1. Answer the following questions.
a. Explain the difference between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror with respect to the type and size of the images produced.
Ans.
Plane Mirror: The image formed by plane mirror is Virtual, Upright. And size of image is same as the size of the object. Also distance between object and mirror is same as the distance between mirror and image.
Concave Mirror: The image formed by concave mirror is both real and virtual. If image is real then it is inverted and is found in front of mirror. If the image is virtual then image is upright and is formed behind the mirror. The size of image can be smaller and larger than the object size depending on the position of the object.
Convex Mirror: The image formed by convex mirror is always virtual, upright and smaller than size of the object.
b. Describe the positions of the source of light with respect to a concave mirror in 1. Torch light 2. Projector lamp 3. Floodlight
Ans.
(i) Torch light: The source of light is placed at the focus. Because in Concave Mirror if the object is placed at Focus then its image is formed at the infinity hence we can get a light to longer distances.
(ii) Projector lamp : The source of light is placed at the centre of curvature. Because if object is placed at the center of curvature then its image is same as the size of the object, and real. Hence image can be taken on the screen.
(iii) Flood light : The source of light is placed just beyond the centre of curvature. Because the image formed is real and Magnified , hence we can get wider area of light.
c. Why are concave mirrors used in solar devices?
Ans.
(1) Concave Mirrors are used in the solar devices like Solar Cooker, Solar Furnace etc.
(2) When sun rays fall on the concave mirror, they converge and come together in the focus.
(3) Due to convergence, the intensity of sun rays increases and the light collected at the focus has lot of thermal energy so the food or water is heated faster. Hence, concave mirrors are used in solar devices.
d. Why are the mirrors fitted on the outside of cars convex?
Ans.
(1) A convex mirror is used as rear view mirror because they form erect, virtual, and diminished images.
(ii) This, allows the driver to view a large area in a small mirror.
e. Why does obtaining the image of the sun on a paper with the help of a concave mirror burn the paper?
Ans.
(1) When sun rays fall on the concave mirror, they converge and come together at the focus.
(ii) Due to convergence the intensity of sun rays increases.
(iii) Hence, image of the sun on a paper with the help of a concave mirror burns the paper.
f. If a spherical mirror breaks, what type of mirrors are the individual pieces?
Ans.
The individual pieces of the broken spherical mirror are the spherical mirror itself. It may be of two types:
a.) Concave (reflecting surface curved inwards).
b.) Convex (reflecting surface curved outwards).
2. What sign conventions are used for reflection from a spherical mirror?
a. Bleaching powder has the odour of chlorine.
Ans.
According to the Cartesian sign convention, the pole of the mirror is taken as the origin. The principal axis is taken as the X-axis of the frame of reference. The sign conventions are as follows.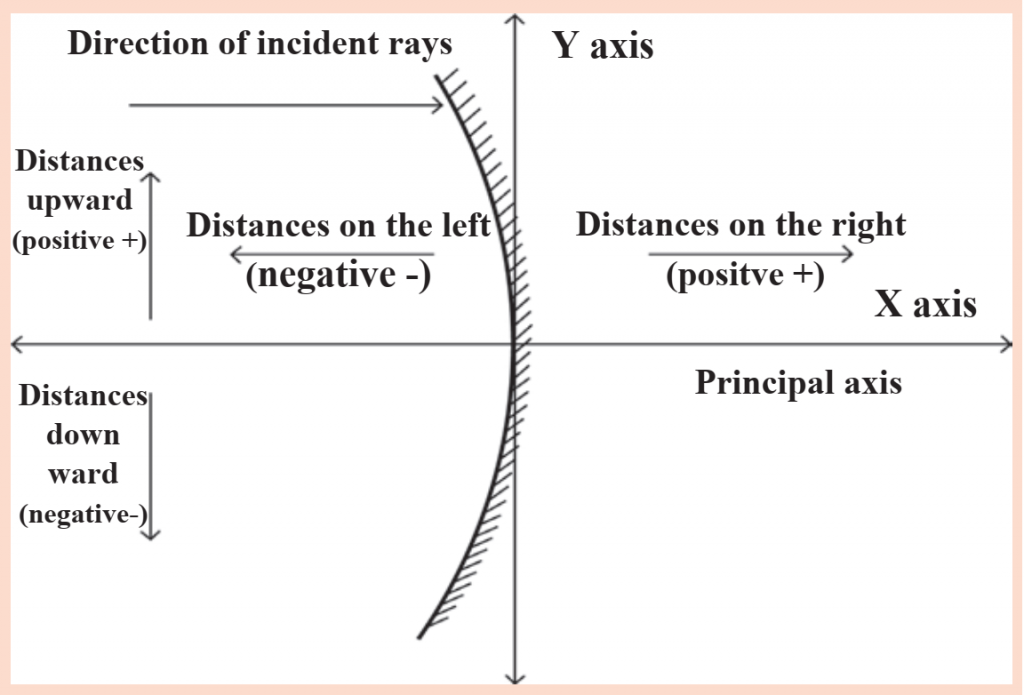
1. The object is always kept on the left of the mirror. All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
2. All distances measured towards the right of the pole are taken to be positive, while those measured towards the left are taken to be negative.
3. Distances measured vertically upwards from the principal axis are taken to be positive.
4. Distances measured vertically downwards from the principal axis are taken to be negative.
5. The focal length of a concave mirror is negative while that of a convex mirror is positive.
3. Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors as described in the table on page 122.
Ans.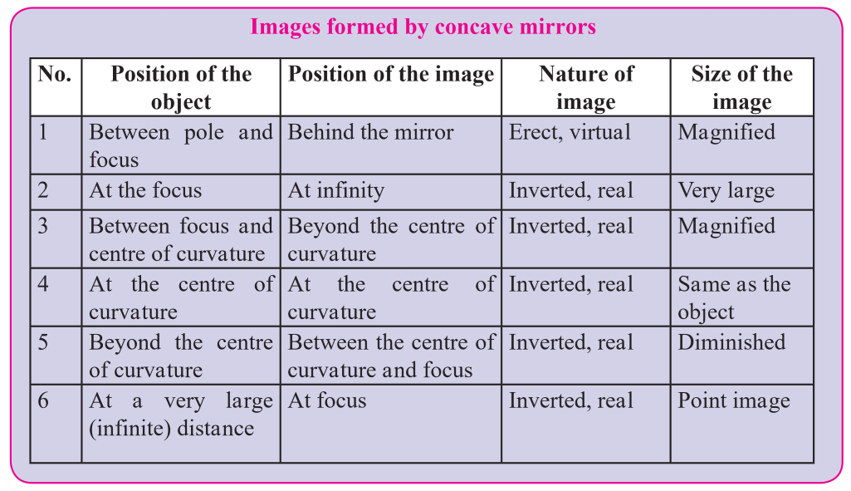
(1) Between Pole and Focus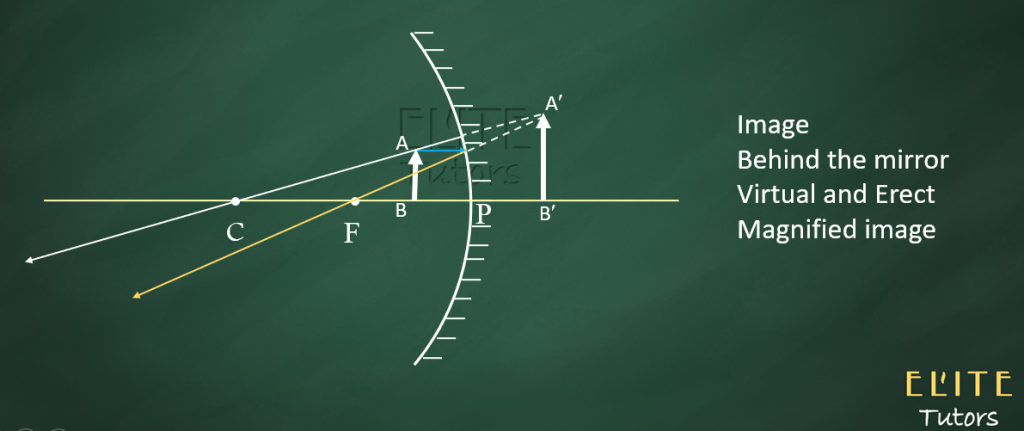
(2) at the Focus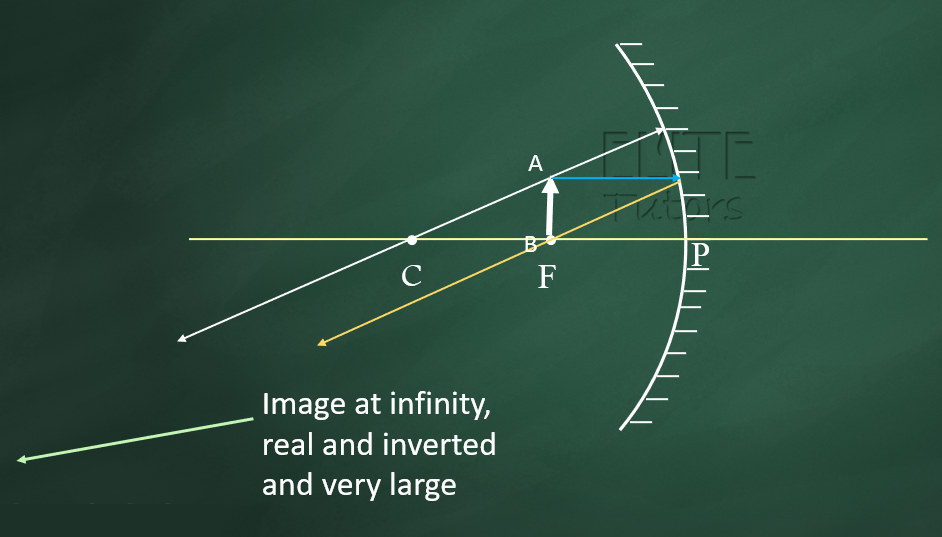
(3) Between Focus and Centre of Curvature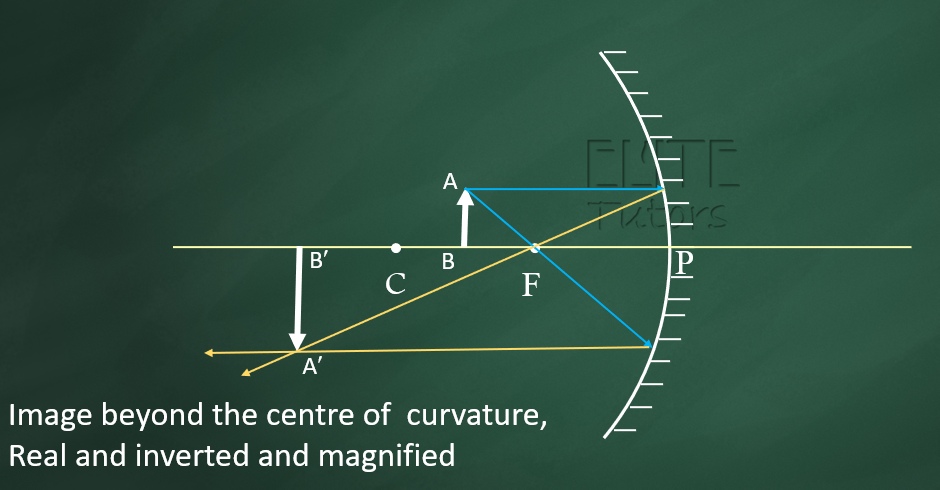
(4) At Centre of Curvature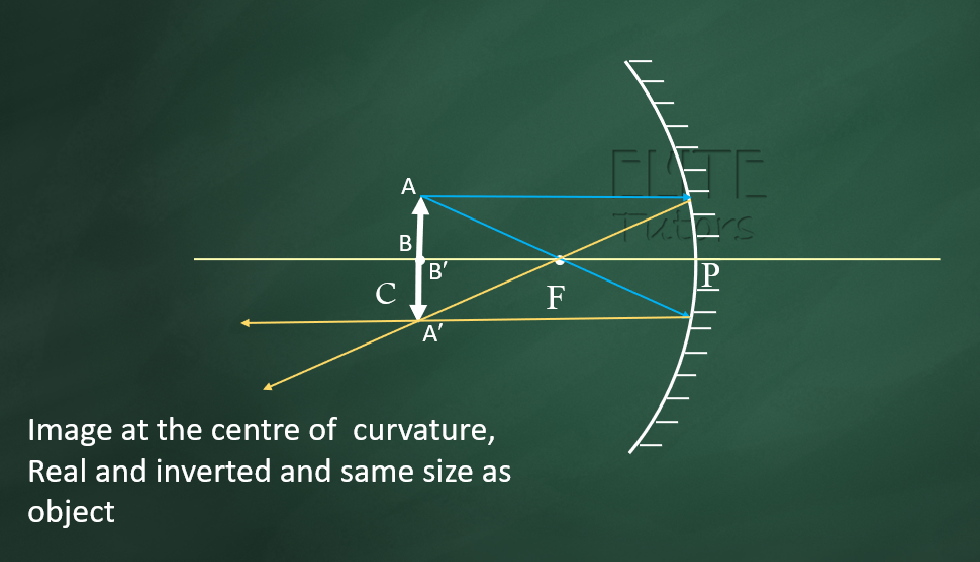
(5) Beyond Centre of Curvature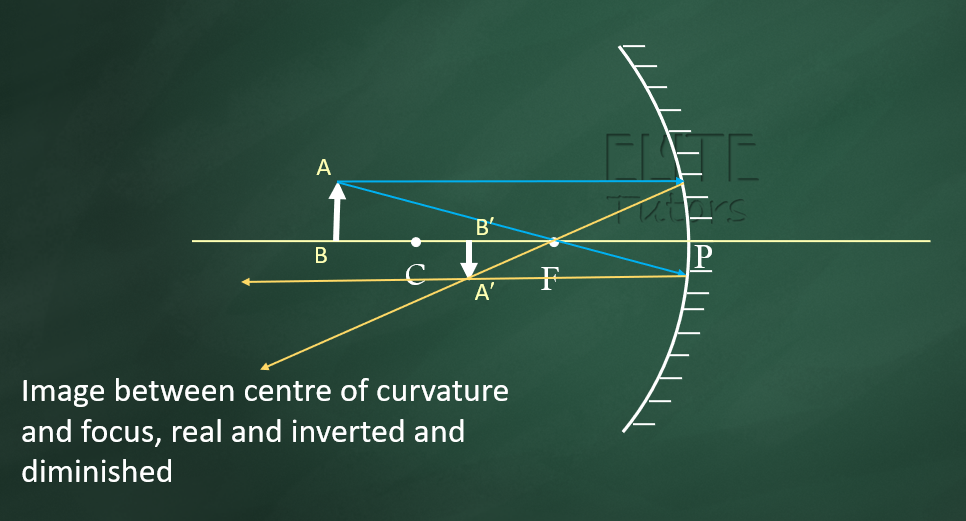
(6) At a very large (infinite) distance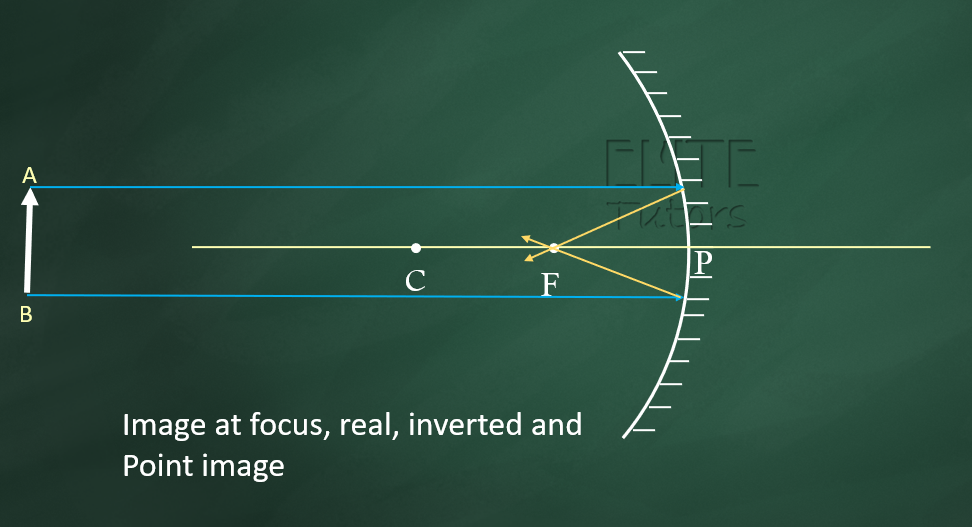
4. Which type of mirrors are used in the following?
Ans.
Periscope – Plane mirror
Floodlights – Concave mirror
Shaving mirror – Concave mirror
Kaleidoscope – Plane mirror
Street lights – Convex mirror
Head lamps of car – Concave mirror
5. Solve the following examples
a. An object of height 7 cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm in front of a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 15 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be kept so as to get a clear image? What will be the size and nature of the image?
b. A convex mirror has a focal length of 18 cm. The image of an object kept in front of the mirror is half the height of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
c. A 10 cm long stick is kept in front of a concave mirror having focal length of 10 cm in such a way that the end of the stick closest to the pole is at a distance of 20 cm. What will be the length of the image?
6. Three mirrors are created from a single sphere. Which of the following – pole, centre of curvature, radius of curvature, principal axis – will be common to them and which will not be common? 
Ans.
(i) Centre of curvature and Radius of curvature will be common for all three pieces.
(ii) Pole and Principal axis will not be common.