Que 2B) III.write short notes. (2m each)
1. Sodium burns in air
Ans. On burning, sodium metal combines with oxygen in the air to form sodium oxide.
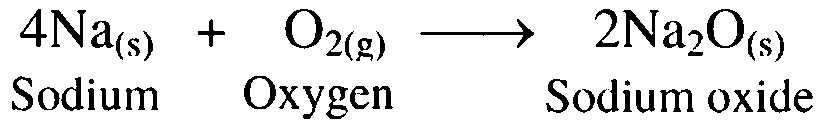
2. Reaction of aluminium with oxygen
Ans. Aluminium combines with oxygen to form aluminium oxide.
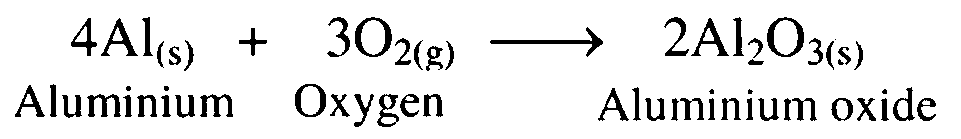
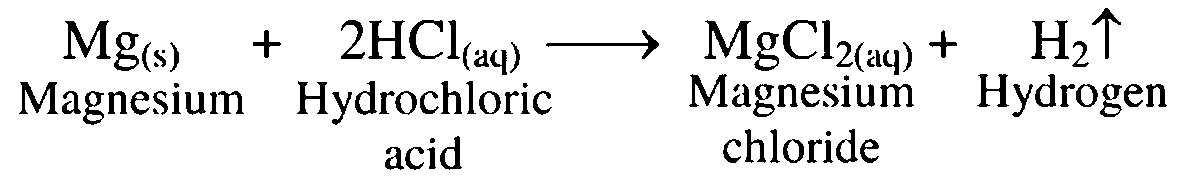
3. Magnesium reacts with dil HCl
Ans. When magnesium is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms magnesium chloride with release of hydrogen gas.
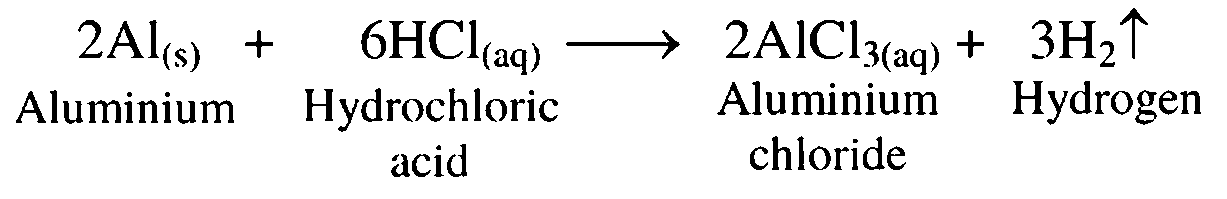
4. Aluminium reacts with dil hydrochloric acid.
Ans. When aluminium is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms aluminium chloride with release of hydrogen gas.
5. Reaction of zinc with dil. hydrochloric acid
Ans. Zinc, on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid, forms zinc chloride with release of hydrogen gas.
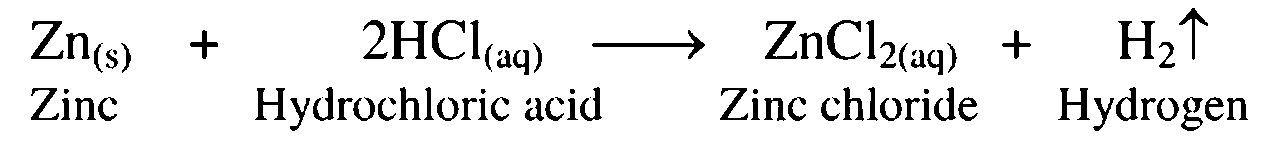
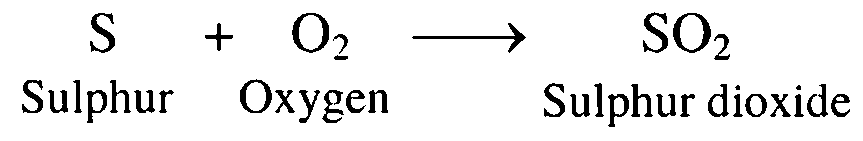
6. Sulphur burns in air
Ans. Sulphur bums in air to form sulphur dioxide.
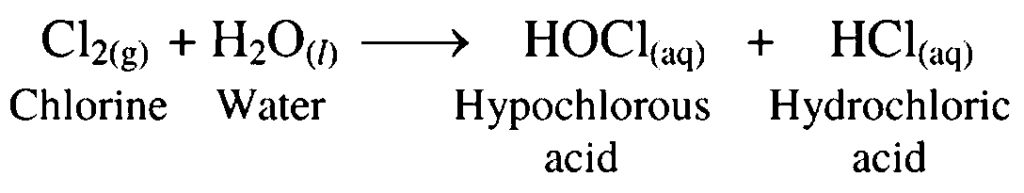
7. Chlorine dissolved in water
Ans. Chlorine dissolves in water to form hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid.
8. Sodium aluminate reacts with water
Ans. Sodium aluminate reacts with water to give aluminium hydroxide as a precipitate and sodium hydroxide.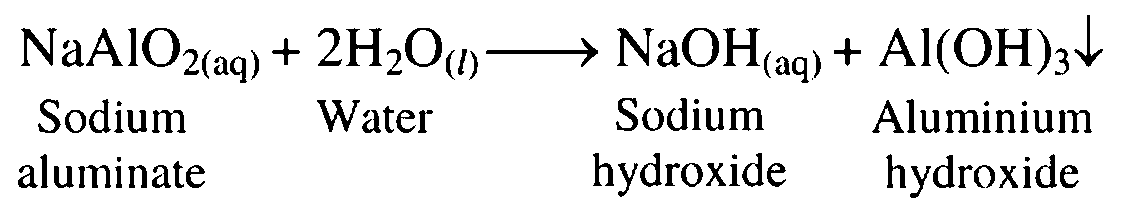
9. Iron (ferrous) dissolved in aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Ans. Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution forming ferrous sulphate and copper.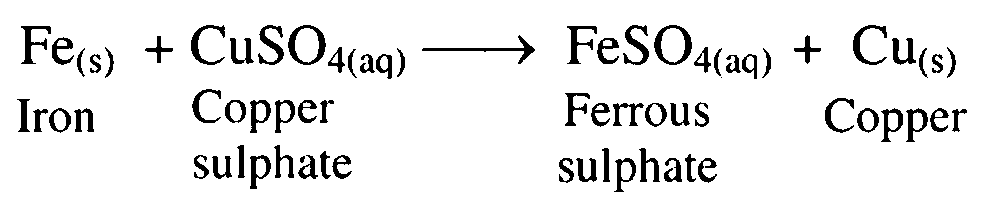
10. Ferric oxide is reacted with aluminium.
Ans. Ferric oxide reacts with aluminium to form iron and aluminium oxide. This reaction is known as thermit reaction.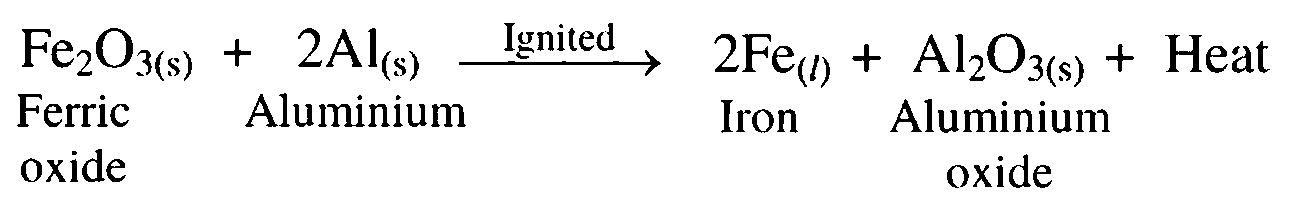
11. Electrolysis of alumina is done.
Ans. When electrolysis of alumina is done, aluminium is formed at the cathode and oxygen gas liberated at the anode.
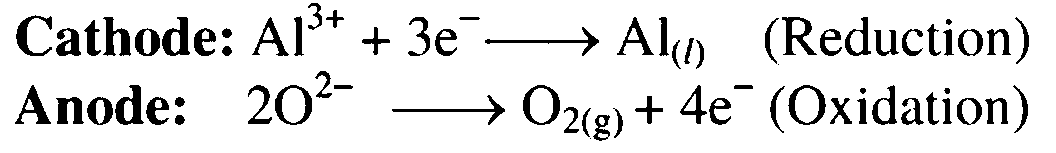
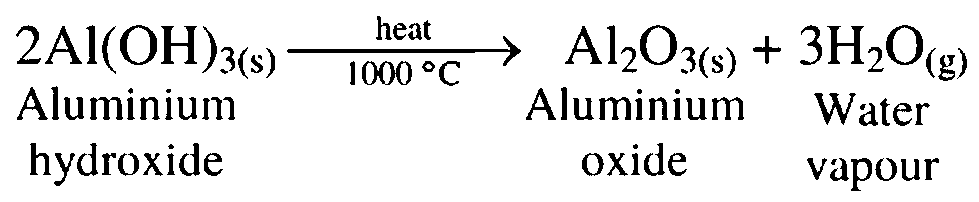
12. Dry aluminium hydroxide is ignited at 1000 °C
Ans. When dry aluminium hydroxide is calcined by at 1000 °C, pure aluminium oxide, called alumina is obtained.
13. Zinc sulphide is heated strongly in excess of air
Ans. Zinc sulphide is heated strongly in excess of air to convert it to zinc oxide. This process is called roasting.
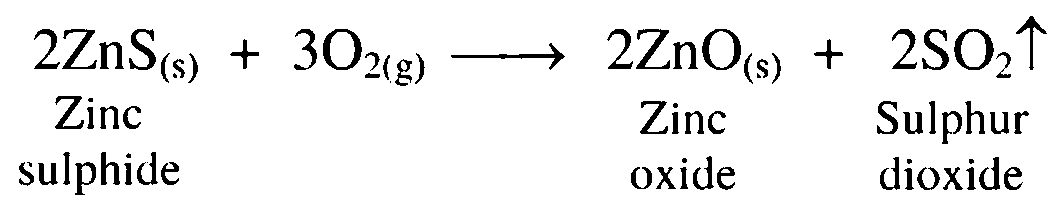
14. Zinc carbonate is heated strongly in limited supply of air
Ans. Zinc carbonate is heated strongly in limited supply of air to convert it to zinc oxide. This process is called calcination.
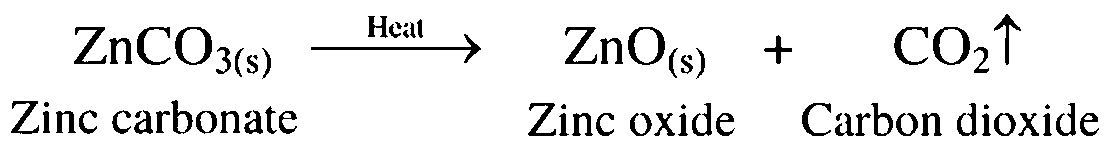
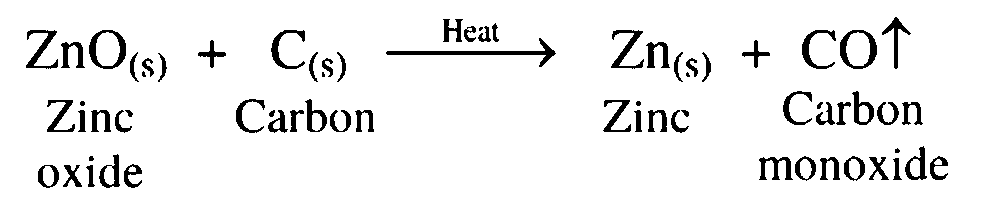
15. Zinc oxide is treated with carbon
Ans. Zinc oxide is reduced to zinc by heating it with carbon.