Q. 1. Complete the following statements :
(1) Rural credit system assumes importance because …………..
(a) It leads to an increase in the rural income.
(b) Savings are inadequate to finance farming and other economic activities.
(c) It leads to overall development of the rural areas.
(d) It leads to reduction in rural inequality.
(2) Productive loans are economically justified because ……………….
(a) They are related to agricultural production.
(b) They are used for personal consumption.
(c) They help in eradication of poverty
(d) They improve the quality of life of the people
(3) Small farmers are unable to access rural credit provided by banks due to …………….
(a) Presence of money lenders.
(b) No branches in rural areas
(c) High transaction costs
(d) Preference given to large farmers.
(4) The rights of socially disadvantaged groups can be safe guarded through ……………….
(a) empowerment of women
(b) proper enforcement of law and order.
(c) infrastructural development
(d) improvement in quality of life.
(5) The quality of life of the rural people can be improved by ……………………..
(a) Providing safe drinking water, health and hygiene facilities.
(b) Effective implementation of land reforms
(c) Providing subsidized credit facilities
(d) Reducing rural inequality
Q. 2. Choose the wrong pair :
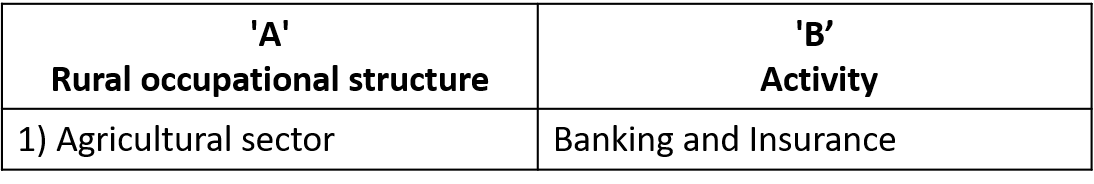
(1)
Ans. Wrong Pair

(2)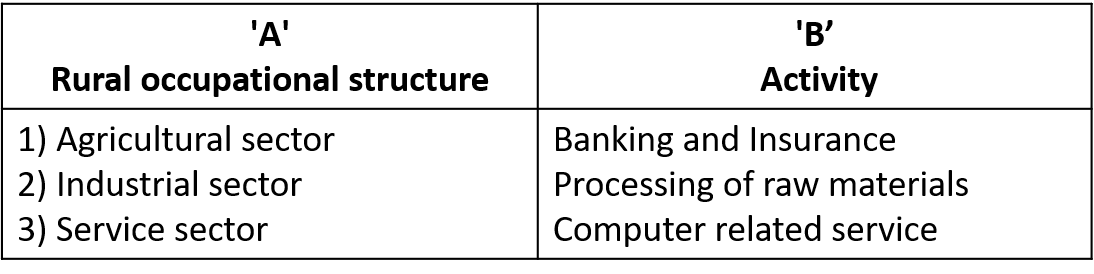
Ans. Wrong Pair
Q. 3. Assertion and Reasoning questions :
1) Assertion (A) : Indian economy is pre-dominantly rural economy
Reasoning (R) : As per 2011 census, the country’s rural population is almost 83.25 crore (68.8% of total population)
Options :
1) (A) is True but (R) is False
2) (A) is False but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
4) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Ans. 3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
2) Assertion (A) : Literacy is a powerful instrument of socio-economic change.
Reasoning (R) : Empowerment of women helps to reduce gender disparity.
Options :
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Ans. 3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
3) Assertion (A) : Agricultural credit is mostly for unproductive purposes.
Reasoning (R) : Agricultural credit is an important pre-requisite for agricultural growth.
Options :
1) (A) is true, but (R) is false
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Ans. 4) Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
4) Assertion (A) : Non-institutional finance forms an important part of rural credit.
Reasoning (R) : Small farmers are unable to access bank credit because of borrower unfriendly products.
Options :
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of A
4) Both (A) and (R) are True, but (R) is not the correct explanation of A
Ans. 4) Both (A) and (R) are True, but (R) is not the correct explanation of A
Q. 4. Identify and explain the concepts from the given illustrations :
1) Kusumtai knowingly set up her business enterprise in the rural area so that people living there could be gainfully employed.
Ans.
A. Identified concept: Rural industrialization.
B. Explanation of concept: Rural industrialization is a strategic process of establishing industries in rural areas to generate employment opportunities in rural areas Which in turn, leads to economic growth and development of the country.
2) Raoji purchased a new tractor for his farm by taking a loan.
Ans.
A. Identified concept: Productive agricultural credit.
B. Explanation of concept: The agricultural credit that is used for agricultural productive activities is called productive agricultural credit.
3) Subsidized credit is provided by banks to small farmers for purchase of high yielding variety (HYV) seeds.
Ans.
A. Identified concept: Short-term credit.
B. Explanation of concept: Short-term credit refers to loans not exceeding two years. It is provided by banks to cultivators for purchase high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, fertilizers, etc.
4) Damaji borrows loan from a credit society established in the village this season rather than taking it from a moneylender.
Ans.
A. Identified concept: Institutional source of agricultural credit.
B. Explanation of concept: A source of agricultural credit that is owned, managed, or regulated by government is called an institutional source of agricultural credit. For example, Primary agricultural credit society.
5) Ramraoji takes a loan from the bank for a period of ten years subject to terms and conditions for the purpose of irrigated farming.
Ans.
A. Identified concept: Long-term agricultural credit.
B. Explanation of concept: Long-term agricultural credit refers to loans that are taken for a period of more than five years.
Q. 5. Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below :
Rural development is one of the thrust areas of administration. As Mahatma Gandhi rightly said, “India lives in villages and the development of the nation cannot be achieved without the development of the villages”. The need of the hour is the convergence of all development interventions, at the grassroot level which can be possible through effective governance at the village level. The movement towards decentralization of the National and State governments through the Panchayati Raj system needs to be strengthened through lessons learned from the successful stories of ‘Model villages’ around India. Though India is progressing in the right direction in reducing education inequalities and increasing literacy levels, there is still a lot that needs to be done. An understanding of social issues is important for effective planning and policy development. Self-governance ensures that Indian citizens, even the previously marginalized, can participate in decision-making.
1) Explain in short Mahatma Gandhi’s views on rural development.
2) Highlight the role of the government in achieving rural development.
3) What measures have been suggested to achieve rural development.
4) Express your idea of a ‘Model Village’.
Ans.