Q.1. B. IX. Identify who I am!
1. Carbon allotropes
2. Amphoteric oxide forming metal
3. Ore of Aluminum
4. Metal in Liquid state
Answers:
1. Diamond and graphite
2. Aluminium
3. Bauxite
4. Mercury
Question 2 (A) Write Scientific reasons. (2 marks each)
1. The value of acceleration g is greater at the pole than at the equator.
Ans:
i. The shape of the earth is not perfectly spherical. It is slightly flattened at the poles and bulged at the equator.
ii. As a result, the radius of the earth at the poles is less than that at the equator.
iii. But, acceleration due to gravity (g) on earth’s surface is given as, 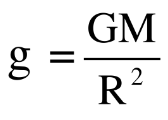 therefore acceleration due to gravity increases with the decrease in radius of earth and vice versa.
therefore acceleration due to gravity increases with the decrease in radius of earth and vice versa.
iv. Hence, the value of acceleration due to gravity (g) is greater at the pole than at the equator.
2. The value of gravitational acceleration (g) decreases as we go above the Earth’s surface.
Ans.
i. As the height of an object from the surface of the earth increases, the distance between the object and the centre of the earth (r) increases.
ii. But, acceleration due to gravity (g) at distance ‘r’ from the centre of earth is given as, 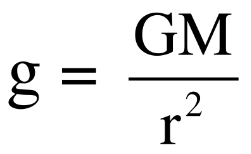 , therefore acceleration due to gravity (g) decreases with the increase in ‘r’
, therefore acceleration due to gravity (g) decreases with the increase in ‘r’
iii. As a result, the value of gravitational acceleration (g) decreases as we go above the earth’s surface.
3. The value of gravitational acceleration (g) decreases as we go deep inside the earth.
Ans.
i. The acceleration due to gravity (g) on earth’s surface is given as, 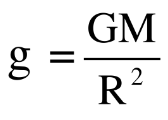 , The value of g depends on the mass M of the earth and the radius R of the earth.
, The value of g depends on the mass M of the earth and the radius R of the earth.
ii. As we go inside the earth, our distance from the centre of the earth decreases and no longer remains equal to the radius of the earth (R).
iii. Along-with the distance, the part of the earth which contributes towards the gravitational force felt also decreases, decreasing the value of (M).
iv. Due to combined result of change in R and M, value of g decreases as we go deep inside the earth.
4. When we drop a feather and a stone at the same time from a height the stone reach the earth faster than a feather. (Omitted for academic year 2021-2022)
5. The weight of an object varies on different planets.
Ans. i. The weight of an object of mass m on a planet is given by, Wp = mgp Where, gp = acceleration due to gravity at the planet.
ii. Also, acceleration due to gravity on the planet is given by 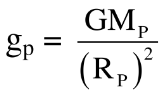 where, Mp = mass of the planet and Rp = radius of the planet
where, Mp = mass of the planet and Rp = radius of the planet
iii. Since MP and RP are different on different planets, the weight of an object will be different on different planets even though its mass remains constant.
6. The value of gravitational acceleration (g) is taken to be -g when studying the motion of an object thrown upwards in a straight line.
Ans. i. For motion of an object thrown upwards, magnitude of g is the same throughout the motion but the velocity of the object decreases with the increase in height.
ii. For object thrown upwards, the direction of acceleration due to gravity is opposite to the velocity of the object.
iii. Hence, the value of gravitational acceleration (g) is taken to be -g when studying the motion of an object thrown upwards in a straight line.
7. The value of g at the center of the earth is zero.
Ans. i. The acceleration due to gravity (g) on earth’s surface is given as, 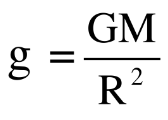 The value of g depends on the mass M of the earth and the radius R of the earth.
The value of g depends on the mass M of the earth and the radius R of the earth.
ii. As we go inside the earth, our distance from the centre of the earth decreases and no longer remains equal to the radius of the earth (R).
iii. Along-with the distance, the part of the earth which contributes towards the gravitational force felt also decreases, decreasing the value of (M).
iv. Due to combined result of change in R and M, value of g becomes zero at the centre of the earth.
8. Mendeleev kept vacant places in the periodic table.
Ans. i. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, the elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses such that chemically similar elements are placed together in a group.
ii. However, while arranging the elements, Mendeleev kept vacant places in the periodic table for elements not discovered till then.
iii. Three of these unknown elements were given the names eka-boron, eka-aluminium and eka-silicon from the known neighbours.
iv. The atomic masses of these elements were indicated as 44, 68 and 72, respectively. He also predicted their properties.
9. There was ambiguity about the correct position of hydrogen in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Ans. i. Hydrogen resembles alkali metals. It has one electron in its outermost shell like alkali metals. Its valency is 1 like alkali metals. It forms oxides (H2O) similar to alkali metals (Na2O). However, hydrogen also resembles halogens. It is a diatomic molecule (H2) like halogens (F2, Cl2). It is one electron deficient to achieve stable electronic configuration similar to halogens.
ii. Due to this unique behaviour of hydrogen, it could not be decided whether the correct position of hydrogen is in the group of alkali metals or in the group of halogens.
Thus, there was ambiguity about the correct position of hydrogen in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
10. Boron and oxygen elements are placed in the second period in periodic table.
Ans. i. Electronic configuration of boron is (2, 3). Electronic configuration of oxygen is (2, 6).
ii. Both boron and oxygen have electrons in the two shells, K and L.
iii. The elements with the same number of shells occupied by electrons belong to the same period.
Hence, boron and oxygen elements are placed in the second period in periodic table.
11. There was no definitive place for isotope in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Ans. i. Isotopes were diseovered long time after Mendeleev developed the periodic table.
ii. Isotopes have same chemical properties but different atomic masses.
Therefore, there was no definitive place for isotope in Mendeleev’s periodic table.
12. Lithium and sodium are included in the same group in periodic table.
Ans. i. Electronic configuration of lithium is (2, 1). Electronic configuration of sodium is (2, 8, 1).
ii. Both lithium and sodium have single electron in their outermost shell.
iii. Their valency is 1.
iv. In the periodic table, elements belonging to the same group have the same valency.
Hence, lithium and sodium are included in the same group in periodic table.
13. In same periods boron and oxygen elements have different atomic size.
Ans. i. Boron and oxygen are placed in the same period. However, their atomic numbers are different.
ii. Atomic number of boron is 5 and that of oxygen is 8.
iii. In a period, as atomic number increases from boron to oxygen, the positive charge on the nucleus increases. At the same time, electrons get added in the same outermost shell. This increases effective nuclear charge.
iv. As a result, electrons are attracted closer to the nucleus decreasing the size of the oxygen atom.
Hence, in same period, boron and oxygen elements have different atomic size.
14. The metallic character of elements increases while going down the groups.
Ans. i. While going down a group a new shell gets added, resulting in an increase in the distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
ii. This results in lowering the effective nuclear charge and thereby lowering the attractive force on the valence electrons.
iii. As a result of this, the tendency of the atom to form cation by losing electrons increases.
iv. The metallic character of an atom is its tendency to lose electrons.
Hence, the metallic character of elements increases while going down the groups.
15. The non-metallic character increasing while going from left to right in a period.
Ans. i. While going from left to right in a period, electrons are added to the same outermost shell. At the same time, protons get added in the nucleus increasing the nuclear charge.
ii. Hence, these electrons experience greater pull from the nucleus due to increased effective nuclear charge.
iii. As a result, the ability of an atom to become anion by accepting outside electrons increases.
iv. The non-metallic character of an atom is its tendency to gain electrons.
Hence, non-metallic character increases while going from left to right in a period.
16. In a group , the size of the atom increases as it goes down from the top.
Ans. i. While going down from the top to bottom in a group, number of shells increases.
ii. The outermost electrons go farther and farther from the nucleus, extending the radius and ultimately increasing the size of the atom even though the nuclear charge increases.
Hence, in a group, the size of the atom increases as it goes down from the top.
17. In group 2, beryllium and calcium elements, calcium is the most electropositive element than beryllium.
Ans. i. Electronic configuration of beryllium is (2, 2). Electronic configuration of calcium is (2, 8, 8, 2).
ii. Among beryllium and calcium elements, calcium has the least effective nuclear charge exerting attractive force on valence electrons.
iii. This is because of the electrons in the inner shells, which lie in between the valence shell and the nucleus.
iv. These electrons act as a shield reducing the attractive force of the nucleus on the valence electrons. Therefore, calcium can lose its valence electrons more readily than beryllium.
Hence, in group 2, calcium is more electropositive element than beryllium.
18. Elements belonging to the same group have the same valency.
Ans. i. The electronic configuration of the outermost – shell is same for all the elements belonging to the same group.
ii. So, the number of valence electrons for all the elements in a group is the same.
iii. The valency of an element is determined by the valence electrons.
Hence, elements belonging to the same group have the i same valency.
19. Always Paints door and windows before using their nets./Always paint grills of doors and windows before using them.
Ans. i. Grills of doors and windows are generally made up of iron metal.
ii. Before painting, iron metal is in direct contact with the moisture in atmosphere.
iii. Moist air attacks the surface of iron metal and causes rusting (i.e., corrosion of iron).
iv. Contact between iron and moist air can be avoided by applying paint on grills of doors and windows. This prevents rusting and protects them from damage.
Hence, grills of doors and windows are always painted before they are used.
20. It is recommended to use air tight container for storing oil for long time.
Ans. i. When edible oil is left aside for long time, it undergoes air oxidation.
ii. Due to this, the taste and smell of oil changes and it becomes rancid. If food is cooked in this oil, its taste also changes.
iii. Thus, the oil will become unfit for consumption.
iv. The process of oxidation reaction of oil can be slowed down by storing it in air tight container.
Hence, it is recommended to use air tight container for storing oil for long time.
21. When the gas formed heating the limestone is passed through the freshly prepared lime water, the lime water turns milky.
Ans.
(1) When limestone is heated, calcium oxide and carbon dioxide gas are formed.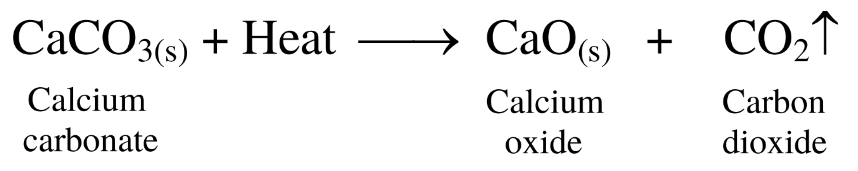
(2) When carbon dioxide gas is passed through freshly prepared lime water, the solution turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate, which is insoluble in water.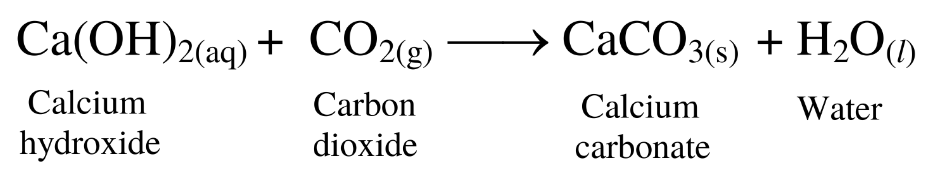
22. It takes time for pieces of Shahabadi tile to disappear in HCl but it’s powder disappears rapidly.
Ans.
(1) The rate of a chemical reaction depends upon the size of the reactant particles taking part in the reaction.
(2) Smaller the size of the reactant particles, higher is the rate of reaction.
(3) The size of reactant particles is more in pieces of Shahabad tile as compared to powder of Shahabad tile.
(4) When HCl is added to pieces of Shahabad tile, the CO2 effervescence is formed slowly. However, when HCl is added to Shahabad powder, the CO2 effervescence is formed at a faster rate.
Hence, it takes time for pieces of Shahabad tile to disappear in HCl, but its powder disappears rapidly.
23. In practice the unit of kWh is used for the measurement of electrical energy, rather than Joule. (Omitted for academic year 2021-2022)
Ans.
(1) Electrical energy = Electrical power × time.
(2) For practical applications, devices consuming high electrical power are used over the period of time.
(3) This leads to heavy expenditure of electrical energy. To measure such value of energy unit joule is significantly small.
Hence, unit kWh is used in practice. Unit 1 kWh represents power of 1 kW used for 1 hour and equals 3.6 × 106 J.
24. Tungsten metal is used to make a solenoid type coil in an electric bulbs.
Ans.
(1) Electric bulb works on the principle of heating effect of electric current.
(2) The solenoid type coil of bulb has high resistivity and very high melting point.
(3) When current is passed through the bulb, solenoid type coil of bulb gets heated to high temperature (upto 3400 °C) and starts glowing.
Hence, tungsten metal is used to make a solenoid type coil in an electric bulb.
25. For electric power transmission , Copper or aluminum wires is used.
Ans.
(1) Copper and aluminium contain large number of free electrons.
(2) These free electrons can move throughout conductor easily.
(3) This results into copper and aluminium having low values of resistivity.
(4) Thus, copper and aluminium are good conductors of electricity and offer low resistance to the flow of current.
Hence, copper or aluminium arc used for electric power transmission.
26. Nowadays MCBs are used in homes,to stop the current in the circuit which suddenly increases. (Omitted for academic year 2021-2022)
Ans.
(1) Electrical appliances used in homes like geyser, heater, motor, oven, washing machine, etc. have high power consumption.
(2) If such appliances are connected simultaneously, large amount of current flows in the circuit.
(3) This current may exceed permissible value and cause overloading.
Hence, nowadays MCBs arc used in homes, to stop the current in the circuit which suddenly increases due to overloading.
27. A coil made up of alloy Nichrome is used in the electric heater-cooker as a resistor.
Ans.
(1) The electric heater-cooker works on the principle of heating effect of electric current.
(2) Alloys (such as nichrome) as compared to metals have higher resistivity.
(3) Unlike metals they can be heated to higher temperature.
Hence, a coil made up of alloy nichrome is used in the electric heater-cooker as a resistor.
28. It is beneficial to carry electrical energy in reverse form as it is carried over long distances. (Omitted for academic year 2021-2022)
Ans.
(1) There is minimum power loss, when an electrical energy is carried over long distances in the form of AC.
(2) Hence, it is beneficial to carry electrical energy in AC form as it is carried over long distances.
29. In cold regions, in winter the pipes for water supply breaks.
Ans.
(1) In cold region, as temperature reaches below 4°C, water instead of contracting, starts expanding due to its anomalous behaviour.
(2) As temperature decreases from 4°C to 0°C, volume of water increases continuously.
(3) At the same time, metal pipes carrying water undergo contraction.
(4) As a result, pipes experience force applied by water and break.
30. Even if boiling water is constantly heated, its temperature does not rise.
Ans.
(1) The heat energy absorbed at constant temperature during transformation of liquid into gas is called the latent heat of vaporisation.
(2) When heat is supplied to boiling water, it is used to weaken the bonding between molecules of a water, causing transformation from liquid state to gaseous state, i.e., steam.
(3) As the heat supplied is utilised for the change of state entirely, temperature of water does not change.
31. Use a pressure cooker to cook food in cold air.
Ans.
(1) Normally, in cold air, more heat energy needs to be supplied to attain high temperatures required for cooking food. It also consumes more time.
(2) Whereas, pressure cooker operates by giving out the air within the cooker and trapping steam produced from the liquid, (mostly water) boiling inside.
(3) Due to high internal pressure, boiling point of liquid increases and liquid boils at temperature higher than its boiling point.
(4) The increased boiling point allows more absorption of heat by liquid and steam formed is superheated causing food to get cooked quickly.
Hence, it is advisable to use a pressure cooker to cook food in cold air.
32. In the cold regions, snow falls in winter.
Ans.
(1) Snow is formed high in the clouds from water vapour.
(2) In cold regions when temperature is extremely low, water vapour freezes around smoke or dust particles forming ice crystals.
(3) When these ice particles combine with each other they turn heavy and start falling to the ground.
This gives rise to snowfall in cold regions in winter.
33. The bottom of some steel utensils used for cooking is copper.
Ans.
(1) Copper is better conductor of heat as compared to steel.
(2) Also, copper can conduct faster than steel.
(3) As a result, copper bottom gets heated faster than the steel.
(4) This reduces time for cooking as well as saves heat energy and fuel.
Hence, the bottom of some steel utensils used for cooking is copper.
34. Drops of water can be seen accumulating on the glass of vehicles in the early hours of w inter.
Ans.
(1) When temperature of air at early hours in winter falls, air becomes saturated with vapour.
(2) As a result, the excess vapour condenses on surface of objects in the form of dew.
(3) When the dew settles on glass of vehicles, drops of water accumulating on glass can be seen.
35. During winter season, we may have observed a white trail at the back of the aeroplane flying high in the clear sky or sometimes it may not get formed.
Ans.
(1) The ratio of actual mass of vapour content in the air for a given volume and temperature to that required to make the air saturated with vapour at that temperature is called the relative humidity.
(2) The white trail is basically the vapour released by aeroplane engine condensing in sky to form cloud.
(3) If the relative humidity of surrounding air is more then, we may get to observe this white trail at the back of the aeroplane flying high in the clear sky.
(4) If the relative humidity of surrounding air is less then, either small sized white trail may get formed or it may not get formed at all.
36. Fish can survive even in frozen ponds in cold regions.
Ans.
(1) In cold climate, temperature of water in ponds and lakes starts falling.
(2) On getting colder, water contracts. As a result, density of water increases and it goes down. To replace it, warmer water from below rises up. This process continues till temperature of water at the bottom of pond becomes 4°C.
(3) Water, due to its anomalous behaviour possesses maximum density at 4°C.
(4) If the temperature lowers further, ice is formed at the surface of pond with water below it.
(5) Ice being poor conductor of heat blocks the further heat exchange between atmosphere and water in the pond.
(6) This prevents freezing of water below surface of ponds or lakes enabling survival of fishes.
37. Placing a plastic bottle filled with water in the freezing compartment in the freezer can cause the bottle to explode.
Ans.
(1) Temperature of freezer section in a refrigerator is maintained below 0°C.
(2) When a plastic bottle filled completely with water is placed in the freezer, temperature of water starts falling down.
(3) When the temperature of water reaches 4°C, due to its anomalous behaviour, water starts expanding.
(4) As temperature of water continues to fall upto 0°C, water continues to expand. When water is converted into ice at 0 °C, there is an increase in the volume.
(5) This exerts pressure on the sides of the bottle. As a result, there is a probability of breaking or exploding of the bottle.
38. Even the wire moves through the ice slab, the ice slab does not break.
Ans.
(1) When the wire with weights attached to its two ends is placed on the ice slab, its weight acts along very small area of contact between the wire and ice.
(2) As a result, pressure gets applied on that part of ice-slab.
(3) This lowers the melting point of ice below 0°C and ice is converted into water.
(4) The wire cuts through water and shifts downward.
(5) As the wire displaces, pressure applied by wire on ice slab vanishes and its melting point is restored to 0°C causing freezing of ice.
(6) In this manner, due to regelation wire moves through the ice slab completely without breaking it.
39. The sun appears on the western horizon for some time after sunset.
Ans.
(1) As ray of light from the Sun enters the earth’s atmosphere, it follows a curved path due to refraction, before reaching the observer.
(2) This makes the apparent position of the Sun slightly higher than actual position for the observer.
(3) Hence, due to atmospheric refraction of sunlight, the observer on the earth continues to see the setting Sun for two minutes after the Sun has dipped below the horizon, thus delaying the sunset.
40. The bottom of a pond appears raised. (Question Edited)
Ans:
(1) The rays of light coming from the bottom of a pond bend away from the normal as they travel from water (denser medium) to air (rarer medium).
(2) Hence, they appear to come from a point above the actual point from which they come. Therefore, the bottom of the pond appears raised.
41. The stars twinkle but we don’t see twinkling of planets.
Ans.
(1) Due to the motion of atmospheric air and change in density and temperature, the atmosphere is not steady. As a result, refractive index of air in given region changes continuously and randomly.
(2) Due to this, the position and brightness of the star keeps changing continuously and the star appears to be twinkling.
(3) The rays of light from a planet pass through the atmosphere of the earth. As compared to stars, planets are nearer to earth. So a planet can be considered as a collection of large number of point sources of light.
(4) If the intensity of light from one point source decreases, it increases from the other source. Thus, the average intensity remains the same. Hence, stars twinkle but we do not see the twinkling of planets.
42. The coin disappears in a vessel as it is seen from a specific location. But as soon as the water is poured into the vessel to a certain level, the coin appears.
Ans.
(1) Light rays coming from the coin emerge out of water and change their direction due to refraction of light.
(2) Hence, as soon as the water is poured into the pot to a certain level, the coin appears.
43. A pencil appears to be broken near the surface of water.
Ans.
(1) When one look at the portion of the pencil that is inside the water, light travels from water to air via glass.
(2) This light ray changes the medium and undergoes refraction.
(3) As a result, the pencil inside the water appears to be broken near the surface of water.
44. A convex lens is called a converging lens.
Ans.
(1) When light rays parallel to the principal axis are incident on a convex lens, they converge to a point on the principal axis.
(2) Due to its ability of collecting rays together, a convex lens is called as converging lens.
45. Nearsightedness, this defect can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lens.
Ans.
(1) Nearsightedness arises due to slight elongation of eyeball causing in increase in the distance between the eye lens and the retina or due to increase in the curvature of the cornea and eye lens resulting in increased converging power.
(2) As a result, light from a distant object arriving at the eye-lens gets converged at a point in front of the retina.
(3) When a concave lens of suitable focal length is placed between the eye and object, due to the diverging effect of the concave lens, the image gets focused on the retina.
Thus, nearsightedness can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lens.
46. Farsightedness, this defect can be corrected by using convex lens.
Ans.
(1) Farsightedness arises due to slight flattening of the eyeball causing in decrease in the distance between the eye lens and the retina or due to decrease in the curvature of the cornea and eye lens resulting in decreased converging power.
(2) As a result, light from a distant object arriving at the eye-lens gets converged at a point behind the retina.
(3) When a convex lens of suitable focal length is placed between the eye and object, due to the converging effect of the convex lens, the image gets focused on the retina.
Thus, farsightedness can be corrected by using spectacles with convex lens.
47. Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
Ans.
(1) The ability of the ciliary muscles near the eye lens to change the focal length of the lens decreases with age.
(2) As a result, sometimes adults suffer from both nearsightedness and farsightedness.
Therefore, adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
48. Presbyopia effect is more common in people over 40 years of age.
Ans.
(1) Focusing power of the eye lens decreases with age.
(2) Also, with progressing age, ciliary the muscles near the eye lens lose their ability to adjust the focal length of the lens.
(3) This defect of vision is called as presbyopia.
(4) Thus, it is more common in people over 40 years of age.
49. Simple microscope is used for watch repairs.
Ans.
(1) A magnification of about 20 times is obtained by simple microscope.
(2) When an object is placed within the focal length of convex lens, one gets a magnified and erect image of the object.
(3) Thus, the watch repairer can see the minute parts of the watch more clearly with the help of simple microscope than the naked eye, without any strain on the eye.
Hence, simple microscope is used for watch repairs.
50. One can sense colours only in bright light
Ans.
(1) The retina in human eyes is made of different cells viz., rod-shaped and cone-shaped.
(2) The rod-shaped cells respond to intensity of light and send the information to brain. While cone shaped cells send information of different colours of light to the brain.
(3) Rod like cells are sensitive to faint light, whereas, the conical cells do not respond to faint light.
Hence, one can sense colours only in bright light.
 (2) The reaction is exothermic and therefore, the released hydrogen gas readily catches fire on exposure to air.
Hence, to prevent accidents, sodium is stored in kerosene.
54. Pine oil is use in froth floatation.
Ans.
(1) Pine oil is hydrophobic.
(2) The particles of the metal sulphide ores which are hydrophobic get wetted by pine oil.
(3) They float with the foam on the surface of water.
(4) Thus, by using this property some ores which contain hydrophobic particles in them can be concentrated by froth floatation process.
Hence, pine oil is used in froth floatation.
55. Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Ans.
(1) The green colour on copper vessels is due to formation of copper carbonate on it.
(2) Copper carbonate reacts with acids present in lemon or tamarind and as a result, this copper carbonate layer gets removed.
Hence, lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned green.
56. Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
Ans.
(1) During the electrolysis of alumina, oxygen gas is liberated at the anode.
(2) Oxygen reacts with the graphite anode to form carbon dioxide.
(3) Thus, the mass of graphite rods decrease over the time.
Hence, anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
57. Generally the ionic compounds have high melting points.
Ans.
(1) Ionic compounds are composed of cations and anions.
(2) These ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
(3) Considerable amount of energy is required to break these strong forces of attraction.
Hence, melting points of ionic compounds are high.
58. Adding zinc particles to a solution of copper sulphate makes the blue solution colorless.
Ans.
(1) Zinc is more reactive than copper.
(2) Therefore, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
(2) The reaction is exothermic and therefore, the released hydrogen gas readily catches fire on exposure to air.
Hence, to prevent accidents, sodium is stored in kerosene.
54. Pine oil is use in froth floatation.
Ans.
(1) Pine oil is hydrophobic.
(2) The particles of the metal sulphide ores which are hydrophobic get wetted by pine oil.
(3) They float with the foam on the surface of water.
(4) Thus, by using this property some ores which contain hydrophobic particles in them can be concentrated by froth floatation process.
Hence, pine oil is used in froth floatation.
55. Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Ans.
(1) The green colour on copper vessels is due to formation of copper carbonate on it.
(2) Copper carbonate reacts with acids present in lemon or tamarind and as a result, this copper carbonate layer gets removed.
Hence, lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned green.
56. Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
Ans.
(1) During the electrolysis of alumina, oxygen gas is liberated at the anode.
(2) Oxygen reacts with the graphite anode to form carbon dioxide.
(3) Thus, the mass of graphite rods decrease over the time.
Hence, anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
57. Generally the ionic compounds have high melting points.
Ans.
(1) Ionic compounds are composed of cations and anions.
(2) These ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction.
(3) Considerable amount of energy is required to break these strong forces of attraction.
Hence, melting points of ionic compounds are high.
58. Adding zinc particles to a solution of copper sulphate makes the blue solution colorless.
Ans.
(1) Zinc is more reactive than copper.
(2) Therefore, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
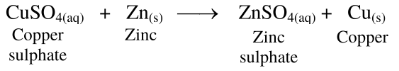 (3) The blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate.
Hence, adding zinc particles to a solution of copper sulphate makes the blue solution colorless.
59. Anodization method is useful for prevention of the corrosion of the aluminium.
Ans.
(1) The process of coating metals such as aluminium and copper with a thin and strong layer of their oxides by electrolysis is called anodizing process.
(2) When aluminium is anodized, the thin layer of aluminium oxide is formed all over the surface. This restricts the contact of aluminium metal with oxygen and water and prevents corrosion of aluminium.
Hence, anodization method is useful for prevention of the corrosion of the aluminium.
60. On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
Ans.
(1) On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time. This is because silver undergoes corrosion when it is exposed to air containing hydrogen sulphide.
(2) Silver reacts with hydrogen sulphide in air to form a layer of silver sulphide (Ag2S), which gives blackish appearance to silver articles.
(3) The blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate.
Hence, adding zinc particles to a solution of copper sulphate makes the blue solution colorless.
59. Anodization method is useful for prevention of the corrosion of the aluminium.
Ans.
(1) The process of coating metals such as aluminium and copper with a thin and strong layer of their oxides by electrolysis is called anodizing process.
(2) When aluminium is anodized, the thin layer of aluminium oxide is formed all over the surface. This restricts the contact of aluminium metal with oxygen and water and prevents corrosion of aluminium.
Hence, anodization method is useful for prevention of the corrosion of the aluminium.
60. On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
Ans.
(1) On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time. This is because silver undergoes corrosion when it is exposed to air containing hydrogen sulphide.
(2) Silver reacts with hydrogen sulphide in air to form a layer of silver sulphide (Ag2S), which gives blackish appearance to silver articles. 61. Magnetic separation method is used to separate the magnetic ingredients in the ores.
Ans.
(1) The magnetic separation process is based on the differences in magnetic properties of the ore components.
(2) When the powdered ore is dropped over the moving belt near nonmagnetic roller, the nonmagnetic particles arc carried further along with belt and fall in the collector vessel placed away from magnetic roller. At the same time, the magnetic portion of the ore is attracted by the magnetic roller and falls in the collector vessel near the magnetic roller.
Thus, magnetic separation method is used to separate the magnetic ingredients in the ores.
62. Coins are made from metals and alloys.
Ans.
(1) Coins are made from metals and alloys because metals and their alloys possess the property of malleability. So, they can be hammered into flat shape without breaking.
(2) Metals and alloys used for making coins should be corrosion resistance and bright in colour. They should also be hard and wear resistance.
63. Meena’s mother uses lemon or tamarind for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Ans.
(1) The greenish colour on copper vessels is due to formation of copper carbonate on it.
(2) Copper carbonate reacts with acids present in lemon or tamarind and as a result, this copper carbonate layer gets removed.
Hence, Meena’s mother uses lemon or tamarind for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
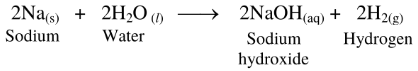
64. In the laboratory, sodium is immersed in kerosene.
Ans.
(1) Sodium reacts with moisture present in air, even at room temperature, to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
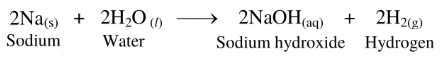
(2) The reaction is exothermic and therefore, the released hydrogen gas readily catches fire on exposure to air.
Hence, to prevent accidents in the laboratory, sodium is immersed in kerosene.
65. Ethylene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Ans.
(1) Hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon-carbon double or triple bond are called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(2) The structure of ethylene is CH2 = CH2.
It has a double bond and hence, it is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
66. The flame appears yellow in the ignition of naphthalene.
Ans.
(1) Naphthalene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
(2) Unsaturated hydrocarbons bums with a yellow flame and releases black soot/smoke.
Hence, the flame appears yellow in the ignition of naphthalene.
67. The color of iodine disappears in the reaction between vegetable oil and tincture iodine.
Ans.
(1) Vegetable oils are unsaturated fatty acids.
(2) They contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds and thus, undergo addition reaction with iodine.
Hence, the color of iodine disappears in the reaction between vegetable oil and tincture iodine.
68. Vegetable ghee is formed from the hydrogenation of vegetable oil in presence of nickel catalyst.
Ans.
(1) Vegetable oil contains carbon-carbon multiple bonds while vanaspati ghee contains carbon-carbon single bonds. So, vegetable oil is an unsatured compound while vegetable ghee is a saturated compound.
(2) An unsaturated compound undergoes addition reaction with hydrogen in presence of nickel catalyst to form a saturated compound. This reaction is called hydrogenation.
Hence, vegetable ghee is formed from the hydrogenation of vegetable oil in presence of nickel catalyst.
69. Carbon has the property of forming many compounds.
Ans.
(1) Carbon is a tetravalent atom with the property of catenation. Thus, it forms compounds in which the carbon atoms arc arranged in the form of straight chains, branched chains or rings.
(2) It can form single and multiple covalent bonds with other carbon atoms.
(3) Carbon is tetravalent. Thus, it can form four covalent bonds with carbon or other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, halogens and phosphorus.
(4) One more characteristics of carbon, which is responsible for large number of carbon compounds is isomerism.
Hence, carbon has the property of forming many compounds.
70. Benzene compounds are called aromatic compounds.
Ans.
(1) Benzene compounds are a cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons having structure similar to benzene.
(2) There arc three alternate double bonds in the six membered ring structure of benzene.
(3) Compounds having this characteristic unit in their structures are called aromatic compounds.
Hence, benzene compounds are called aromatic compounds.
71. The velocity of spacecraft at the earth’s surface must be greater than the escape velocity of the earth.
Ans.
(1) The spacecraft must escape the earth’s gravitational force to travel into the outer space.
(2) To achieve this, the initial velocity of the moving object must be greater than the escape velocity of the earth.
72. Space debris can be harmful to the artificial satellites.
Ans.
(1) In space non-essential objects revolving around the earth are termed as debris in space.
(2) Along with the artificial satellites, some other objects like non-functional satellites, parts of the launcher detached during launching and debris generated due to collision of satellite with other satellite or any other object in the space are also revolving around the earth.
(3) This debris can collide with the satellites or spacecrafts and damage them.
(4) Hence, Space debris can be harmful to the artificial satellites.
73. Satellite launch vehicles are used to place satellites in their specific orbits.
Ans.
(1) The working of the satellite launch vehicle is based on the Newton’s third law of motion.
(2) The launch vehicle uses specific type of fuel which w’hen burned, produces a gas. The gas expands due to its high temperature and is expelled forcefully through the nozzles at rear side of the launch vehicle. As a result, a thrust acts on the vehicle, which drives the vehicle high into the space.
(3) The structure of the launch vehicle and the fuel to be used is decided by the weight of the satellite and the type of satellite orbit.
(4) In this way, satellite launch vehicles are used to place satellites in their specific orbits.
74. The Launch vehicles are very costly.
Ans.
(1) The launch vehicles can be used only once.
(2) Hence, launch vehicles are costly.