According to Mendeleev’s periodic law, properties of elements are periodic function of their atomic masses.

The vapour content in the air is measured using a physical quantity called absolute humidity.
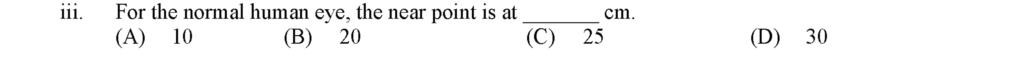
For the normal human eye, the near point is at 25 cm.
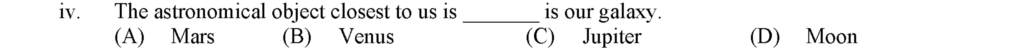
The astronomical object closest to us is Moon is our galaxy.
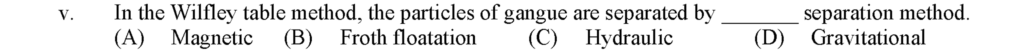
In the Wilfley table method, the particles of gangue are separated by Gravitational separation method.
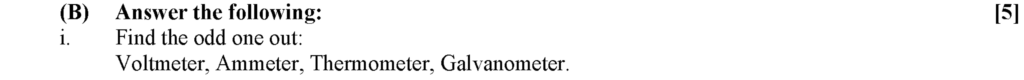
Thermometer

Alkene : C = C :: Alkyne : C ≡ C.

The frequency of AC is 50 Hz. – True
Sputnik
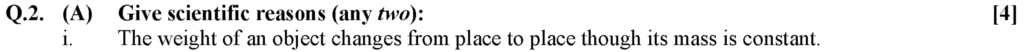
i. Mass is a fundamental quantity whose value remains the same everywhere. Hence, the mass of an object on earth will not change from place to place.
ii. Weight of an object is a product of mass and gravitational acceleration, i.e., W = F = mg
iii. As the weight depends on the value of acceleration due to gravity (g) which changes from place to place, the weight of an object changes from place to place though its mass is constant.
i. Due to the motion of atmospheric air and change in density and temperature, the atmosphere is not steady. As a result, a refractive index of air in a given region changes continuously and randomly.
ii. Due to this, the position and brightness of the star keep changing continuously and the star appears to be twinkling.
iii. The rays of light from a planet pass through the atmosphere of the earth. As compared to stars, planets are nearer to earth. So a planet can be considered as a collection of a large number of point sources of light.
iv. If the intensity of light from one point source decreases, it increases from the other source. Thus, the average intensity remains the same. Hence, stars twinkle but we do not see the twinkling of planets.
i. The electronic configuration of the outermost shell is the same for all the elements belonging to the same group.
ii. So, the number of valence electrons for all the elements in a group is the same.
iii. The valency of an element is determined by the valence electrons. Hence, elements belonging to the same group have the same valency.
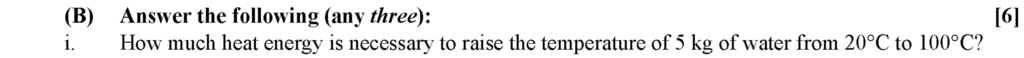
Given: Mass (m) = 5 kg, specific heat of water (c) = 1 kcal/kg °C, Change in temperature (ΔT) = 100 – 20 = 80°C
To find: Heat energy (Q)
Formula: Q = m c ΔT
Calculation:
According to the principle of heat exchange,
Energy supplied to water = Energy gained by water
From the formula,
Q = 5 × 1 × 80 = 400 kcal
Heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of the water is 400 kcal.
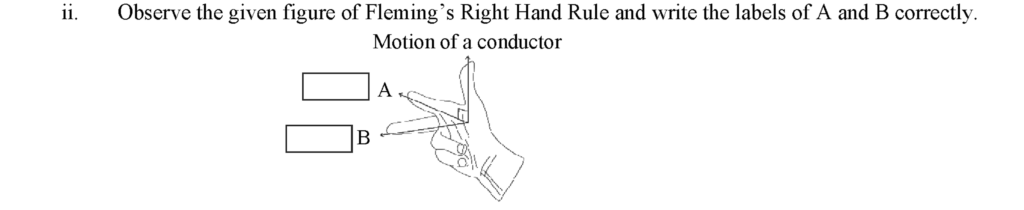
• Label A: Direction of magnetic field
• Label B: Direction of induced current
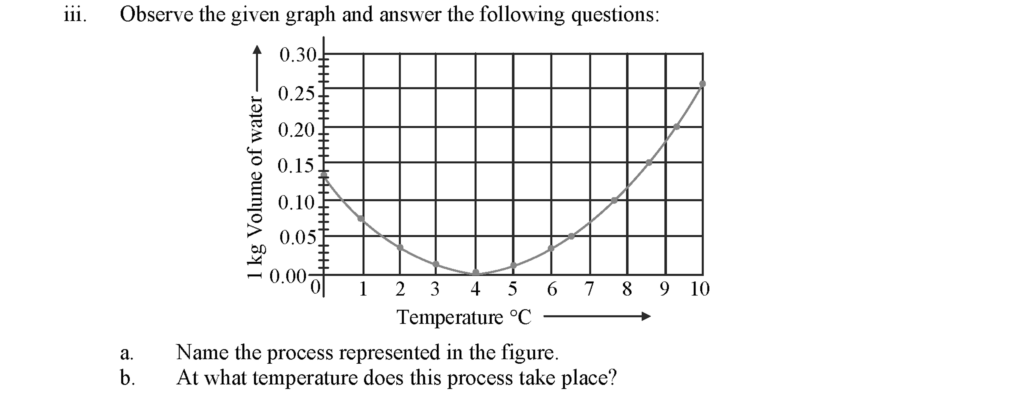
a. Anomalous behaviour of water
b. This process takes place between the temperature interval of 0 °C to 4 °C.

• CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
• This reaction is displacement reaction.
i. The homogenous mixture formed by mixing metal with other metals or nonmetals in a certain proportion is called an alloy.
ii. Majority of the metallic substances used presently are in the form of alloys. The main intention behind this is to decrease the intensity of corrosion of metals.
iii. For example, bronze is an alloy formed from 90% copper and 10% tin. Bronze statues do not get affected by the sun and rain. Stainless steel does not get stains with air or water and also does not rust. It is an alloy made from 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% carbon.
iv. In recent times various types of alloys are used for minting coins.

a. The atomic number of this element is 12.
b. The group number of this element is second.
c. This element belongs to third period.
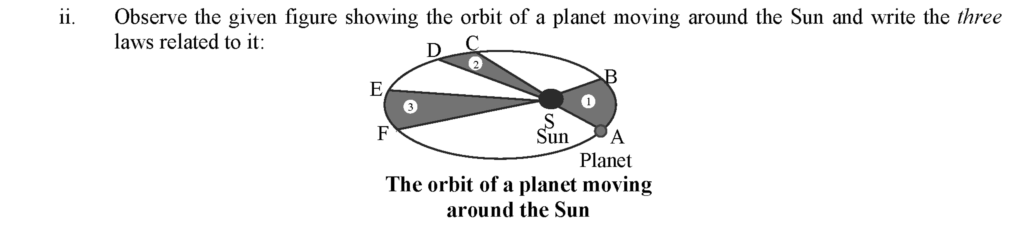
i. Kepler’s first law: The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the sun at one of the foci.
ii. Kepler’s second law: The line joining the planet and the sun sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
iii. Kepler’s third law: The square of the orbital period of revolution of a planet around the Sun is directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance of the planet from the Sun.

a. The ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires have potential difference of 220 V.
b. Due to a fault in the equipment or if the plastic coating on the ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires gives away the two wires come in contact with each other and a large current flows through it producing heat. This is known as short circuiting.
c. Fuse wire protects circuits and appliances by stopping the flow of any excess electric current.

a. Refraction of light
b. Laws of refraction:
1. Incident ray and refracted ray at the point of incidence N are on the opposite sides of the normal to the surface of the slab at that point i.e. CD, and the three, incident ray, refracted ray and the normal, are in the same plane.
2. For a given pair of media, here air and glass, the ratio of sin i to sin r is a constant. Here, i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction.
A manmade object revolving around a planet in a fixed orbit is known as artificial satellites.
Based on their functions, satellites are classified as following: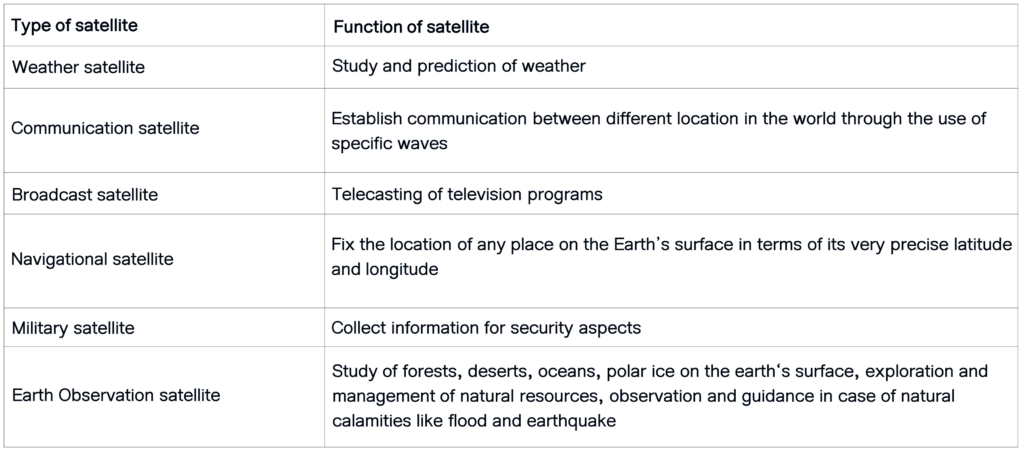
(Students are supposed to write any two artificial satellites with their functions as per question asked here)

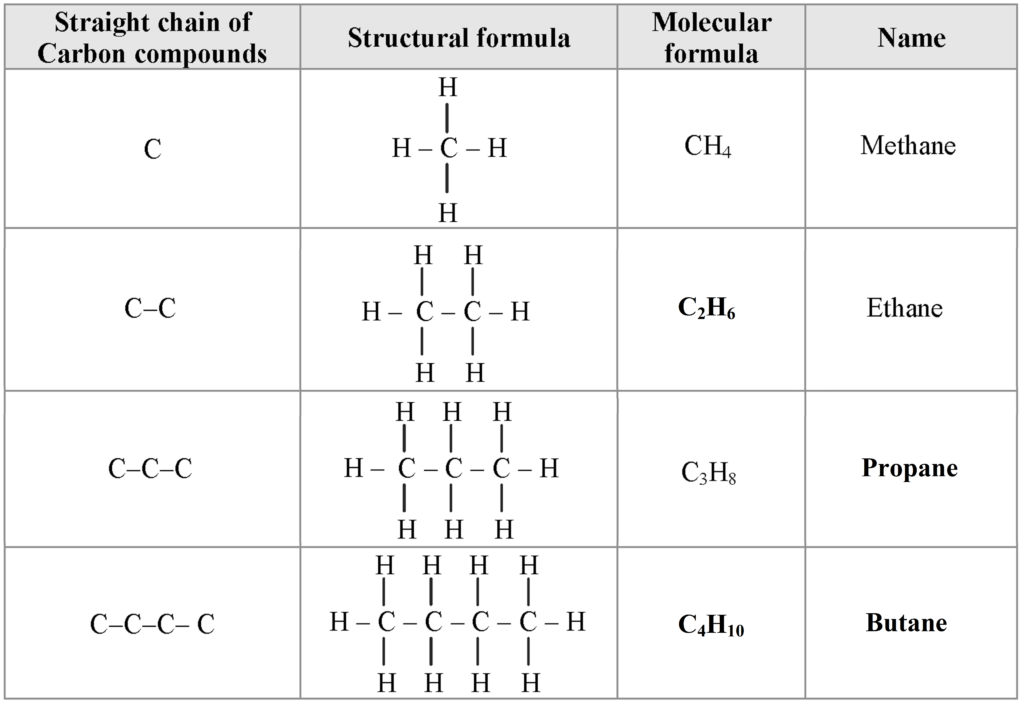
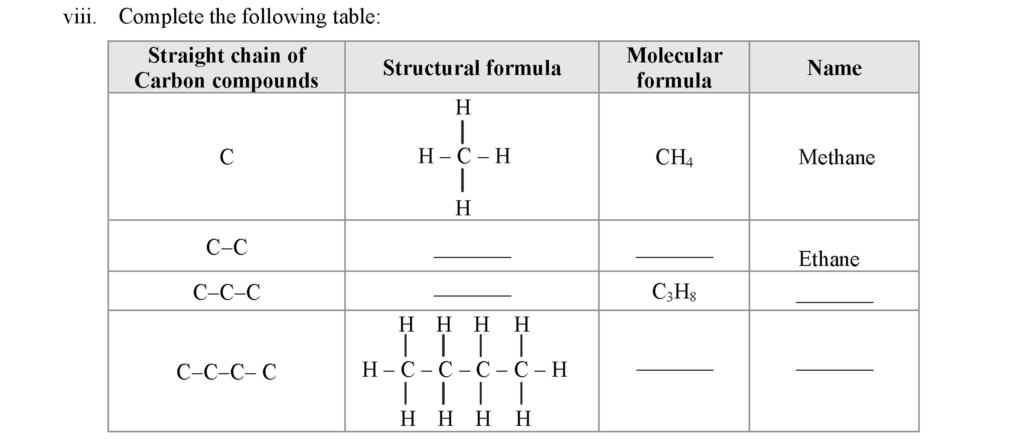
a. The compounds which contain carbon and hydrogen as the only two elements are called hydrocarbons.
b. There are two types of hydrocarbons; saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
c. 1. Cooking gas which is used in day-to-day life contains a carbon compound called butane.
2. Table sugar which is used in day-to-day life contains a carbon compound called sucrose.
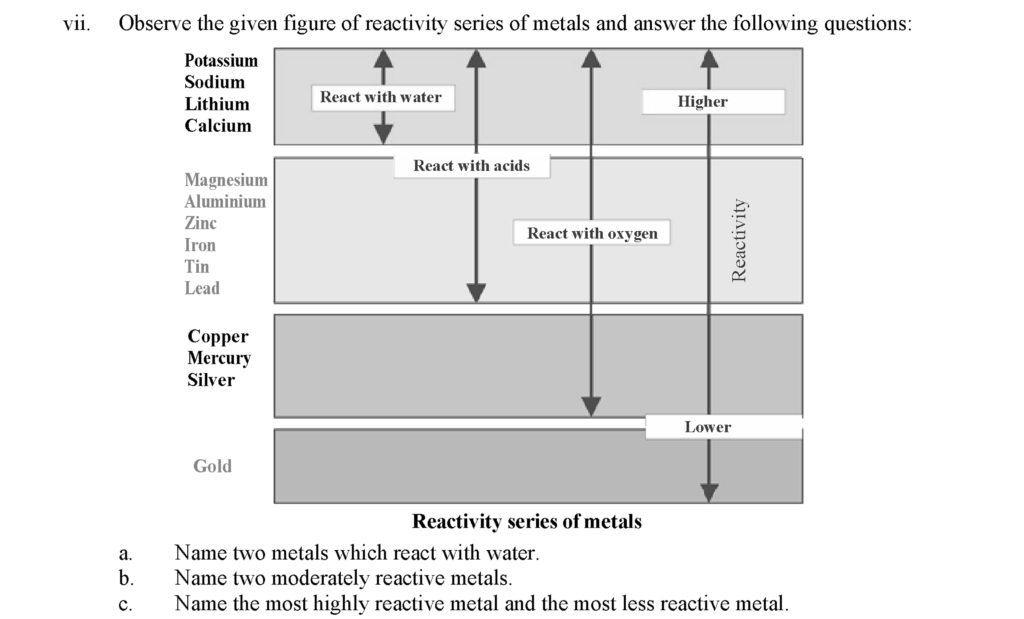
a. Two metals that react with water: Potassium, sodium
b. Two moderately reactive metals: Zinc, iron
c. 1. Most highly reactive metal: Potassium
2. Most less reactive metal: Gold

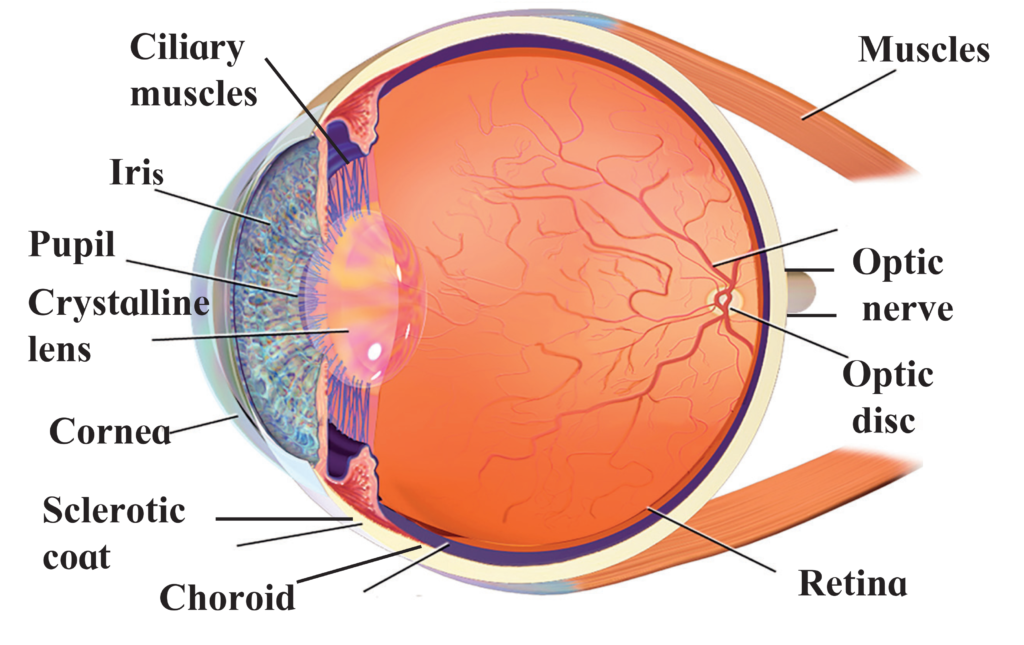
a. Convex lens
b. Cornea
c. Real and inverted

a. Rust is a reddish-brown coloured hydrated ferric oxide layer deposited on the surface of iron objects that are exposed to moist air.
b. Chemical formula of rust is Fe2O3.xH2O.
c. Anode region: Fe(s) → Fe 2+ (aq) + 2e−
d. Cathode region: Fe 2+ (aq) → Fe3+(aq) + e−
e. Metals get attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acids, etc. Metal is said to ‘corrode’ due to this attack and the process is called corrosion.