1. Working of the Constitution
Que. 6. Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the sentences.
(1) Maharashtra …………. seats are reserved for women in local self-governing institutions.
(a) 25%
(b) 30%
(c) 40%
(d) 50%
(2) Which of the following laws created a favorable environment for women to secure freedom and
self-development?
(a) Right to Information Act
(b) Dowry Prohibition Act
(c) Food Security Act
(d) None of the above
(3) The essence of democracy is ………
(a) Universal adult franchise
(b) decentralization of power
(c) Policy of reservation of seats
(d) Judicial decisions
(4) ————- ensures transparency and accountability of government.
(a) Right to Information Act
(b) Dowry Prohibition Act
(c) Food Security Act
(d) POCSO Act
Que.7. State whether the following statements are true or false. Give reasons for your answers.
1. Indian democracy is considered the largest democracy in the world.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reasons:
(1) In democracy, there is direct representation of the Indian people in the Parliament, State legislature and local government.
(2) Free and fair elections are held at regular intervals in democracy. Everyone has the right to vote irrespective of religion, gender, caste, etc.
(3) Earlier the voting age was 21 years. It was later reduced to 18 years. This lowering of voting age led to an increased participation of younger generation in the political process.
(4) Today, India has the largest number of voters compared to any other democratic nation.
Therefore, Indian democracy is considered as the largest democracy in the world.
2. Secrecy in the working of government has increased due to the right to information.
Ans. The above statement is False.
Reasons:
(1) The main objective of the Right to Information Act enacted in 2005 is to empower the citizens, promote transparency and accountability in the working of the Government and make democracy work for the people in real sense.
(2) Accordingly, it keeps the citizens informed about the functioning of the Government.
(3) Due to this act, the government has become more transparent and accountable.
Therefore, secrecy in the working of the Government has decreased due to Right to Information.
3. The nature of Constitution is seen as a living document.
Ans: The above statement is True.
Reasons:
(1) Indian Constitution is dynamic. It accepts the necessity of modifications according to changing needs of the society. These changes can be brought about by the process of amendment.
(2) The Parliament has the power to make these changes. But the judiciary has declared that the parliament while amending the Constitution should not alter the ‘basic structure’ of the Constitution.
Therefore, it can be said that the Constitution is a living document rather than a closed and static rulebook.
4. Decentralization of power is central to democratic government.
Ans. The above statement is True.
Reasons:
(1) Decentralisation controls the misuse of power.
(2) It also creates opportunities for the common people to participate in the working of the government.
Therefore, decentralization power is central to democratic government.
Que. 8. (A) Explain the following concepts.
1. Right based approach
Ans.
(1) In the decades after independence, efforts were made towards democratisation of India.
(2) In this process, citizens were considered as ‘beneficiaries’ of reforms.
(3) In the last few decades, this approach has changed and the democratic reforms which lead to development are considered as ‘rights’ of citizens.
(4) Accordingly, citizens in India have got Right to Education, Right to Information and Rights to Food Act.
2. Right to information
Ans.
(1) In 2005, the Parliament of India enacted a new legislation called the ‘Right to Information Act’.
(2) The main objective of the Right to Information Act is to empower the citizens, promote transparency and accountability in the working of the Government and make our democracy work for the people in real sense.
(3) It increases people’s participation in administration. It also makes administration more responsive to the requirements of people. This increased communication between citizens and government helps in strengthening democracy and in building a relationship of trust between them.
(4) Thus, Right to Information is a big step towards making the citizens informed about the functioning of the Government. Also, it has made the government more transparent and has reduced the element of secrecy in the working of the government.
3. Policy of reservation of seats
Ans.
(1) Policy of reservation of seats is meant for those sections of society who have been deprived of the opportunities for education and employment for a long period of time.
(2) Accordingly, in educational institutions and in government service, some seats are kept reserved for scheduled castes (SC) and scheduled tribes (ST). There is also a provision of reservation of seats for other backward classes.
(3) Thus, the policy of reservation of seats enhances the social and educational status of underprivileged communities and thus, improves their lives.
4. Prevention of atrocities act
Ans.
(1) The Scheduled Castes and Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, prevents injustice against the people belonging to Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribes.
(2) If any act of atrocity is committed against them, then the guilty person is liable for punishment.
(B) Complete the activity.
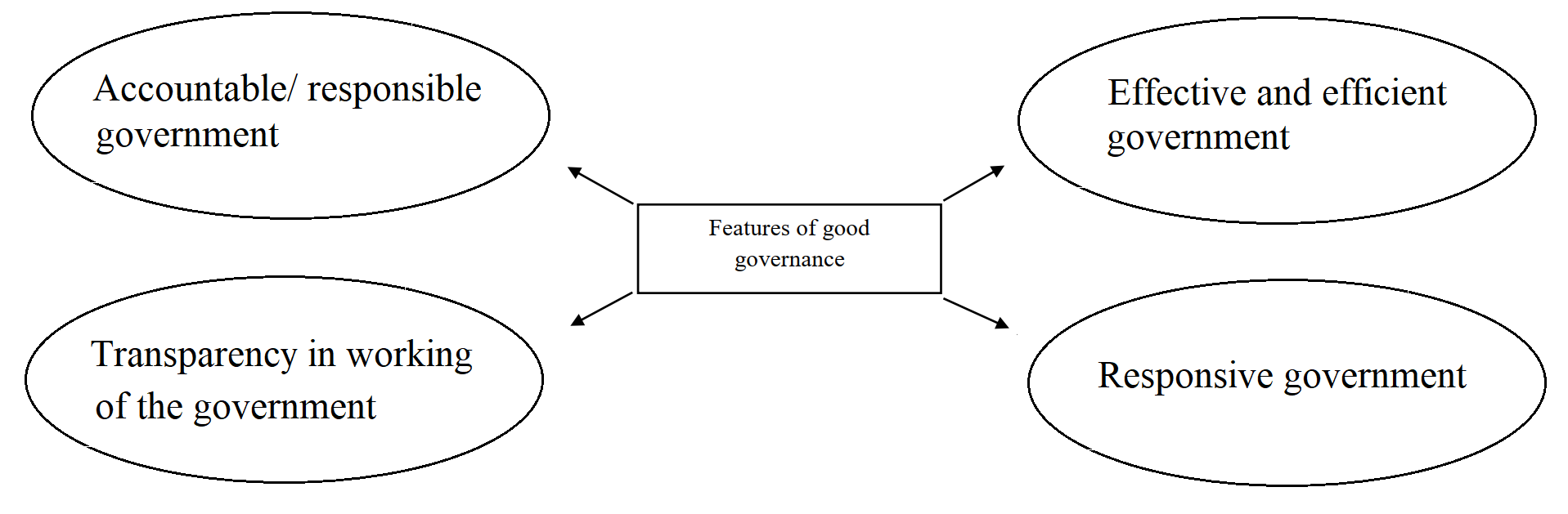
(1) Complete the following diagram:
Ans.
Que. 9. Answer in brief.
1. What are the effects of reducing the voting age from 21 years to18 years?
Ans. The effects of reducing the voting age from 21 years to 18 years are as follows:
(1) It has encouraged more young voters to take part in the political process.
(2) Therefore, at present, India has the largest number of voters compared to any other democratic nation. Due to this provision, India has become largest democracy in the world.
(3) Also, increased support of young voters in the political process has led to the emergence of new political parties.
(4) Thus, the effect of reducing the voting age from 21 years to 18 years is not only quantitative but also qualitative.
2. What is meant by establishment of social justice?
Ans.
(1) Social justice means that in the society the citizens must interact and treat one another on the basis of equality.
(2) Establishing a progressive developed society based on social justice and equality is one of the objectives of the Indian Constitution. It stands for the elimination of social discrimination on the grounds of colour, caste, creed, religion, gender or place of birth.
(3) Democratic policies must be inclusive i.e. one must try to bring all sections of the society into mainstream.
(4) Accordingly, various efforts have been taken to establish social justice in India.
For e.g. To establish justice and equality, certain efforts are made like Policy of reservation of seats for SC and ST, Prevention of Atrocities Act, provision for minorities and laws relating to women and provisions for representation.
3. Which decisions of the court has resulted in protection of honor and dignity of women?
Ans. Following are the decisions of the court that have resulted in the protection of honour and dignity of women.
(1) The enforcement of the Domestic Violence Prohibition Act by the Court has resulted in the protection of honour and dignity of women.
(2) This Act has rejected traditional forms of domination and authoritarianism. It also expanded the scope of Indian democracy to make it inclusive in true sense.
(3) Even the Dowry Prohibition Act, act against sexual harassment and the right to have an equal share in the property of the father and husband has resulted in the protection of honour and dignity of women and thus, created a favourable environment for securing their development.
4. What includes the basic structure of the Constitution?
Ans. The basic structure of the constitution generally includes following provisions:
(1) Federal structure of the Constitution
(2) Promotion of unity and integrity of the nation
(3) Sovereignty of the nation
(4) Secularism and supremacy of the Constitution