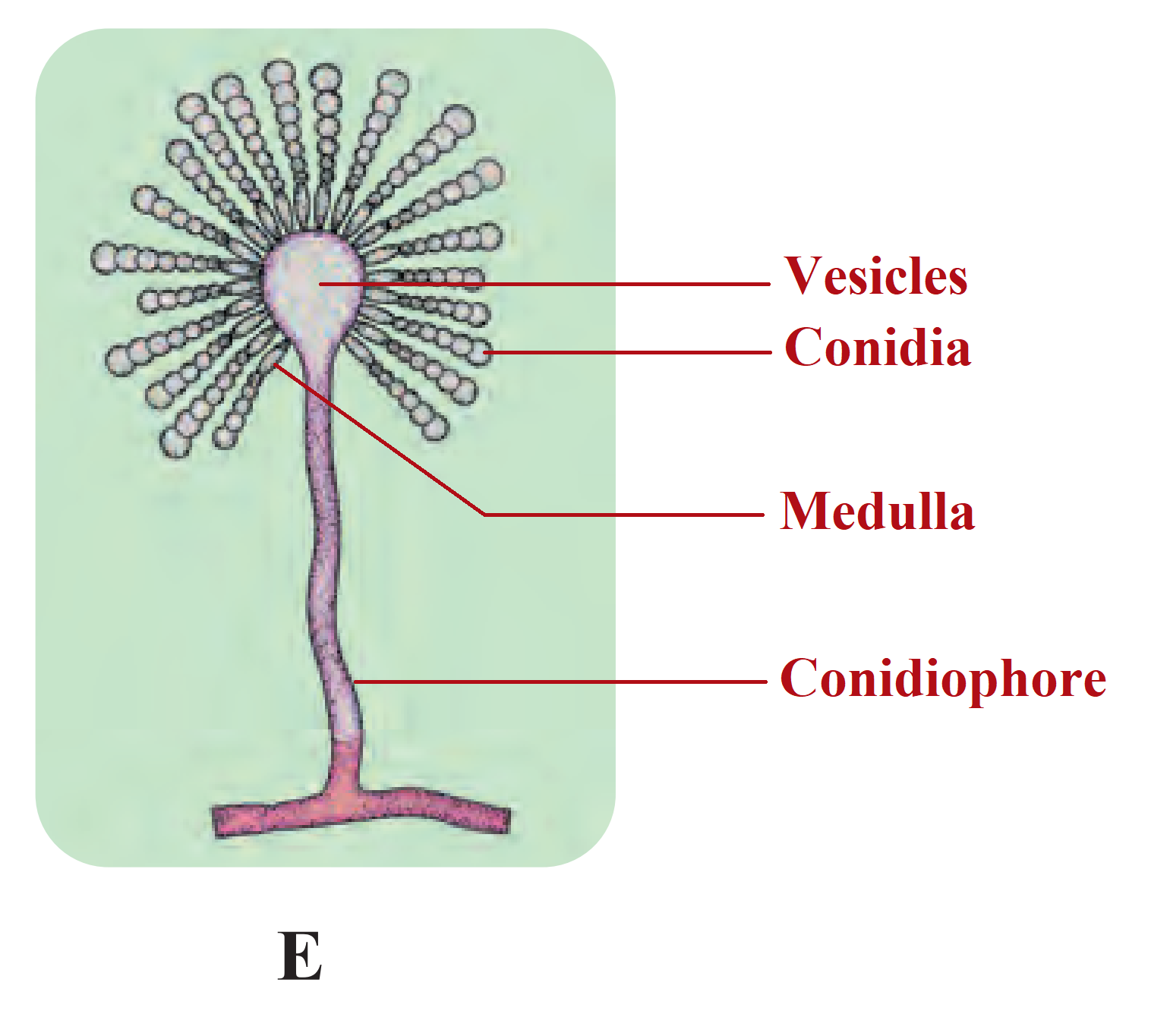
(1) The given diagram is that of Aspergillus.
(2) Aspergillus belongs to kingdom Fungi and class Ascomycetes.
(3) Commonly it is known as mould. It grows well in the damp and moist regions.
(4) A majority have been shown to be terricolous, which means that they are largely found in soil/land.
(5) They have become increasingly important in human health, agriculture as well as in biological sciences among others.
(6) They are also called conidial fungi because they reproduce asexually through the production.
 Ans.
Ans.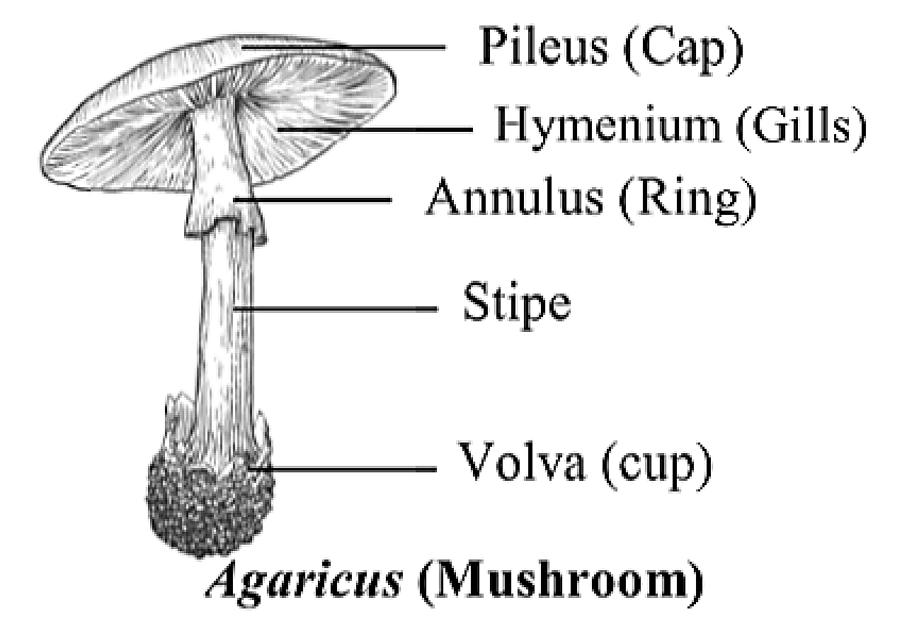
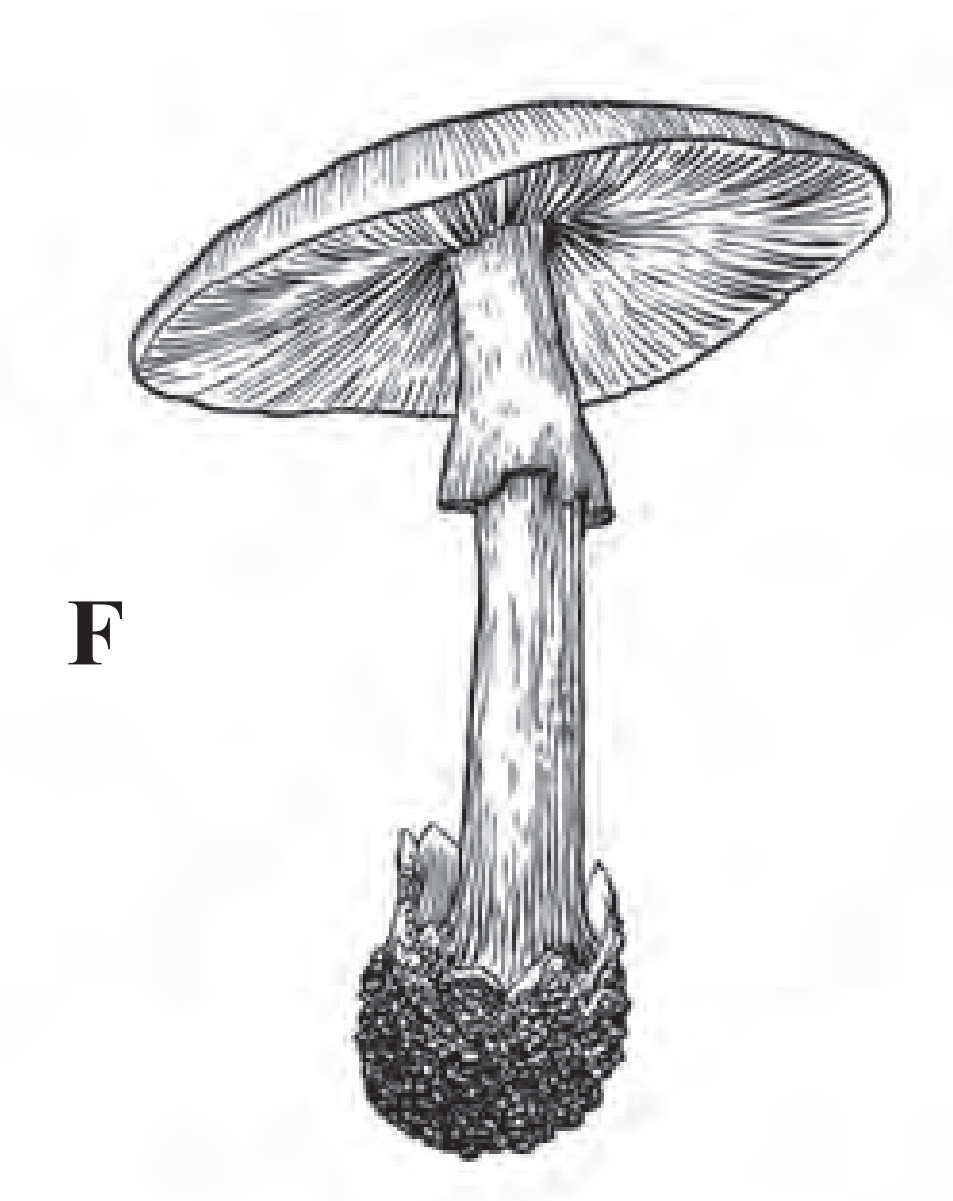
(1) The given figure represents Agaricus (Mushroom).
(2) It belongs to class basidiomycetes of kingdom Fungi.
(3) It has branched septate hyphae.
(4) It grows in soil, on rotten wood, etc.
(5) It is edible and rich in proteins.
(6) Vegetative reproduction takes place by fragmentation.
8. The scientific name of sunflower is given below. Identify the correctly written name.
A. Helianthus annuus L.
B. Helianthus Annuus l.
Ans. The correctly written scientific name of sunflower is Helianthus annuus L.
9. Match the following.
Kingdom Example
i. Monera a. Riccia
ii. Protista b. Cyanobacteria
iii. Plantae c. Rhizopus
iv. Fungi d. Diatoms
Ans.
(i) Monera- (b) Cyanobacteria
(ii) Protista – (d) Diatoms
(iii) Plantae – (a) Riccia
(iv) Fungi – (c) Rhizopus
10. Complete the following
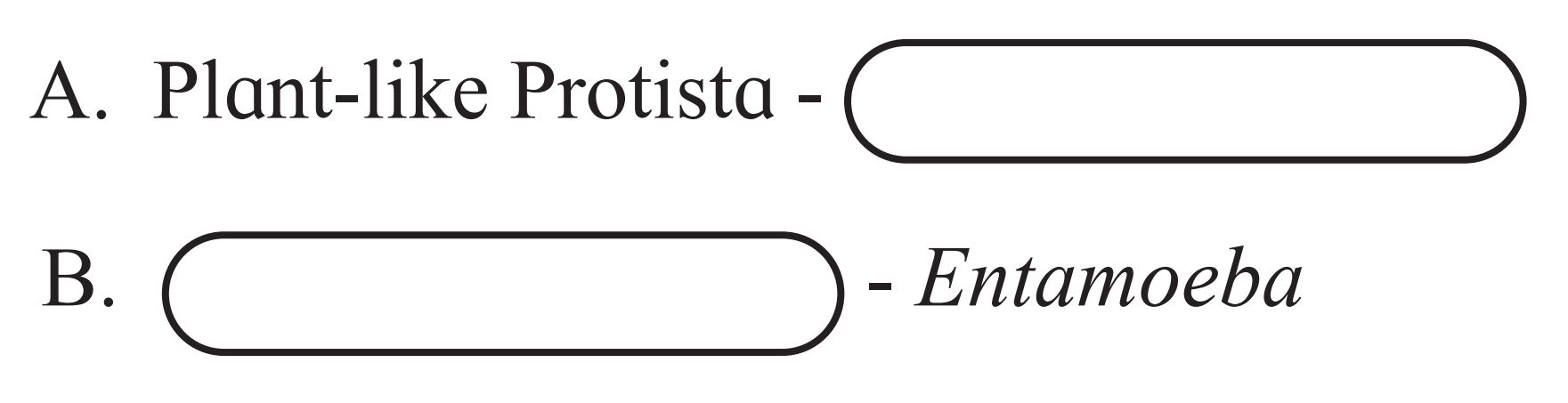
Ans.