1. Choose correct option:
A. Which of the following belongs to a minor phylum?
a. Comb jelly
b. Jelly fish
c. Herdmania
d. Salpa
B. Select the animal having venous heart.
a. Crocodile
b. Salamander
c. Rohu
d. Toad
C. In Ascaris, __________.
a. mesoglea is present
b. endoderm is a discontinuous layer
c. mesoderm is present in patches
d. body cavity is absent
D. Which of the following is incorrect in case of birds?
a. Presence of teeth
b. Presence of scales
c. Nucleated RBCs
d. Hollow bones
E. Chitinous exoskeleton is a characteristic of ___________.
a. Dentalium
b. Antedon
c. Millipede
d. Sea urchin
2. Answer the following questions
A. Reptiles are known for having three chambered heart. Which animal shows a near four chambered condition in reptiles?
Ans:- Crocodiles have a four chambered heart.
B. The circulatory system has evolved from open to closed type in Animal kingdom. Which Phylum can be called first to represents closed circulation?
Ans:- Phylum Annelida is the first phylum to represent closed circulations.
C. Pinna is part of external ear and it is found in mammals. Do aves and reptiles show external ear in any form?
Ans:- No, Aves and Reptiles do not show external ear in any form. They possess tympanum which represents the ear.
D. Fish and frog can respire in water. Can they respire through their skin? If yes, why do they have gills?
Ans:- (1) Yes, fishes and frogs can respire through their skin. (2) The larval stage of frog i. e. tadpole respires through gills. During metamorphosis, tadpoles lose their gills and develop lungs. (3) Frogs do not have scales and breathe through their skin underwater. (4) Fishes respire primarily via gills. The body of fishes is covered with scales which limits cutaneous respiration in them.
E. Birds need to keep their body light to help in flying. Hence, they show presence of some organs only on one side. How their skeleton helps in reducing their weight?
Ans:- (1) In birds, the forelimbs are modified into wings for flying. (2) They possess stream-lined body to reduce resistance during flight. (3) Bones are hollow or pneumatic to reduce body weight. (4) In order to reduce body weight, urinary bladder is absent. Also females possess oly left ovary and oviduct. (5) Body is covered by feathers facilitate flying.
F. Cnidarians and Ctenophorans are both diploblastic. Which other character do they have in common, which is not found in other Phyla?
Ans:- Cnidarians and ctenophorans show tissue level of body organization. They have sac body plan and radially symmetrical body.
G. Crab and Snail both have a protective covering. Is it made up of the same material?
Ans:- No, the protective covering is not made up of same material in crab and snail. The protective covering of crabs is made up of chitin and protective covering of snails is made up of calcium carbonate.
H. Sponge and sea star show calcareous protective material. Do they belong to the same Phylum?
Ans:- No, they do not belong to same phylum. Sponges belong to phylum Porifera and sea star belong to phylum Echinodermata.
I. Fish and snake both have scales. How do these scales differ from each other?
Ans:- Fishes have dermal scales covering the body surface whereas snakes have epidermal scales or scutes.
J. Lower Phyla like Arthropods and Cnidarians show metamorphosis. Is it also found in any class of Phylum Chordata?
Ans:- Yes, it is also found in class Amphibia of phylum Chordata.
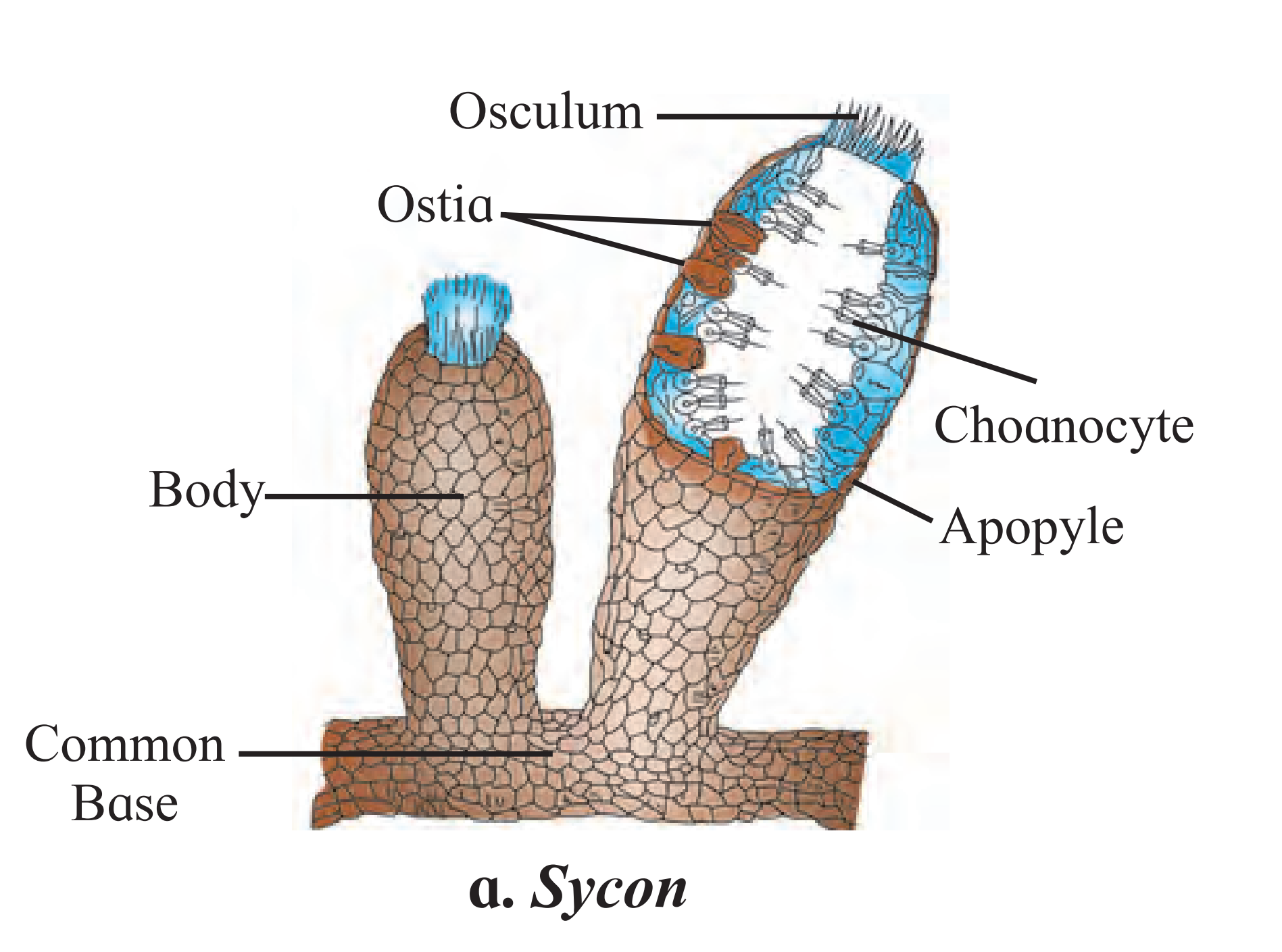
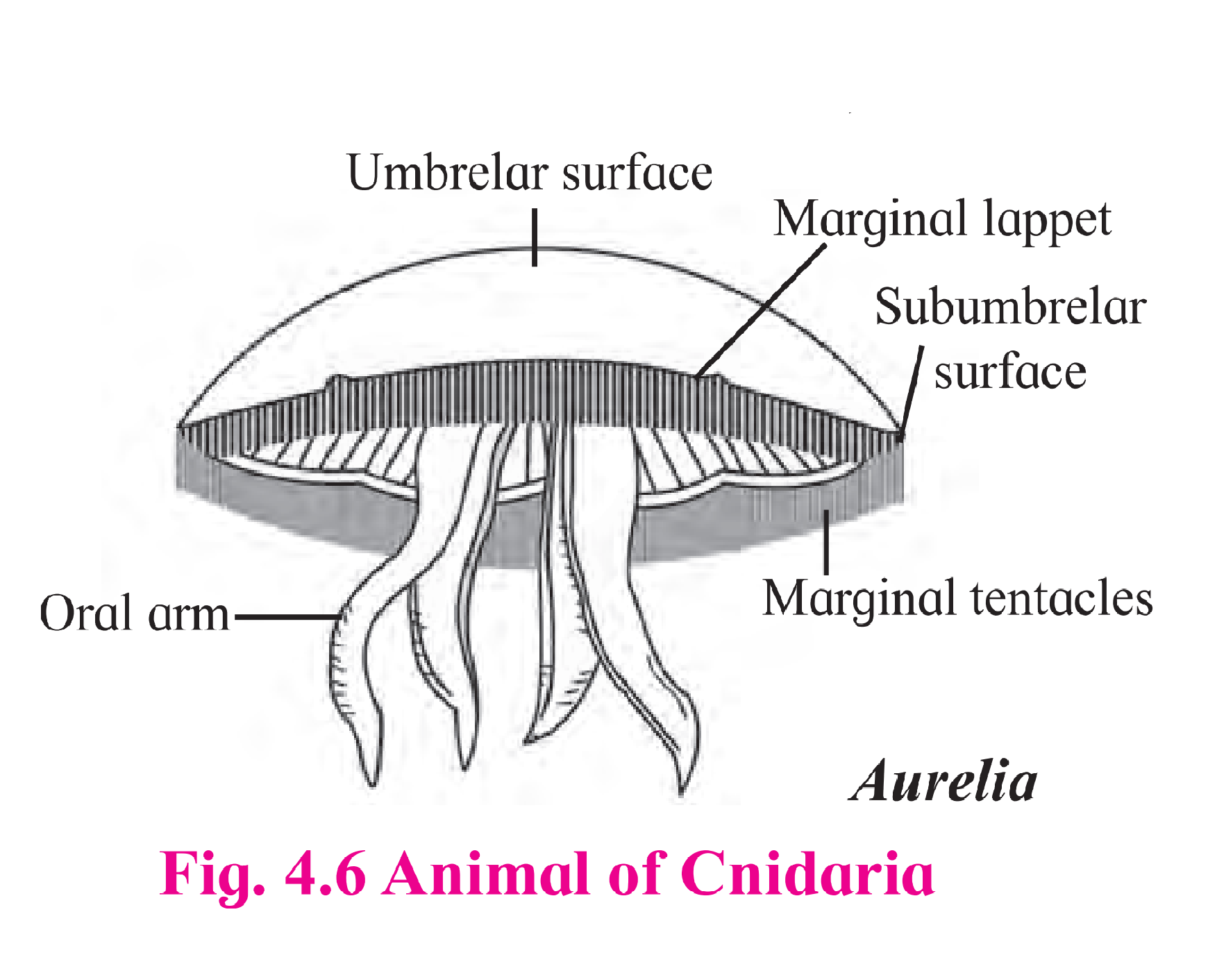
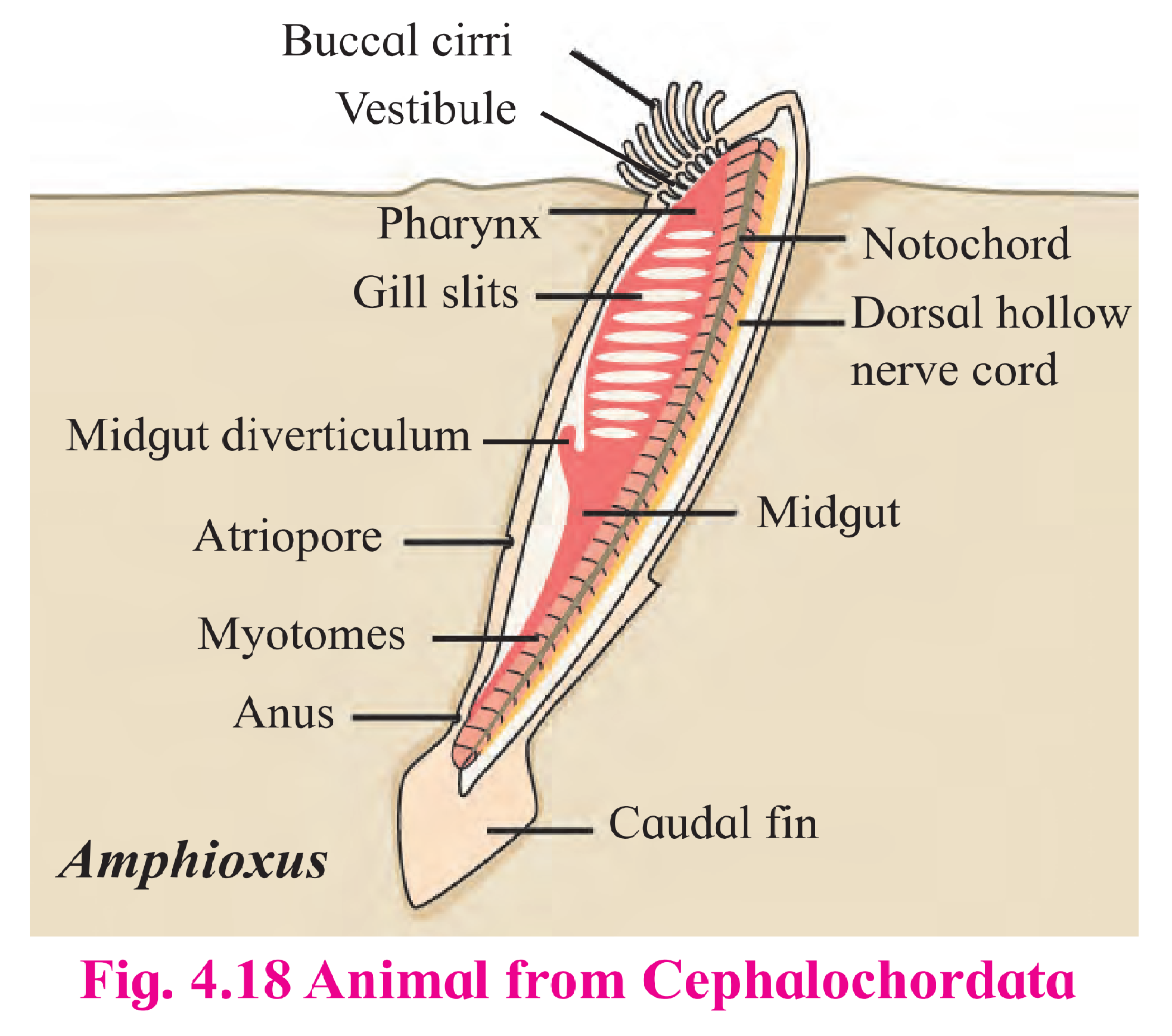
3. Draw neat labelled diagram
A. Sycon
B. Aurelia
C. Amphioxus
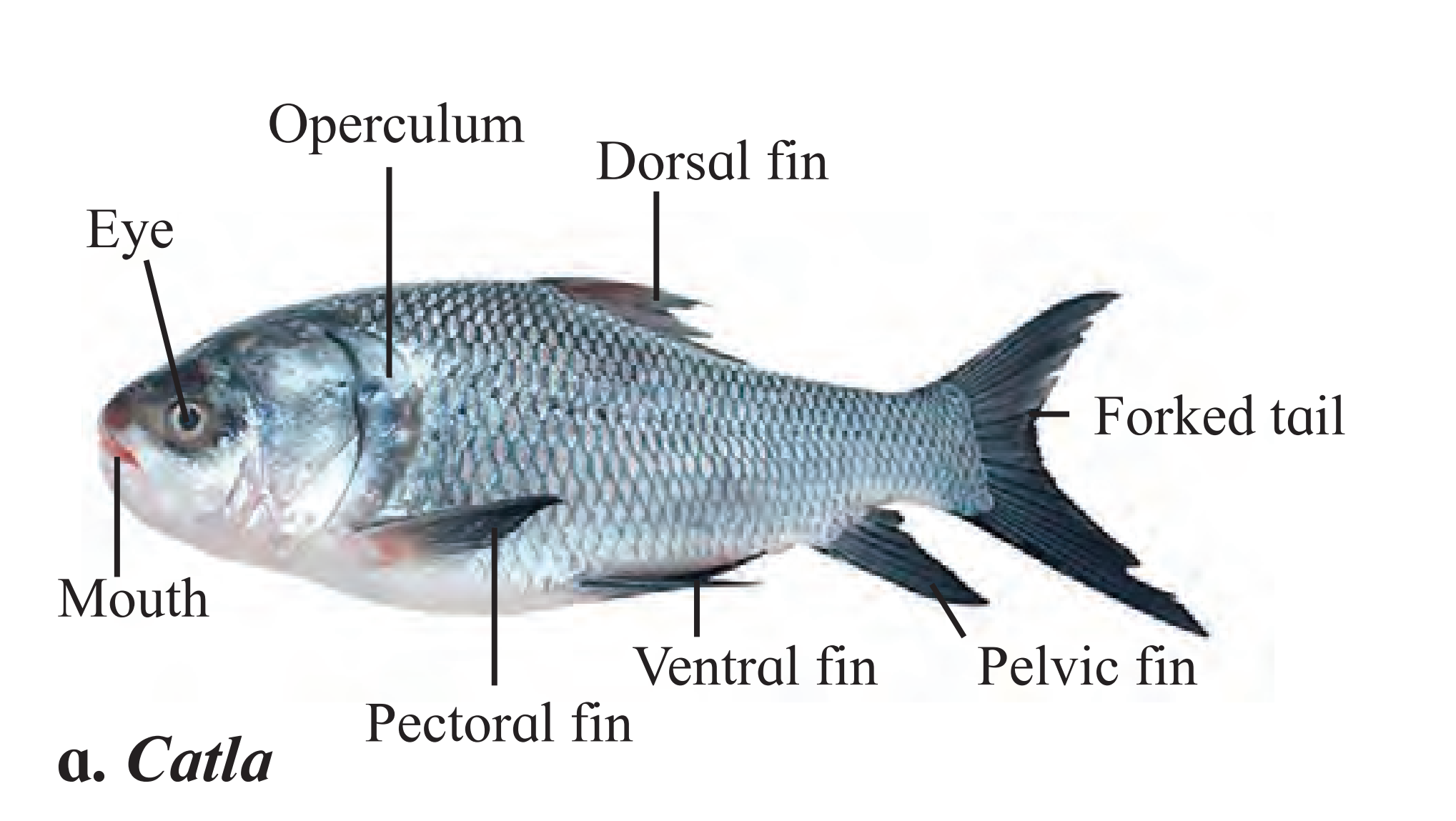
D. Catla
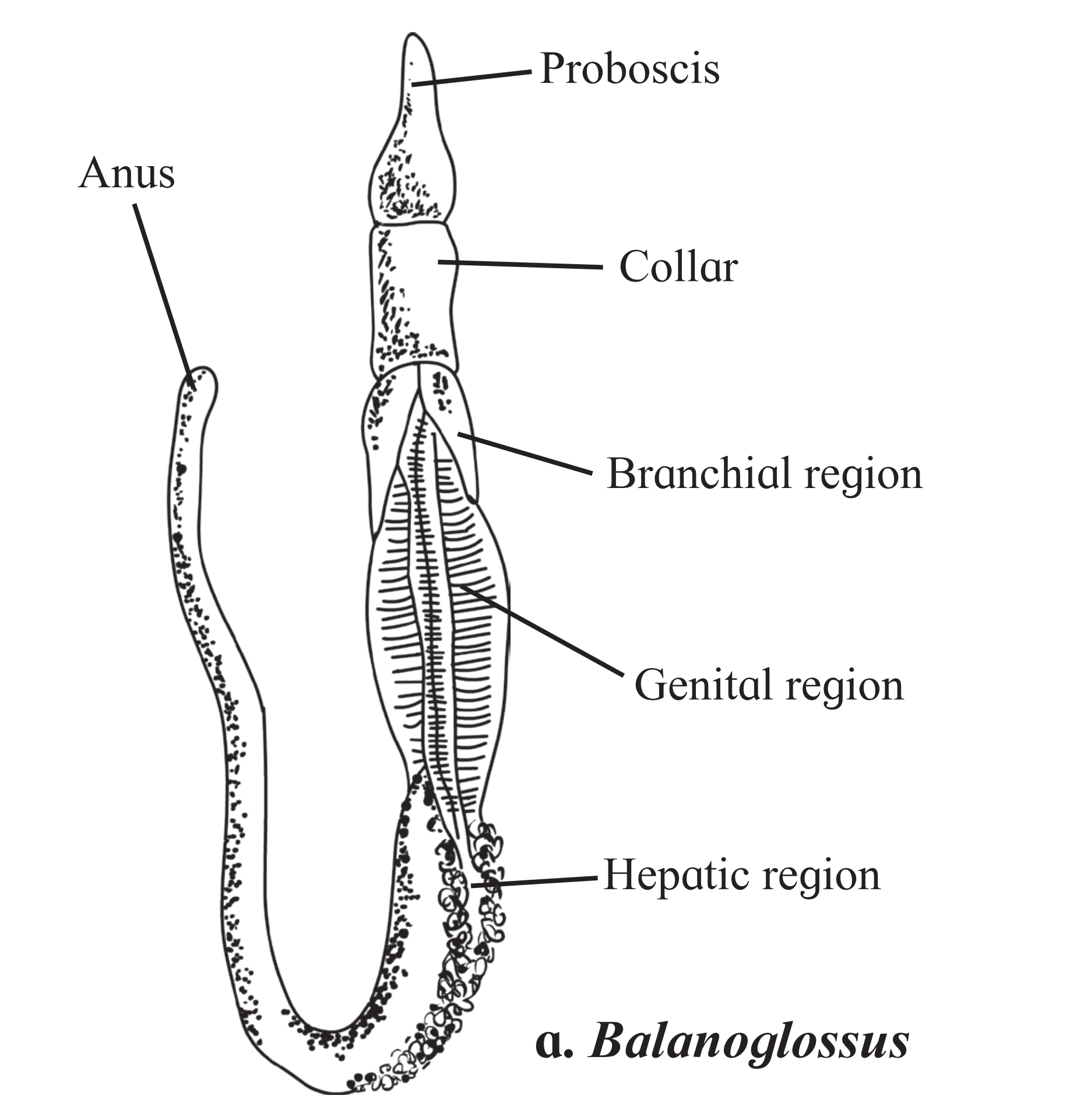
E. Balanoglossus
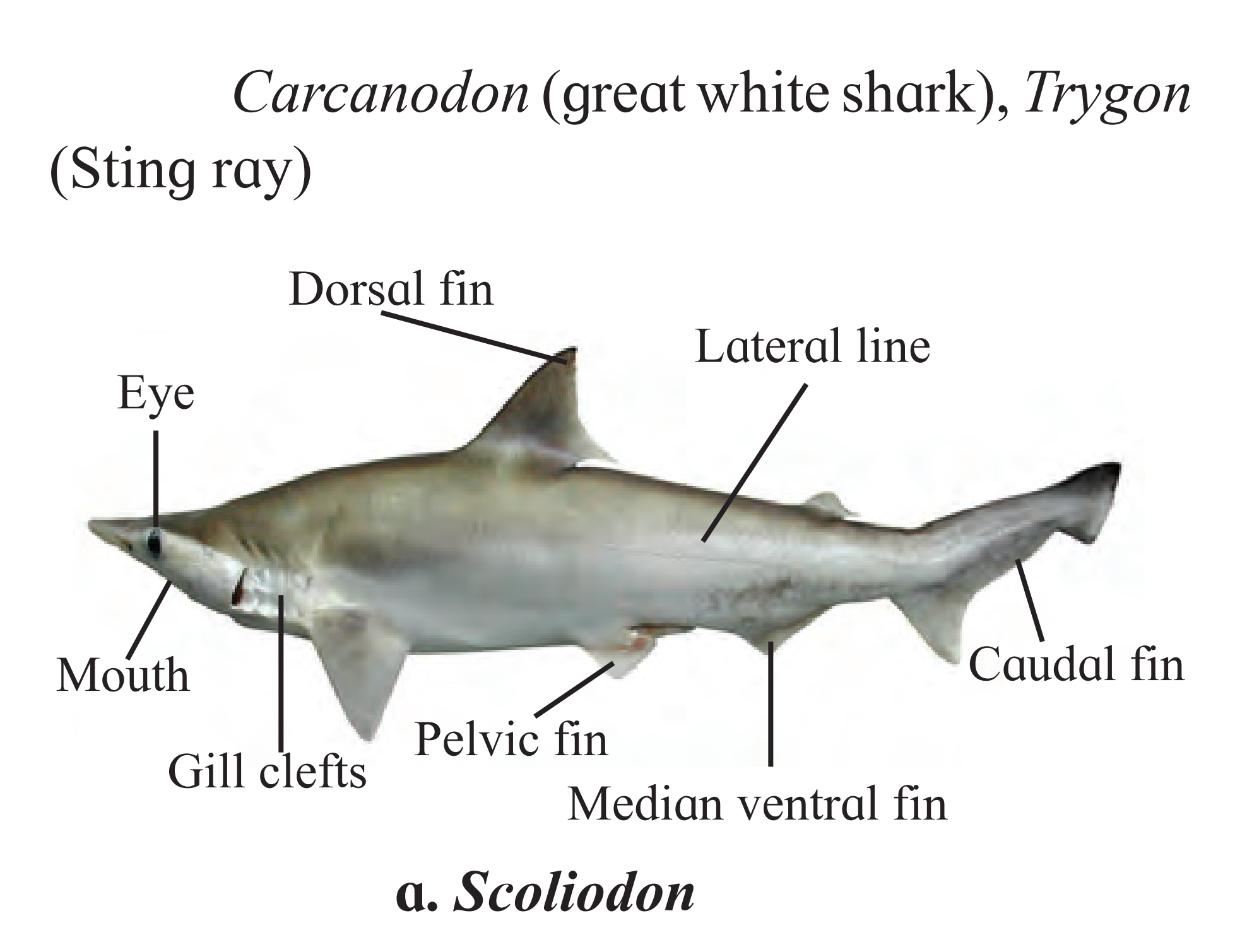
F. Scolidon
4. Match the following
Ans: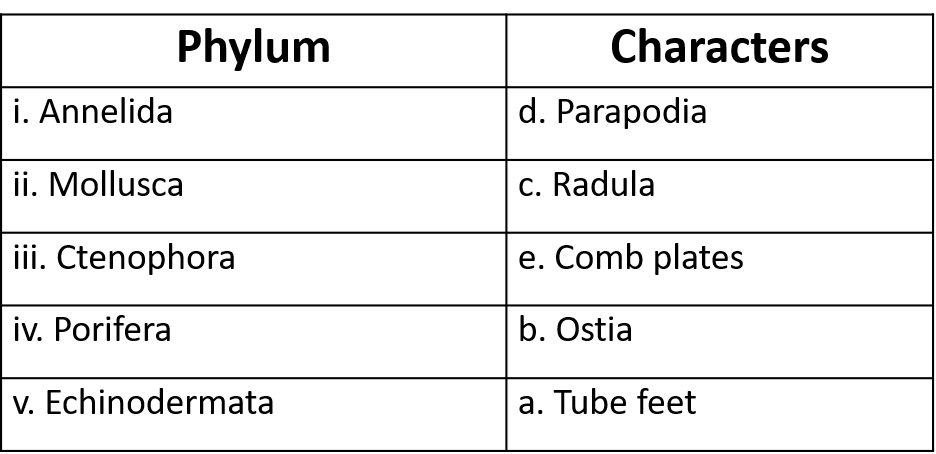
5. Identify the animals given in pictures and write features of its phylum / class
(A.)
Ans: The organism in the given picture is comb jelly and it belongs to phylum Ctenophora.
Features of phylum Ctenophora:
(1) Habitat: They are exclusively marine.
(2) Forms: They are free swimming animals.
(3) Germ layers: Members of this phylum are diploblastic.
(4) Body Symmetry: They are radially symmetrical.
(5) Body plan: The animals of this phylum show blind-sac body plan.
(6) Body organization: They show tissue level organization.
(7) Locomotion: It is carried out by eight rows of ciliated comb plates.
(8) Bioluminescence: It is the characteristic feature of the members of this phylum.
(9) Digestion: It is extracellular and intracellular.
(10) Reproduction: Reproduction is sexual with indirect development
(11) Colloblasts: These sticky cells are used to capture prey.
Eg. Pleurobrachia, Ctenoplana
(B.)

Ans: The organism in the give picture is Eel and it belongs to phylum Chordata.
Features of phylum Chordata :
(1) Notochord present at least in the early embryonic life.
(2) Nerve cord is single, dorsal and non-ganglionated.
(3) The heart is ventral in position.
(4) Pharyngeal gill slits are present at least in embryonic stage.
(5) Post-anal tail is present at least in embryonic stage.
(C)

Ans: The given organism in this picture is Dolphin and it belongs to class Mammalia.
Features of class Mammalia:
(1) Special feature: Presence of mammary glands (milk producing glands) for the nourishment of young ones. Mammary glands are modified sweat glands.
(2) Habitat: Mammals are omnipresent (present everywhere). These are mostly terrestrial, some are aquatic and few are aerial and arboreal (living on trees).
(3) Locomotion: Limbs are the organs of locomotion and are modified for walking, climbing, burrowing. Swimming, etc.
(4) Body division: Body is differentiated into head, neck, trunk and tail. They have external ear.
(5) Body temperature: Mammals are homeotherms or warm-blooded animals.
(6) Exoskeleton: It is in the form of hair, fur, nails, hooves, horns, etc.
(7) Skin: Skin is glandular and has sweat glands and sebaceous (oil) glands.
(8) Mouth cavity: Mammals show heterodont dentition (various types of teeth like incisors, canines, premolars and molars).
(9) Circulation: Heart is ventral in position, four chambered with two auricles and two ventricles. RBCs are biconcave and enucleated (except camel). Blood is red in color.
(10) Respiration: Respiration takes place by lungs.
(11) Nervous system: Brain is highly developed. Cerebrum shows a transverse band called corpus callosum.
(12) Reproduction and development: Only few mammals are oviparous. e.g. Duck billed platypus. Some have pouches for development of immature young ones. These are called marsupials. e.g. Kangaroo. Most of the mammals are placental and viviparous.
(D)

Ans:- The given organism is Snake and it belongs to class Reptiles.
Features of class Reptiles:
(1) Habitat: They are crawling animals. They are the first true terrestrial vertebrates. Few may be aquatic or semi-aquatic and are also found in marshy areas.
(2) Locomotion: Locomotion occurs by limbs in most animals. The limbs are pentadactyl with clawed digits, which help the animal to walk, creep or crawl. Snakes are limbless and crawl on their belly.
(3) Body temperature: They are poikilotherms.
(4) Exoskeleton: Skin is dry, non-glandular and covered by an exoskeleton of epidermal scales or scutes, shields or plates. Lizards and snake shed their skin periodically.
(5) Ear: Tympanum is present
(6) Circulatory system: It has two complete auricles but the ventricles are incompletely partitioned. Therefore, the heart of reptiles is not perfectly four chambered (except in crocodile the heart is four chambered).
(7) Nervous system: The brain is well developed. The olfactory lobes and cerebellum are better developed as compared to amphibians.
(8) Reproduction: Sexes are separate and exhibit prominent sexual dimorphism. Fertilization is internal and the animals are oviparous (exception – viper, it is viviparous). They show little parental care.
(E)

Ans:- The given organism is urchin and belongs to phylum Echinodermata.
Features of Phylum Echinodermata:
(1) Habitat: These are exclusively marine.
(2) Forms: Members of this phylum are solitary, sedentary or free-living and gregarious, benthic.
(3) Body symmetry: These animals are radially symmetrical with pentamerous symmetry.
(4) Shape: Members of Echinodermata are spherical, elongated or star shaped.
(5) Body: The endoskeleton is made up of calcareous ossicles. Spines are formed on the body. Hence, they are known as echinoderms. The body has two sides oral and aboral and lacks definite divisions. Mouth is ventrally present on oral surface and anus on aboral surface.
(6) Water vascular system: Presence of water vascular system is the peculiar character of echinoderms. Madreporite is the opening of water vascular system through which water enters. Water vascular system is useful in locomotion, food capturing, respiration.
(7) Digestion: Digestive system is complete.
(8) Respiration: Peristomial gills, papillae, respiratory tree, ete. are used for respiration.
(9) Circulatory and excretory systems: Absent in echinoderms.
(10) Nervous system: Nervous system is simple with a nerve ring around the mouth and radial nerves in arms.
(11) Reproduction and development: Sexes are separate (sometimes bisexual). Fertilization is external Development is indirect, i.e. through larval stages They show high power of regeneration.
(F)

Ans: The given organism is flying lizard and belongs to class Reptiles.
Features of Class Reptiles:
(1) Habitat: They are crawling animals. They are the first true terrestrial vertebrates. Few may be aquatic or semi-aquatic and are also found in marshy areas.
(2) Locomotion: Locomotion occurs by limbs in most animals. The limbs are pentadactyl with clawed digits, which help the animal to walk, creep or crawl. Snakes are limbless and crawl on their belly.
(3) Body temperature: They are poikilotherms.
(4) Exoskeleton: Skin is dry, non-glandular and covered by an exoskeleton of epidermal scales or scutes, shields or plales. Lizards and snake slhed their skin perioditally.
(5) Ear: Tympanum is present
(6) Circulatory system: It has two complete auricles but the ventricles are incompletely partitioned. Therefore, the heart of reptiles is not perfectly four chambered (except in crocodile the heart is four chambered).
(7) Nervous system: The brain is well developed. The olfactory lobes and cerebellum are better developed as compared to amphibians.
(8) Reproduction: Sexes are separate and exhibit prominent sexual dimophism. Fertilization is internal and the animals are oviparous (exception – viper, it is viviparous). They show little parental care.
(G)
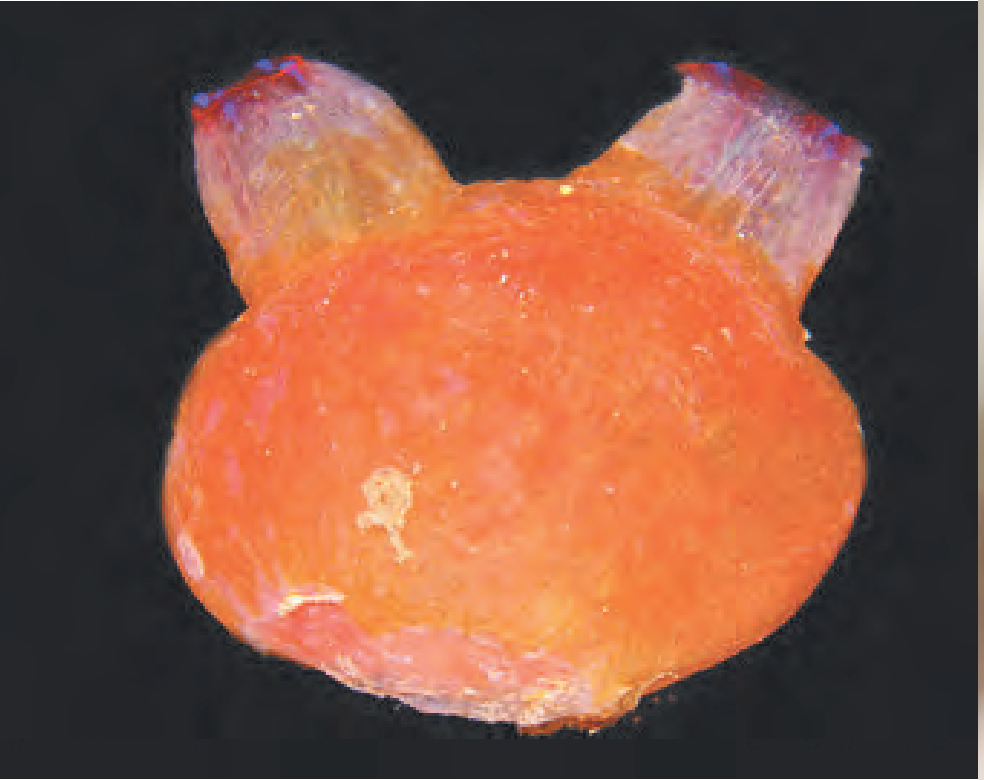
Ans: The give organism is Herdmania and belongs to Phylum Chordata.
Features of Phylum Chordata:
(1) Presence of hollow, dorsal nerve chord, running throughout the length of the body.
(2) Habitat: They are exclusively marine.
(3) Body covering: Soft body is covered by ‘test or ‘tunic which is made up of tunicine.
(4) Notochord: Notochord is present only in the tail of the larva and is lost during metamorphosis. Hence, the name Urochordata.
(5) Respiration: Pharynx with many gill slits for respiration.
(6) Circulation: Closed circulatory system is present.
(7) Reproduction: Development is indirect.
eg. Herdmania. Salpa. Doliolum. Ascidia.
(H)
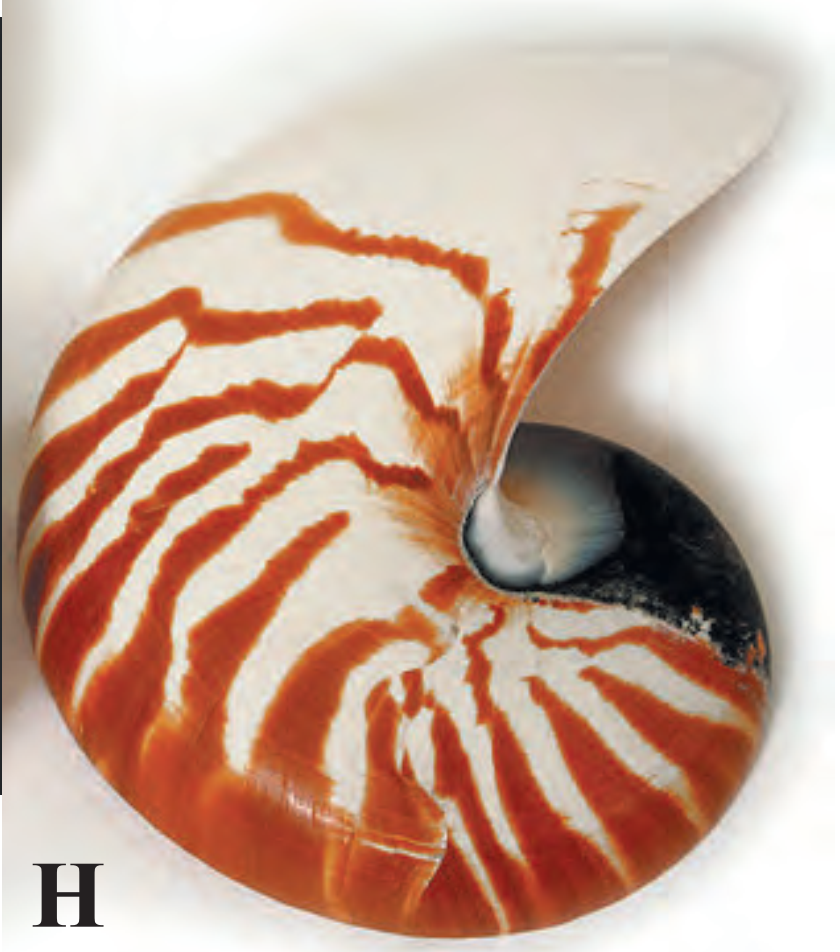
Ans : The organism in this picture is Nautilus and it belongs to phylum Mollusca.
Features of Phylum Mollusca:
(1) Habitat: They are aquatic or seen in marshy places. Few of them are terrestrial.
(2) Forms: Molluscs are either free-living or sedentary.
(3) Body plan: These are soft bodied and show tube within a tube type of body plan.
(4) Body symmetry: Most of the Molluscs show bilateral symmetry but few are asymmetrical due to torsion.
(5) Body division: Body consists of head, foot and visceral mass. Visceral mass is enclosed in thick, muscular fold of body wall called mantle. Mantle secretes a hard-calcareous shell, that may be external or internal or absent. Muscular foot is present ventrally.
(6) Digestive system: Digestive system is well-developed and complete with anterior mouth and posterior anus. Buccal cavity has a rasping organ called radula (helps in feeding), which is provided with transverse rows of teeth.
(7) Respiration: In aquatic forms, numerous feather-like gills called ctenidia, help in aquatic respiration. Terrestrial forms may show the presence of lungs.
(8) Circulatory system: Circulatory system is of open type (except in Sepia, where it is of the closed type). Blood contains a copper containing blue coloured respiratory pigment called haemocyanin.
(9) Excretion: Excretion occurs by kidney like structures, also called ‘Organ of Bojanus’.
(10) Nervous system and sense organs: Nervous system has three pairs of ganglia. All these ganglia are interconnected by commissures and connectives.
(11) Sense organs: Sense organs such as eyes for vision, tentacles for tactile sensation and osphradia for testing purity of water is present.
(12) Sexual reproduction: Sexes are usually separate. Animals of this phylum are mostly oviparous and the development is direct or indirect.
(I)
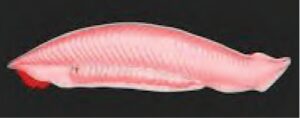
Ans :- The organism in this picture is Amphioxus its belongs to phylum Chordata (Subphylum Cephalochordata).
Features of phylum Chordata (Subphylum Cephalochordata):
(1) Cephalochordates are also known as lancelets and are small fish-like animals that rarely exceed 5 cm in length.
(2) Lancelets are exclusively marine and live partly buried in soft marine sediments.
(3) Notochord extends throughout entire length of the body and persists throughout life.
(4) Myotomes (muscle blocks) are present.
(5) Post anal tail is present.
(6) Circulatory system is closed type. Blood lacks pigment.
eg. Branchiostoma
6. Observe and identify body symmetry of given animals.
Fig i.
Ans: Represents asymmetry
Fig ii.
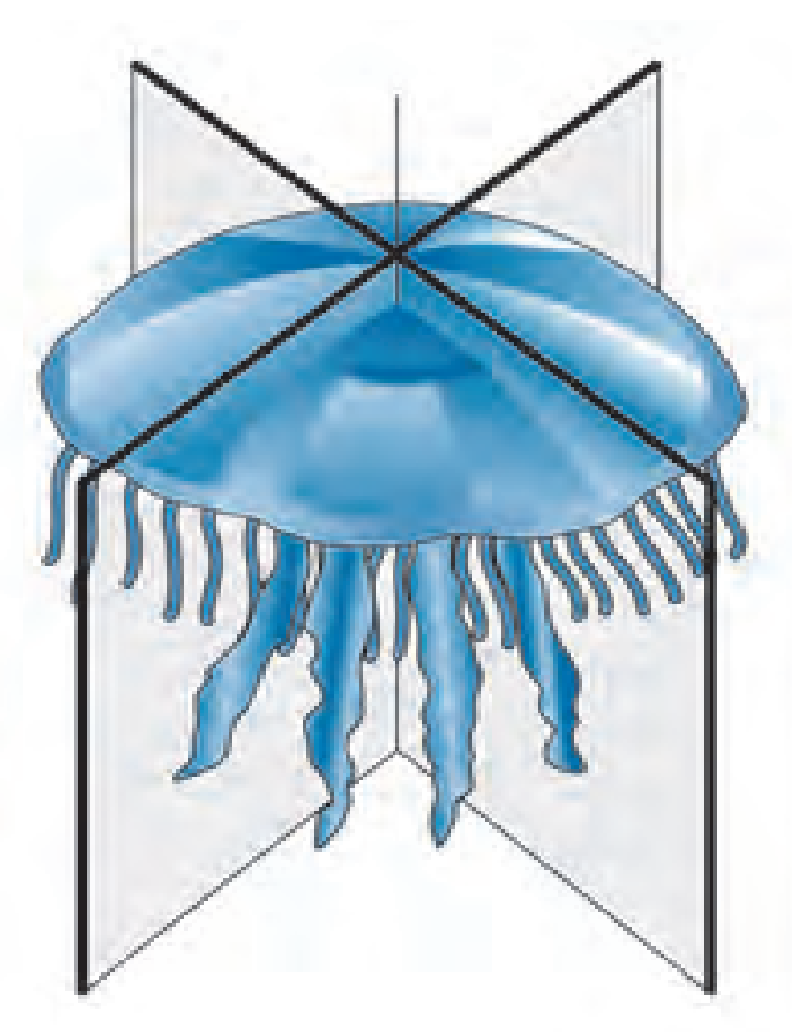
Ans: Represents radial symmetry
Fig iii.